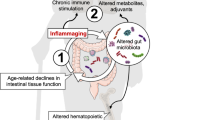
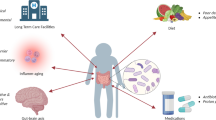
Abstract
The human gut microbiome is highly variable among individuals and is known to be influenced by numerous environmental and host factors. The gut microbiome is modified by diet and shows changes with aging. The gut microbiome is believed to interact with the host’s immune system. Thus, there is interest in whether dietary probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics might benefit immune function in older adults, acting through modified gut microbiota to prevent or slow the changes associated with immunosenescence. Here the available evidence from human studies of probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics and immune function in older adults is reviewed. There is good evidence that probiotics can improve in vivo and ex vivo measures of immune function in older adults. Further research is required before conclusions can be made regarding the role that prebiotics or synbiotics may have on immune function in the elderly. Future studies will need to ensure that the gut microbiome and immune markers relevant to immunosenescence are fully evaluated in robust study designs in order to have greater confidence in the application of these interventions, ensuring that the potential translational value of research in this field is realized.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- APC:
-
Antigen-presenting cell
- CD:
-
Cluster of differentiation
- CFU:
-
Colony-forming unit
- CMV:
-
Cytomegalovirus
- ConA:
-
Concanavalin A
- CRP:
-
C-reactive protein
- DTH:
-
Delayed-type hypersensitivity
- EMRA cells:
-
Terminally differentiated effector memory cells
- FISH:
-
Fluorescence in situ hybridization
- FOS:
-
Fructo-oligosaccharides
- GOS:
-
Galacto-oligosaccharides
- hBD-2:
-
Human β-defensin
- hs:
-
High sensitivity
- IFN:
-
Interferon
- Ig:
-
Immunoglobulin
- IL:
-
Interleukin
- iNOS:
-
Inducible nitric oxide synthase
- LPS:
-
Lipopolysaccharide
- MFI:
-
Mean fluorescence intensity
- NK:
-
Natural killer
- NKT cell:
-
Natural killer T cell
- NS:
-
Nonsignificant
- NSAIDS:
-
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
- OTU:
-
Operational taxonomic units
- PBMC:
-
Peripheral blood mononuclear cell
- PGE:
-
Prostaglandin E
- PHA:
-
Phytohemagglutinin
- qPCR:
-
Quantitative polymerase chain reaction
- SCFA:
-
Short-chain fatty acid
- TGF-β:
-
Transforming growth factor β
- TNF:
-
Tumor necrosis factor
- TREC:
-
T cell receptor excision circle
- WBC:
-
White blood cell
References
Akatsu H, Arakawa K, Yamamoto T, Kanematsu T, Matsukawa N, Ohara H, Maruyama M (2013a) Lactobacillus in jelly enhances the effect of influenza vaccination in elderly individuals. J Am Geriatr Soc 61:1828–1830
Akatsu H, Iwabuchi N, Xiao JZ, Matsuyama Z, Kurihara R, Okuda K, Yamamoto T, Maruyama M (2013b) Clinical effects of probiotic Bifidobacterium longum BB536 on immune function and intestinal microbiota in elderly patients receiving enteral tube feeding. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr 37:631–640
Akatsu H, Nagafuchi S, Kurihara R, Okuda K, Kanesaka T, Ogawa N, Kanematsu T, Takasugi S, Yamaji T, Takami M, Yamamoto T, Ohara H, Maruyama M (2016) Enhanced vaccination effect against influenza by prebiotics in elderly patients receiving enteral nutrition. Geriatr Gerontol Int 16:205–213
Albers R, Antoine JM, Bourdet-Sicard R, Calder PC, Gleeson M, Lesourd B, Samartin S, Sanderson IR, van Loo J, vas Dias FW, Watzl B (2005) Markers to measure immunomodulation in human nutrition intervention studies. Br J Nutr 94:452–481
