Abstract
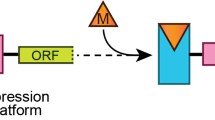
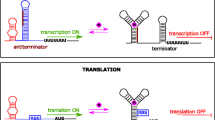
Riboswitches are regulatory noncoding RNAs, predominantly located in the 5′ untranslated region of mRNA, that can serve as molecular switches able to regulate the level of gene expression. This occurs through the conformational changes caused by binding to a specific metabolite. Riboswitches contain two structural domains: an aptamer domain that senses and binds to a metabolite and an expression platform that undergoes a conformational change in response to aptamer-ligand binding resulting in regulation of expression of downstream gene. In addition to natural riboswitches found in living organisms, a variety of synthetic riboswitches that respond to nonnatural small molecules have been developed. Synthetic riboswitches can be engineered to regulate expression of any gene in response to any nonnatural molecule that is capable of being bound by RNA and is not toxic to cells. This feature demonstrates a strong possibility for RNA switches to serve as sensor entities for design and development of cell-based biosensors with a variety of different applications. This chapter gives an overview of riboswitch selection techniques, describes reporter systems for monitoring riboswitch activation and approaches for riboswitch tuning and performance optimization in order to fulfill biosensor requirements, and discusses riboswitch applications as sensor entities.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antunes D, Jorge NAN, Caffarena ER, Passetti F (2018) Using RNA sequence and structure for the prediction of riboswitch aptamer: a comprehensive review of available software and tools. Front Genet 8:231
Barrick JE, Breaker RR (2007) The distributions, mechanisms, and structures of metabolite-binding riboswitches. Genome Biol 8:R239
Beisel CL, Smolke CD (2009) Design principles for riboswitch function. PLoS Comput Biol 5(4):e1000363
Berens C, Suess B (2015) Riboswitch engineering – making the all-important second and third steps. Curr Opin Biotechnol 31:10–15
Berens C, Thain A, Schroeder R (2001) A tetracycline-binding RNA aptamer. Bioorg Med Chem 9(10):2549–2556
Blouin S, Mulhbacher J, Penedo JC, Lafontaine DA (2009) Riboswitches: ancient and promising genetic regulators. Chembiochem 10:400–416
Breaker RR (2012) Riboswitches and the RNAworld. Cold Spring Harbor Perspect Biol 4:a003566
Brenner K, Karig DK, Weiss R, Arnold FH (2007) Engineered bidirectional communication mediates a consensus in a microbial biofilm consortium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:17300–17304
Caron M-P, Bastet L, Lussier A et al (2012) Dual-acting riboswitch control of translation initiation and mRNA decay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:3444–3453
Carothers JM, Goler JA, Kapoor Y et al (2010) Selecting RNA aptamers for synthetic biology: investigating magnesium dependence and predicting binding affinity. Nucleic Acids Res 38:2736–2747
Ceres P, Trausch JJ, Batey RT (2013) Engineering modular ‘ON’ RNA switches using biological components. Nucleic Acids Res 41:10449–10461
Cheah MT, Wachter A, Sudarsan N, Breaker RR (2007) Control of alternative RNA splicing and gene expression by eukaryotic riboswitches. Nature 447:497–500
Coppins RL, Hall KB, Groisman EA (2007) The intricate world of riboswitches. Curr Opin Chem Biol 10:176–181
Davidson ME, Harbaugh SV, Chushak YG et al (2013) Development of 2,4-dinitrotoluene-responsive synthetic riboswitch in E. coli cells. ACS Chem Biol 8:234–241
Desai SK, Gallivan JP (2004) Genetic screens and selections for small molecules based on a synthetic riboswitch that activates protein translation. J Am Chem Soc 126:13247–13254
Dixon N, Duncan JN, Geerlings T et al (2010) Reengineering orthogonally selective riboswitches. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:2830–2835
