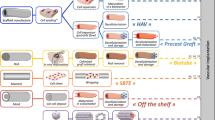
Abstract
While the need for a small diameter arterial bypass graft is clear, the hemodynamics of small diameter arteries like the coronary artery have led to the failure of synthetic materials that are successful for large diameter grafts like the aorta. Many patients do not have autologous vessels suitable for use due to systemic vascular disease and previous harvest, and second site morbidity is substantial. Vascular tissue engineering has explored the use of tissue cells or stem cells combined with various types of scaffolds to make tubular constructs subjected to chemical and/or mechanical stimulation in an attempt to develop small diameter arterial bypass grafts without a proven clinical success, yet. Here, we review the use of biopolymer gels as the scaffold and preclinical successes, and we discuss their advantages and challenges.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmann KA, Weinbaum JS, Johnson SL, Tranquillo RT (2010) Fibrin degradation enhances vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and matrix deposition in fibrin-based tissue constructs fabricated in vitro. Tissue Eng A 16(10):3261–3270. https://doi.org/10.1089/ten.TEA.2009.0708
Alberts B, Bray D, Lewis J, Raff M, Roberts K, Watson JD (1994) Molecular biology of the cell, 3rd edn. Garland Publishing, Inc., New York
Barocas VH, Girton TS, Tranquillo RT (1998) Engineered alignment in media equivalents: magnetic prealignment and mandrel compaction. J Biomech Eng 120(5):660–666
Bjork JW, Johnson SL, Tranquillo RT (2011) Ruthenium-catalyzed photo cross-linking of fibrin-based engineered tissue. Biomaterials 32(10):2479–2488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.12.010
Bockeria LA, Svanidze O, Kim A, Shatalov K, Makarenko V, Cox M, Carrel T (2017) Total cavopulmonary connection with a new bioabsorbable vascular graft: first clinical experience. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 153(6):1542–1550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcvs.2016.11.071
Canham PB, Talman EA, Finlay HM, Dixon JG (1991) Medial collagen organization in human arteries of the heart and brain by polarized light microscopy. Connect Tissue Res 26(1–2):121–134
Clark RA (2003) Fibrin glue for wound repair: facts and fancy. Thromb Haemost 90(6):1003–1006
Clark RA, Nielsen LD, Welch MP, McPherson JM (1995) Collagen matrices attenuate the collagen-synthetic response of cultured fibroblasts to TGF-beta. J Cell Sci 108(Pt 3):1251–1261
Conte MS (1998) The ideal small arterial substitute: a search for the Holy Grail? FASEB J 12(1):43–45. https://doi.org/10.1096/fasebj.12.1.43
Dahl SL, Kypson AP, Lawson JH, Blum JL, Strader JT, Li Y, Manson RJ, Tente WE, DiBernardo L, Hensley MT, Carter R, Williams TP, Prichard HL, Dey MS, Begelman KG, Niklason LE (2011) Readily available tissue-engineered vascular grafts. Sci Transl Med 3(68):68–69. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.3001426
Elbjeirami WM, Yonter EO, Starcher BC, West JL (2003) Enhancing mechanical properties of tissue engineered constructs via lysyl oxidase crosslinking activity. J Biomed Mater Res 66A:513–521
Fung Y-C (1993) Biomechanics: mechanical properties of living tissues. Springer-Verlag, New York
Ghezzi CE, Marelli B, Muja N, Nazhat SN (2012) Immediate production of a tubular dense collagen construct with bioinspired mechanical properties. Acta Biomater 8(5):1813–1825. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2012.01.025
Girton TS, Oegema TR, Grassl ED, Isenberg BC, Tranquillo RT (2000) Mechanisms of stiffening and strengthening in media-equivalents fabricated using glycation. J Biomech Eng 122(3):216–223
Glagov S (1979) Relation of structure to function in arterial walls. Artery 5(4):295–304
Grassl ED, Tranquillo RT (2005) Fibrillar fibrin gels in scaffolding in tissue engineering. Marcel Dekker, New York
Grassl ED, Oegema TR, Tranquillo RT (2002) Fibrin as an alternative biopolymer to type-I collagen for the fabrication of a media equivalent. J Biomed Mater Res 60(4):607–612