Albers R, Bourdet-Sicard R, Braun D, Calder PC, Herz U, Lambert C, Lenoir-Wijnkoop I, Meheust A, Ouwehand A, Phothirath P, Sako T, Salminen S, Siemensma A, van Loveren H, Sack U (2013) Monitoring immune modulation by nutrition in the general population: identifying and substantiating effects on human health. Br J Nutr 110(Suppl 2):S1–30
Arboleya S, Watkins C, Stanton C, Ross RP (2016) Gut bifidobacteria populations in human health and aging. Front Microbiol 7:1204
Arunachalam K, Gill HS, Chandra RK (2000) Enhancement of natural immune function by dietary consumption of Bifidobacterium lactis (HN019). Eur J Clin Nutr 54:263–267
Biagi E, Candela M, Turroni S, Garagnani P, Franceschi C, Brigidi P (2013) Ageing and gut microbes: perspectives for health maintenance and longevity. Pharmacol Res 69:11–20
Boge T, Remigy M, Vaudaine S, Tanguy J, Bourdet-Sicard R, van der Werf S (2009) A probiotic fermented dairy drink improves antibody response to influenza vaccination in the elderly in two randomised controlled trials. Vaccine 27:5677–5684
Bosch M, Mendez M, Perez M, Farran A, Fuentes MC, Cune J (2012) Lactobacillus plantarum CECT7315 and CECT7316 stimulate immunoglobulin production after influenza vaccination in elderly. Nutr Hosp 27:504–509
Buigues C, Fernandez-Garrido J, Pruimboom L, Hoogland AJ, Navarro-Martinez R, Martinez-Martinez M, Verdejo Y, Mascaros MC, Peris C, Cauli O (2016) Effect of a prebiotic formulation on frailty syndrome: a randomized double-blind clinical trial. Int J Mol Sci 17:E932
Bunout D, Hirsch S, Pia De La Maza M, Munoz C, Haschke F, Steenhout P, Klassen P, Barrera G, Gattas V, Petermann M (2002) Effects of prebiotics on the immune response to vaccination in the elderly. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr 26:372–376
Bunout D, Barrera G, Hirsch S, Gattas V, de la Maza MP, Haschke F, Steenhout P, Klassen P, Hager C, Avendano M, Petermann M, Munoz C (2004) Effects of a nutritional supplement on the immune response and cytokine production in free-living Chilean elderly. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr 28:348–354
Claesson MJ, Jeffery IB, Conde S, Power SE, O’Connor EM, Cusack S, Harris HM, Coakley M, Lakshminarayanan B, O’Sullivan O, Fitzgerald GF, Deane J, O’Connor M, Harnedy N, O’Connor K, O’Mahony D, van Sinderen D, Wallace M, Brennan L, Stanton C, Marchesi JR, Fitzgerald AP, Shanahan F, Hill C, Ross RP, O’Toole PW (2012) Gut microbiota composition correlates with diet and health in the elderly. Nature 488:178–184
Dong H, Rowland I, Thomas LV, Yaqoob P (2013) Immunomodulatory effects of a probiotic drink containing Lactobacillus casei Shirota in healthy older volunteers. Eur J Nutr 52:1853–1863
Enani S, Przemska-Kosicka A, Childs CE, Maidens C, Dong H, Conterno L, Tuohy K, Todd S, Gosney M, Yaqoob, P (2017) Impact of ageing and a synbiotic on the immune response to seasonal influenza vaccination; a randomised controlled trial. Clin Nutr https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2017.01.011
Franceschi C, Campisi J (2014) Chronic inflammation (inflammaging) and its potential contribution to age-associated diseases. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 69(Suppl 1):S4–S9
Fujihashi K, Kiyono H (2009) Mucosal immunosenescence: new developments and vaccines to control infectious diseases. Trends Immunol 30:334–343
Gibson GR, Brummer RJ, Isolauri E, Lochs H, Morelli L, Ockhuizen T, Rowland IR, Schrezenmeir J, Stanton C, Verbeke K (2011) The design of probiotic studies to substantiate health claims. Gut Microbes 2:299–305