Dixon N, Robinson CJ, Geerling T et al (2012) Orthogonal riboswitches for tuneable coexpression in bacteria. Angew Chem Int Ed 51:3620–3624
Domin G, Findeiß S, Wachsmuth M et al (2017) Applicability of a computational design approach for synthetic riboswitches. Nucleic Acids Res 45:4108–4119
Edwards AL, Batey RT (2010) Riboswitches: a common RNA regulatory element. Nat Educ 3:9
Ehrentreich-Förster E, Orgel D, Krause-Griep A et al (2008) Biosensor-based on-site explosives detection using aptamers as recognition elements. Anal Bioanal Chem 391:1793–1800
Ellington AD, Szostak JW (1990) In vitro selection of RNA molecules that bind specific ligands. Nature 346:818–822
Emadpour M, Karcher D, Bock R (2015) Boosting riboswitch efficiency by RNA amplification. Nucleic Acids Res 43:e66
Espah Borujeni A, Mishler DM, Wang J et al (2015) Automated physics-based design of synthetic riboswitches from diverse RNA aptamers. Nucleic Acids Res 44:1–13
Etzel M, Mörl M (2017) Synthetic riboswitches: from plug and pray toward plug and play. Biochemistry 56:1181–1198
Filonov GS, Moon JD, Svensen N, Jaffrey SR (2014) Broccoli: rapid selection of an RNA mimic of green fluorescent protein by fluorescence-based selection and directed evolution. J Am Chem Soc 136:16299–16308
Findeiß S, Etzel M, Will S, Mörl M, Stadler PE (2017) Design of artificial riboswitches as biosensors. Sensors 17:1990
Folliard T, Mertins B, Steel H et al (2017) Ribo-attenuators: novel elements for reliable and modular riboswitch engineering. Sci Rep 7:4599–4610
Fowler CC, Brown ED, Li Y (2008) A FACS-based approach to engineering artificial riboswitches. Chembiochem 9:1906–1911
Friedland AE, Lu TK, Wang X et al (2009) Synthetic gene networks that count. Science 324:1199–1202
Ghazi Z, Fowler CC, Li Y (2014) Artificial riboswitch selection: a FACS-based approach. Methods Mol Biol 1111:57–75
Gong S, Wang Y, Wang Z, Zhang W (2017a) Computational methods for modeling aptamers and designing riboswitches. Int J Mol Sci 18:2442
Gong S, Wang Y, Wang Z, Zhang W (2017b) Co-transcriptional folding and regulation mechanisms of riboswitches. Molecules 22:1169–1183
Goodson MS, Harbaugh SV, Chushak YG, Kelley-Loughnane N (2015) Integrating and amplifying signal from riboswitch biosensors. Methods Enzymol 550:73–91
Goodson MS, Bennett AC, Jennewine BR et al (2017) Amplifying riboswitch signal output using cellular wiring. ACS Synth Biol 18:1440–1444
Groher F, Suess B (2014) Synthetic riboswitches – a tool comes of age. Biochim Biophys Acta 1839:964–973
Groher F, Bofill-Bosch C, Schneider C et al (2018) Riboswitching with ciprofloxacin – development and characterization of a novel RNA regulator. Nucleic Acids Res 46:2121–2132
Hallberg ZF, Su Y, Kitto RZ, Hammond MC (2017) Engineering and in vivo applications of riboswitches. Annu Rev Biochem 86:515–539
Han SR, Yu J, Lee S-W (2014) In vitro selection of RNA aptamers that selectively bind danofloxacin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 448:397–402
Hanson S, Berthelot K, Fink B et al (2003) Tetracycline-aptamer-mediated translational regulation in yeast. Mol Microbiol 49:1627–1637
Harbaugh S, Kelley-Loughnane N, Davidson M et al (2009) FRET-based optical assay for monitoring riboswitch activation. Biomacromolecules 10:1055–1060
Harbaugh SV, Goodson MS, Dillon K et al (2017) Riboswitch-based reversible dual color sensor. ACS Synth Biol 6:766–781
Harvey I, Garneau P, Pelletier J (2002) Inhibition of translation by RNA-small molecule interactions. RNA 8:452–463
Hybarger Z, Bynum J, Robert F. Williams, James J. Valdes, James P. Chambers (2006) A microfluidic SELEX prototype. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry 384 (1):191–198
Jenison RD, Gill SC, Pardi A, Polisky B (1994) High-resolution molecular discrimination by RNA. Science 263:1425–1429
Jin Y, Watt RM, Danchin A, Huang JD (2009) Use of a riboswitch-controlled conditional hypomorphic mutation to uncover a role for the essential csrA gene in bacterial autoaggregation. J Biol Chem 284:28738–28745