Grassl ED, Oegema TR, Tranquillo RT (2003) A fibrin-based arterial media equivalent. J Biomed Mater Res A 66(3):550–561
Greco Song HH, Rumma RT, Ozaki CK, Edelman ER, Chen CS (2018) Vascular tissue engineering: progress, challenges, and clinical promise. Cell Stem Cell 22(4):608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stem.2018.03.014
Helgerson S, Seelich T, DiOrio J, Tawil B, Bittner K, Spaethe R (2004) Fibrin. In: Bowlin G, Wnek G (eds) Encyclopedia of biomaterials and biomedical engineering. Marcel Dekker, New York
Hirai J, Matsuda T (1995) Self-organized, tubular hybrid vascular tissue composed of vascular cells and collagen for low-pressure-loaded venous system. Cell Transplant 4(6):597–608
Hirashima M, Imamura T, Yano K, Kawamura R, Meta A, Tokieda Y, Nakashima T (2016) High-level expression and preparation of recombinant human fibrinogen as biopharmaceuticals. J Biochem 159(2):261–270. https://doi.org/10.1093/jb/mvv099
Hoerstrup SP, Cummings Mrcs I, Lachat M, Schoen FJ, Jenni R, Leschka S, Neuenschwander S, Schmidt D, Mol A, Gunter C, Gossi M, Genoni M, Zund G (2006) Functional growth in tissue-engineered living, vascular grafts: follow-up at 100 weeks in a large animal model. Circulation 114(1 Suppl):I159–I166. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.001172
Isenberg BC, Tranquillo RT (2003) Long-term cyclic distention enhances the mechanical properties of collagen-based media-equivalents. Ann Biomed Eng 31(8):937–949
Isenberg BC, Williams C, Tranquillo RT (2005) Small-diameter artificial arteries engineered in vitro. Circ Res 98:25–35
Kanda K, Matsuda T (1994) In vitro reconstruction of hybrid arterial media with the molecular and cellular orientations. Cell Transplant 3(6):537–545
Khosravi R, Best CA, Allen RA, Stowell CE, Onwuka E, Zhuang JJ, Lee YU, Yi T, Bersi MR, Shinoka T, Humphrey JD, Wang Y, Breuer CK (2016) Long-term functional efficacy of a novel electrospun poly(glycerol sebacate)-based arterial graft in mice. Ann Biomed Eng 44(8):2402–2416. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-015-1545-7
Kurobe H, Maxfield MW, Breuer CK, Shinoka T (2012) Concise review: tissue-engineered vascular grafts for cardiac surgery: past, present, and future. Stem Cells Transl Med 1(7):566–571. https://doi.org/10.5966/sctm.2012-0044
L’Heureux N, Germain L, Labbe R, Auger FA (1993) In vitro construction of a human blood vessel from cultured vascular cells: a morphologic study. J Vasc Surg 17(3):499–509
Lawson JH, Glickman MH, Ilzecki M, Jakimowicz T, Jaroszynski A, Peden EK, Pilgrim AJ, Prichard HL, Guziewicz M, Przywara S, Szmidt J, Turek J, Witkiewicz W, Zapotoczny N, Zubilewicz T, Niklason LE (2016) Bioengineered human acellular vessels for dialysis access in patients with end-stage renal disease: two phase 2 single-arm trials. Lancet 387(10032):2026–2034. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)00557-2
Long JL, Tranquillo RT (2003) Elastic fiber production in cardiovascular tissue-equivalents. Matrix Biol 22(4):339–350
McAllister TN, Maruszewski M, Garrido SA, Wystrychowski W, Dusserre N, Marini A, Zagalski K, Fiorillo A, Avila H, Manglano X, Antonelli J, Kocher A, Zembala M, Cierpka L, de la Fuente LM, L’Heureux N (2009) Effectiveness of haemodialysis access with an autologous tissue-engineered vascular graft: a multicentre cohort study. Lancet 373(9673):1440–1446. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60248-8
Mitchell SL, Niklason LE (2003) Requirements for growing tissue-engineered vascular grafts. Cardiovasc Pathol 12(2):59–64
Neidert MR, Lee ES, Oegema TR, Tranquillo RT (2002) Enhanced fibrin remodeling in vitro with TGF-beta1, insulin and plasmin for improved tissue-equivalents. Biomaterials 23(17):3717–3731
Nerem RM (2000) Tissue engineering a blood vessel substitute: the role of biomechanics. Yonsei Med J 41(6):735–739
Niklason LE (1999) Techview: medical technology. Replacement arteries made to order. Science 286(5444):1493–1494
Ross JJ, Tranquillo RT (2003) ECM gene expression correlates with in vitro tissue growth and development in fibrin gel remodeled by neonatal smooth muscle cells. Matrix Biol 22(6):477–490