Gibson GR, Hutkins R, Sanders ME, Prescott SL, Reimer RA, Salminen SJ, Scott K, Stanton C, Swanson KS, Cani PD, Verbeke K, Reid G (2017) Expert consensus document: the International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of prebiotics. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 14:491–502
Gill HS, Rutherfurd KJ, Cross ML (2001a) Dietary probiotic supplementation enhances natural killer cell activity in the elderly: an investigation of age-related immunological changes. J Clin Immunol 21:264–271
Gill HS, Rutherfurd KJ, Cross ML, Gopal PK (2001b) Enhancement of immunity in the elderly by dietary supplementation with the probiotic Bifidobacterium lactis HN019. Am J Clin Nutr 74:833–839
Goodwin K, Viboud C, Simonsen L (2006) Antibody response to influenza vaccination in the elderly: a quantitative review. Vaccine 24:1159–1169
Guillemard E, Tanguy J, Flavigny A, de la Motte S, Schrezenmeir J (2010a) Effects of consumption of a fermented dairy product containing the probiotic Lactobacillus casei DN-114 001 on common respiratory and gastrointestinal infections in shift workers in a randomized controlled trial. J Am Coll Nutr 29:455–468
Guillemard E, Tondu F, Lacoin F, Schrezenmeir J (2010b) Consumption of a fermented dairy product containing the probiotic Lactobacillus casei DN-114001 reduces the duration of respiratory infections in the elderly in a randomised controlled trial. Br J Nutr 103:58–68
Hibberd PL, Kleimola L, Fiorino AM, Botelho C, Haverkamp M, Andreyeva I, Poutsiaka D, Fraser C, Solano-Aguilar G, Snydman DR (2014) No evidence of harms of probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG ATCC 53103 in healthy elderly-a phase I open label study to assess safety, tolerability and cytokine responses. PLoS One 9:e113456
High KP, Fulop T, Pawelec G, Castle S, Loeb M (2009) Immunosenescence and vaccination in nursing home residents. Clin Infect Dis 48:443–448
Hill C, Guarner F, Reid G, Gibson GR, Merenstein DJ, Pot B, Morelli L, Canani RB, Flint HJ, Salminen S, Calder PC, Sanders ME (2014) Expert consensus document. The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 11:506–514
Hopkins MJ, Sharp R, Macfarlane GT (2001) Age and disease related changes in intestinal bacterial populations assessed by cell culture, 16S rRNA abundance, and community cellular fatty acid profiles. Gut 48:198–205
Human Microbiome Project, C (2012) Structure, function and diversity of the healthy human microbiome. Nature 486:207–214
Jeurink PV, van Esch BC, Rijnierse A, Garssen J, Knippels LM (2013) Mechanisms underlying immune effects of dietary oligosaccharides. Am J Clin Nutr 98:572S–577S
Kau AL, Ahern PP, Griffin NW, Goodman AL, Gordon JI (2011) Human nutrition, the gut microbiome and the immune system. Nature 474:327–336
Lahtinen SJ, Forssten S, Aakko J, Granlund L, Rautonen N, Salminen S, Viitanen M, Ouwehand AC (2012) Probiotic cheese containing Lactobacillus rhamnosus HN001 and Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM(R) modifies subpopulations of fecal lactobacilli and Clostridium difficile in the elderly. Age (Dordr) 34:133–143
Lomax AR, Calder PC (2009a) Prebiotics, immune function, infection and inflammation: a review of the evidence. Br J Nutr 101:633–658
Lomax AR, Calder PC (2009b) Probiotics, immune function, infection and inflammation: a review of the evidence from studies conducted in humans. Curr Pharm Des 15:1428–1518
Macfarlane S, Cleary S, Bahrami B, Reynolds N, Macfarlane GT (2013) Synbiotic consumption changes the metabolism and composition of the gut microbiota in older people and modifies inflammatory processes: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 38:804–816