Karig D, Weiss R (2005) Signal-amplifying genetic circuit enables in vivo observation of weak promoter activation in the Rhl quorum sensing system. Biotechnol Bioeng 89:709–718
Kim D-S, Gusti V, Pillai SG, Gaur RK (2005) An artificial riboswitch for controlling pre-mRNA splicing. RNA 11:1667–1677
Kötter P, Weigand JE, Meyer B et al (2009) A fast and efficient translational control system for conditional expression of yeast genes. Nucleic Acids Res 37:e120
Lemay J-F, Desnoyers G, Blouin S et al (2011) Comparative study between transcriptionally- and translationally-acting adenine riboswitches reveals key differences in riboswitch regulatory mechanisms. PLoS Genet 7:e1001278
Lorenz R, Bernhart SH, Zu Siederdissen CH et al (2011) ViennaRNA Package 2.0. Algorithms Mol Biol 6:26
Lou X, Qian J, Xiao Y et al (2009) Micromagnetic selection of aptamers in microfluidic channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:2989–2994
Lou C, Liu X, Ni M et al (2010) Synthesizing a novel genetic sequential logic circuit: a push-on push-off switch. Mol Syst Biol 6:350
Lynch SA, Gallivan JP (2009) A flow cytometry-based screen for synthetic riboswitches. Nucleic Acids Res 37:184–192
Lynch SA, Desai S, Sajja HK, Gallivan JP (2007) A high-throughput screen for synthetic riboswitches reveals mechanistic insights into their function. Chem Biol 14:173–184
Ma AT, Schmidt CM, Golden JW (2014) Regulation of gene expression in diverse cyanobacterial species by using theophylline-responsive riboswitches. Appl Environ Microbiol 80:6704–6713
Machtel P, Bąkowska-Żywicka K, Żywicki M (2016) Emerging applications of riboswitches – from antibacterial targets to molecular tools. J Appl Genet 57:531–541
Mandal M, Breaker RR (2004) Gene regulation by riboswitches. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5:451–463
Mandal M, Lee M, Barrick JE et al (2004) A glycine-dependent riboswitch that uses cooperative binding to control gene expression. Science 306:275–279
Martini L, Meyer AJ, Ellefson JW et al (2015) In vitro selection for small-molecule-trigged strand displacement and riboswitch activity. ACS Synth Biol 4:1144–1150
Mathews DH, Sabina J, Zuker M, Turner DH (1999) Expanded sequence dependence of thermodynamic parameters improves prediction of RNA secondary structure1. J Mol Biol 288:911–940
Mathews DH, Disney MD, Childs JL et al (2004) Incorporating chemical modification constraints into a dynamic programming algorithm for prediction of RNA secondary structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:7287–7292
Mishler DM, Topp S, Reynoso GM, Gallivan JP (2010) Engineering bacteria to recognize and follow small molecules. Curr Opin Biotechnol 21:653–656
Moon TS, Lou C, Tamsir A et al (2012) Genetic programs constructed from layered logic gates in single cells. Nature 491:249–253
Morse DP (2007) Direct selection of RNA beacon aptamers. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 359:94–101
Muranaka N, Yokobayashi Y (2010) A synthetic riboswitch with chemical band-pass response. Chem Commun 46:6825–6827
Muranaka N, Abe K, Yokobayashi Y (2009a) Mechanism-guided library design and dual genetic selection of synthetic OFF riboswitches. Chembiochem 10:2375–2384
Muranaka N, Sharma V, Nomura Y, Yokobayashi Y (2009b) An efficient platform for genetic selection and screening of gene switches in Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res 37:e39
Nakahira Y, Ogawa A, Asano H et al (2013) Theophylline-dependent riboswitch as a novel genetic tool for strict regulation of protein expression in cyanobacterium Synecbococcus elongatus PCC 7942. Plant Cell Physiol 54:1724–1735
Nomura Y, Yokobayashi Y (2007) Reengineering a natural riboswitch by dual genetic selection. J Am Chem Soc 129:13814–13815
Nudler E (2006) Flipping riboswitches. Cell 126:19–22
Nudler E, Mironov AS (2004) The riboswitch control of bacterial metabolism. Trends Biochem Sci 29:11–17