Sander EA, Grassl ED, Tranquillo RT (2014) Hydrogel scaffolds for regenerative medicine. In: Ma PX (ed) Biomaterials and regenerative medicine. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 295–316
Seliktar D, Black RA, Vito RP, Nerem RM (2000) Dynamic mechanical conditioning of collagen-gel blood vessel constructs induces remodeling in vitro. Ann Biomed Eng 28:351–362
Seliktar D, Nerem RM, Galis ZS (2001) The role of matrix metalloproteinase-2 in the remodeling of cell-seeded vascular constructs subjected to cyclic strain. Ann Biomed Eng 29(11):923–934
Stegemann JP, Nerem RM (2003) Phenotype modulation in vascular tissue engineering using biochemical and mechanical stimulation. Ann Biomed Eng 31(4):391–402
Swartz DD, Russell JA, Andreadis ST (2005) Engineering of fibrin-based functional and implantable small-diameter blood vessels. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 288(3):H1451–H1460. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00479.2004
Syedain ZH, Tranquillo RT (2011) TGF-beta1 diminishes collagen production during long-term cyclic stretching of engineered connective tissue: implication of decreased ERK signaling. J Biomech 44(5):848–855. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiomech.2010.12.007
Syedain ZH, Weinberg JS, Tranquillo RT (2008) Cyclic distension of fibrin-based tissue constructs: evidence of adaptation during growth of engineered connective tissue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105(18):6537–6542. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0711217105
Syedain ZH, Meier LA, Bjork JW, Lee A, Tranquillo RT (2011) Implantable arterial grafts from human fibroblasts and fibrin using a multi-graft pulsed flow-stretch bioreactor with noninvasive strength monitoring. Biomaterials 32(3):714–722. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.09.019
Syedain ZH, Meier LA, Lahti MT, Johnson SL, Tranquillo RT (2014) Implantation of completely biological engineered grafts following decellularization into the sheep femoral artery. Tissue Eng A 20(11–12):1726–1734. https://doi.org/10.1089/ten.TEA.2013.0550
Syedain Z, Reimer J, Lahti M, Berry J, Johnson S, Tranquillo RT (2016) Tissue engineering of acellular vascular grafts capable of somatic growth in young lambs. Nat Commun 7:12951. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms12951
Syedain ZH, Graham ML, Dunn TB, O’Brien T, Johnson SL, Schumacher RJ, Tranquillo RT (2017) A completely biological “off-the-shelf” arteriovenous graft that recellularizes in baboons. Sci Transl Med 9(414):pii: eaan4209. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.aan4209
Teebken OE, Haverich A (2002) Tissue engineering of small diameter vascular grafts. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 23(6):475–485
Thie M, Schlumberger W, Semich R, Rauterberg J, Robenek H (1991) Aortic smooth muscle cells in collagen lattice culture: effects on ultrastructure, proliferation and collagen synthesis. Eur J Cell Biol 55(2):295–304
Tranquillo RT (2002) The tissue-engineered small-diameter artery. Ann N Y Acad Sci 961:1–4
Weinberg CB, Bell E (1986) A blood vessel model constructed form collagen and cultured vascular cells. Science 231(4736):397–400
Wolinsky H, Glagov S (1964) Structural basis for the static mechanical properties of the aortic media. Circ Res 14:400–413
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this entry
Cite this entry
Isenberg, B.C., Williams, C., Syedain, Z.H., Tranquillo, R.T. (2020). Small-Diameter Engineered Arteries: The Gel Approach. In: Walpoth, B., Bergmeister, H., Bowlin, G., Kong, D., Rotmans, J., Zilla, P. (eds) Tissue-Engineered Vascular Grafts. Reference Series in Biomedical Engineering(). Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-71530-8_23-1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-71530-8_23-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-71530-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-71530-8
eBook Packages: Springer Reference EngineeringReference Module Computer Science and Engineering