Makino S, Ikegami S, Kume A, Horiuchi H, Sasaki H, Orii N (2010) Reducing the risk of infection in the elderly by dietary intake of yoghurt fermented with Lactobacillus delbrueckii ssp. bulgaricus OLL1073R-1. Br J Nutr 104:998–1006
Mane J, Pedrosa E, Loren V, Gassull MA, Espadaler J, Cune J, Audivert S, Bonachera MA, Cabre E (2011) A mixture of Lactobacillus plantarum CECT 7315 and CECT 7316 enhances systemic immunity in elderly subjects. A dose-response, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized pilot trial. Nutr Hosp 26:228–235
Maruyama M, Abe R, Shimono T, Iwabuchi N, Abe F, Xiao JZ (2016) The effects of non-viable Lactobacillus on immune function in the elderly: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Int J Food Sci Nutr 67:67–73
Millett ERC, Quint JK, Smeeth L, Daniel RM, Thomas SL (2013) Incidence of community-acquired lower respiratory tract infections and pneumonia among older adults in the United Kingdom: a population-based study. PLoS One 8:e75131
Miyazawa K, Kawase M, Kubota A, Yoda K, Harata G, Hosoda M, He F (2015) Heat-killed Lactobacillus gasseri can enhance immunity in the elderly in a double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical study. Benef Microbes 6:441–449
Moro-garcia MA, Alonso-Arias R, Baltadjieva M, Fernandez Benitez C, Fernandez Barrial MA, Diaz ruisanchez E, Alonso Santos R, Alvarez Sanchez M, Saavedra Mijan J, Lopez-Larrea C (2013) Oral supplementation with Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus 8481 enhances systemic immunity in elderly subjects. Age (Dordr) 35:1311–1326
Nyangale EP, Farmer S, Cash HA, Keller D, Chernoff D, Gibson GR (2015) Bacillus coagulans GBI-30, 6086 modulates Faecalibacterium prausnitzii in older men and women. J Nutr 145:1446–1452
O’Toole PW, Jeffery IB (2015) Gut microbiota and aging. Science 350:1214–1215
Ogra PL (2010) Ageing and its possible impact on mucosal immune responses. Ageing Res Rev 9:101–106
Ouwehand AC, Bergsma N, Parhiala R, Lahtinen S, Gueimonde M, Finne-Soveri H, Strandberg T, Pitkala K, Salminen S (2008) Bifidobacterium microbiota and parameters of immune function in elderly subjects. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 53:18–25
Ouwehand AC, Tiihonen K, Saarinen M, Putaala H, Rautonen N (2009) Influence of a combination of Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM and lactitol on healthy elderly: intestinal and immune parameters. Br J Nutr 101:367–375
Parra D, de Morentin BM, Cobo JM, Mateos A, Martinez JA (2004) Monocyte function in healthy middle-aged people receiving fermented milk containing Lactobacillus casei. J Nutr Health Aging 8:208–211
Pera A, Campos C, Lopez N, Hassouneh F, Alonso C, Tarazona R, Solana R (2015) Immunosenescence: implications for response to infection and vaccination in older people. Maturitas 82:50–55
Przemska-Kosicka A, Childs CE, Enani S, Maidens C, Dong H, Dayel IB, Tuohy K, Todd S, Gosney MA, Yaqoob P (2016) Effect of a synbiotic on the response to seasonal influenza vaccination is strongly influenced by degree of immunosenescence. Immun Ageing 13:6
van Puyenbroeck K, Hens N, Coenen S, Michiels B, Beunckens C, Molenberghs G, van Royen P, Verhoeven V (2012) Efficacy of daily intake of Lactobacillus casei Shirota on respiratory symptoms and influenza vaccination immune response: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in healthy elderly nursing home residents. Am J Clin Nutr 95:1165–1171
Sanders ME, Guarner F, Guerrant R, Holt PR, Quigley EM, Sartor RB, Sherman PM, Mayer EA (2013) An update on the use and investigation of probiotics in health and disease. Gut 62:787–796