Ogawa A (2011) Rational design of artificial riboswitches based on ligand-dependent modulation of internal ribosome entry in wheat germ extract and their applications as label-free biosensors. RNA 17:478–488
Ogawa A (2012) Rational construction of eukaryotic OFF-riboswitches that downregulate internal ribosome entry site-mediated translation in response to their ligands. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 22:1639–1642
Ohbayashi R, Akai H, Yoshikawa H et al (2016) A tightly inducible riboswitch system in Synecbocystis sp. PCC 6803. J Gen Appl Microbiol 159:154–159
Pesci EC, Pearson JP, Seed PC, Iglewski BH (1997) Regulation of las and rhl quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol 179:3127–3132
Peselis A, Serganov A (2014) Themes and variations in riboswitch structure and function. Biochim Biophys Acta 1839:908–918
Pham HL, Wong A, Chua N et al (2017) Engineering a riboswitch-based genetic platform for the self-directed evolution of acid-tolerant phenotypes. Nat Commun 8:411
Reinholt SJ, Ozer A, Lis JT, Craighead HG (2016) Highly multiplexed RNA aptamer selection using a microplate-based microcolumn device. Sci Rep 6:29771
Reuter JS, Mathews DH (2010) RNAstructure: software for RNA secondary structure prediction and analysis. BMC Bioinformatics 11:129
Reynoso CMK, Miller MA, Bina JE et al (2012) Riboswitches for intracellular study of genes involved in Francisella pathogenesis. mBio 3:e00253–e00212
Robinson CJ, Vincent HA, Wu M-C et al (2014) Modular riboswitch toolsets for synthetic genetic control in diverse bacterial species. J Am Chem Soc 136:10615–10624
Rodionov DA, Dubchak I, Arkin A et al (2004) Reconstruction of regulatory and metabolic pathways in metal-reducing delta-proteobacteria. Genome Biol 5:R90
Roßmanith J, Narberhaus F (2017) Modular arrangement of regulatory RNA elements. RNA Biol 14:287–292
Roth A, Breaker RR (2009) The structural and functional diversity of metabolite-binding riboswitches. Annu Rev Biochem 78:305–334
Rudolph MM, Vockenhuber MP, Suess B (2013) Synthetic riboswitches for the conditional control of gene expression in Streptomyces coelicolor. Microbiology 159:1416–1422
Seeliger JC, Topp S, Sogi KM et al (2012) A riboswitch-based inducible gene expression system for mycobacteria. PLoS One 7:e29266
Serganov A, Nudler E (2013) A decade of riboswitches. Cell 152:17–24
Sharma V, Nomura Y, Yokobayashi Y (2008) Engineering complex riboswitch regulation by dual genetic selection. J Am Chem Soc 130:16310–16315
Sinha J, Topp S, Gallivan JP (2011) From SELEX to cell: dual selections for synthetic riboswitches. Methods Enzymol 497:207–220
Suess B, Hanson S, Berens C et al (2003) Conditional gene expression by controlling translation with tetracycline-binding aptamers. Nucleic Acids Res 31:1853–1858
Suess B, Fink B, Berens C et al (2004) A theophylline responsive riboswitch based on helix slipping controls gene expression in vivo. Nucleic Acids Res 32:1610–1614
Szeto K, Craighead HG (2014) Devices and approaches for generating specific high-affinity nucleic acid aptamers. Appl Phys Rev 11:2727–2732
Szeto K, Latulippe DR, Ozer A et al (2013) RAPID-SELEX for RNA aptamers. PLoS One 8:e82667
Tabor JJ, Salis HM, Simpson ZB et al (2009) A synthetic genetic edge detection program. Cell 137:1272–1281
Tamsir A, Tabor JJ, Voigt CA (2011) Robust multicellular computing using genetically encoded NOR gates and chemical ‘wires’. Nature 469:212–215
Topp S, Gallivan JP (2007) Guiding bacteria with small molecules and RNA. J Am Chem Soc 129:6807–6811
Topp S, Gallivan JP (2008a) Random walks to synthetic riboswitches – a high-throughput selection based on cell motility. Chembiochem 9:210–213
Topp S, Gallivan JP (2008b) Riboswitches in unexpected places – a synthetic riboswitch in a protein coding region. RNA 14:2498–2503
Topp S, Gallivan JP (2010) Emerging applications of riboswitches in chemical biology. ACS Chem Biol 5:139–148
Topp S, Reynoso CMK, Seeliger JC et al (2010) Synthetic riboswitches that induce gene expression in diverse bacterial species. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:7881–7884
Tucker BJ, Breaker RR (2005) Riboswitches as versatile gene control elements. Curr Opin Struct Biol 15:342–348
Tuerk C, Gold L (1990) Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment: RNA ligands to bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase. Science 249:505–510
Vallée-Bélisle A, Ricci F, Plaxco KW (2009) Thermodynamic basis for the optimization of binding-induced biomolecular switches and structure-switching biosensors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:13802–13807
Verhounig A, Karcher D, Bock R (2010) Inducible gene expression from the plastid genome by a synthetic riboswitch. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:6204–6209
Wachsmuth M, Findeiß S, Weissheimer N et al (2012) De novo design of a synthetic riboswitch that regulates transcription termination. Nucleic Acids Res 41(4):2541–2551
Wachsmuth M, Domin G, Lorenz R et al (2015) Design criteria for synthetic riboswitches acting on transcription. RNA Biol 12(2):221–231
Wachter A (2010) Riboswitch-mediated control of gene expression in eukaryotes. RNA Biol 7:67–76
Wang S, White KA (2007) Riboswitching on RNA virus replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:10406–10411
Weigand JE, Suess B (2007) Tetracycline-aptamer-controlled regulation of pre-mRNA splicing in yeast. Nucleic Acids Res 35:4179–4185
Weigand JE, Sanchez M, Gunnesch E-B et al (2008) Screening for engineered neomycin riboswitches that control translation initiation. RNA 14:89–97
Welz R, Breaker RR (2007) Ligand binding and gene control characteristics of tandem riboswitches in Bacillus anthracis. RNA 13:573–582
Werstuck G, Green MR (1998) Controlling gene expression in living cells through small molecule-RNA interactions. Science 282:296–298
Wieland M, Hartig JS (2008) Artificial riboswitches: synthetic mRNA-based regulators of gene expression. Chembiochem 9:1873–1878
Winkler WC, Breaker RR (2005) Regulation of bacterial gene expression by riboswitches. Annu Rev Microbiol 59:487–517
Wittmann A, Suess B (2012) Engineered riboswitches: expanding researchers’ toolbox with synthetic RNA regulators. FEBS Lett 586:2076–2083
Wu M-C, Lowe PT, Robinson CJ et al (2015) Rational re-engineering of transcriptional silencing PreQ1 riboswitch. J Am Chem Soc 137:9015–9021
Xiu Y, Jang S, Jones JA et al (2017) Naringenin-responsive riboswitch-based fluorescent biosensor module for Escherichia coli co-cultures. Biotechnol Bioeng 114:2235–2244
Xu J, Carrocci TJ, Hoskins AA (2016) Evolution and characterization of abenzylguanine-binding RNA aptamer. Chem Commun 52:549–552
Zadeh JN, Steenberg CD, Bois JS et al (2011) NUPACK: analysis and design of nucleic acid systems. J Comput Chem 32:170–173
Zuker M (2003) Mfold web server for nucleic acid folding and hybridization prediction. Nucleic Acids Res 31:3406–3415
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Section Editor information
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 This is a U.S. Government work and not under copyright protection in the US; foreign copyright protection may apply
About this entry
Cite this entry
Harbaugh, S., Goodson, M., Chushak, Y., Chávez, J., Kelley-Loughnane, N. (2019). Riboswitches as Sensor Entities. In: Thouand, G. (eds) Handbook of Cell Biosensors. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-47405-2_121-1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-47405-2_121-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-47405-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-47405-2
eBook Packages: Springer Reference Chemistry and Mat. ScienceReference Module Physical and Materials ScienceReference Module Chemistry, Materials and Physics