Schiffrin EJ, Thomas DR, Kumar VB, Brown C, Hager C, van’t Hof MA, Morley JE, Guigoz Y (2007) Systemic inflammatory markers in older persons: the effect of oral nutritional supplementation with prebiotics. J Nutr Health Aging 11:475–479
Sender R, Fuchs S, Milo R (2016) Revised estimates for the number of human and bacteria cells in the body. PLoS Biol 14:e1002533
Spaiser SJ, Culpepper T, Nieves C Jr, Ukhanova M, Mai V, Percival SS, Christman MC, Langkamp-Henken B (2015) Lactobacillus gasseri KS-13, Bifidobacterium bifidum G9-1, and Bifidobacterium longum MM-2 ingestion induces a less inflammatory cytokine profile and a potentially beneficial shift in gut microbiota in older adults: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover study. J Am Coll Nutr 34:459–469
Takeda K, Okumura K (2007) Effects of a fermented milk drink containing Lactobacillus casei strain Shirota on the human NK-cell activity. J Nutr 137:791s–793s
Thomas CM, Versalovic J (2010) Probiotics-host communication: modulation of signaling pathways in the intestine. Gut Microbes 1:148–163
Turchet P, Laurenzano M, Auboiron S, Antoine JM (2003) Effect of fermented milk containing the probiotic Lactobacillus casei DN-114001 on winter infections in free-living elderly subjects: a randomised, controlled pilot study. J Nutr Health Aging 7:75–77
UNFAO, U. N. F. A. A. O. O. T. U. N (2001) Health and nutritional properties of probiotics in food including powder milk with live lactic acid bacteria
Valentini L, Pinto A, Bourdel-Marchasson I, Ostan R, Brigidi P, Turroni S, Hrelia S, Hrelia P, Bereswill S, Fischer A, Leoncini E, Malaguti M, Blanc-Bisson C, Durrieu J, Spazzafumo L, Buccolini F, Pryen F, Donini LM, Franceschi C, Lochs H (2015) Impact of personalized diet and probiotic supplementation on inflammation, nutritional parameters and intestinal microbiota – the “RISTOMED project”: randomized controlled trial in healthy older people. Clin Nutr 34:593–602
Vulevic J, Drakoularakou A, Yaqoob P, Tzortzis G, Gibson GR (2008) Modulation of the fecal microflora profile and immune function by a novel trans-galactooligosaccharide mixture (B-GOS) in healthy elderly volunteers. Am J Clin Nutr 88:1438–1446
Vulevic J, Juric A, Walton GE, Claus SP, Tzortzis G, Toward RE, Gibson GR (2015) Influence of galacto-oligosaccharide mixture (B-GOS) on gut microbiota, immune parameters and metabonomics in elderly persons. Br J Nutr 114:586–595
Wright K, Wright H, Murray M (2015) Probiotic treatment for the prevention of antibiotic-associated diarrhoea in geriatric patients: a multicentre randomised controlled pilot study. Australas J Ageing 34:38–42
Wu GD, Chen J, Hoffmann C, Bittinger K, Chen YY, Keilbaugh SA, Bewtra M, Knights D, Walters WA, Knight R, Sinha R, Gilroy E, Gupta K, Baldassano R, Nessel L, Li H, Bushman FD, Lewis JD (2011) Linking long-term dietary patterns with gut microbial enterotypes. Science 334:105–108
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Section Editor information
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer International Publishing AG
About this entry
Cite this entry
Childs, C.E., Calder, P.C. (2018). Modifying the Gut Microbiome Through Diet: Effects on the Immune System of Elderly Subjects. In: Fulop, T., Franceschi, C., Hirokawa, K., Pawelec, G. (eds) Handbook of Immunosenescence. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-64597-1_160-1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-64597-1_160-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-64597-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-64597-1
eBook Packages: Springer Reference Biomedicine and Life SciencesReference Module Biomedical and Life Sciences