Abstract
The arachnoid trabecular layer, located internally to the arachnoid layer, is composed of fibers that form the spider web–like trabecular structure found in the subarachnoid space and in the adventitial layer of blood vessels. The arachnoid trabeculae give shape to tubular structures (arachnoid sheaths) for each nerve root and for the spinal cord. Some of these arachnoid trabeculae extend to the pia mater. The trabecular arachnoid is an extremely fragile structure, which can easily be damaged. Because of its fragility, this membrane may be destroyed during dissection and manipulation, so that it is not frequently seen or systematically described. Trabecular arachnoid limits nerve root movement to a certain extent, holding each root in its position within the dural sac and in relation to other nerve roots (Figs. 24.1, 24.2, 24.3, 24.4, 24.5, 24.6, 24.7, 24.8, 24.9, 24.10, 24.11, 24.12, 24.13, 24.14, 24.15, 24.16, 24.17, 24.18, 24.19, 24.20, 24.21, 24.22, 24.23, 24.24, 24.25, and 24.26).
Access provided by Autonomous University of Puebla. Download chapter PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Keywords
These keywords were added by machine and not by the authors. This process is experimental and the keywords may be updated as the learning algorithm improves.
The arachnoid trabecular layer, located internally to the arachnoid layer, is composed of fibers that form the spider web–like trabecular structure found in the subarachnoid space and in the adventitial layer of blood vessels [1–6]. The arachnoid trabeculae give shape to tubular structures (arachnoid sheaths) for each nerve root and for the spinal cord. Some of these arachnoid trabeculae extend to the pia mater [1–3]. The trabecular arachnoid is an extremely fragile structure, which can easily be damaged. Because of its fragility, this membrane may be destroyed during dissection and manipulation, so that it is not frequently seen or systematically described [7]. Trabecular arachnoid limits nerve root movement to a certain extent, holding each root in its position within the dural sac and in relation to other nerve roots (Figs. 24.1, 24.2, 24.3, 24.4, 24.5, 24.6, 24.7, 24.8, 24.9, 24.10, 24.11, 24.12, 24.13, 24.14, 24.15, 24.16, 24.17, 24.18, 24.19, 24.20, 24.21, 24.22, 24.23, 24.24, 24.25, and 24.26) [4–6].
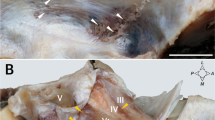
Trabecular arachnoid. Detail of anterior and posterior spinal nerve root and its arachnoid sheath (From Reina et al. [3]; with permission)
Trabecular arachnoid. Detail of spinal nerve roots and their arachnoid sheaths. Scanning electron microscopy. Magnification × 60 (From Reina et al. [3]; with permission)
Trabecular arachnoid. Detail of four spinal nerve roots with their arachnoid sheaths. Scanning electron microscopy. Magnification × 100 (From Reina et al. [1]; with permission)
Trabecular arachnoid. Detail of an arachnoid sheath. Scanning electron microscopy. Magnification × 80 (From Reina et al. [6]; with permission)
Trabecular arachnoid. Detail of a spinal nerve root with its arachnoid sheath. Scanning electron microscopy. Magnification × 100 (From Reina et al. [3]; with permission)
Trabecular arachnoid. Detail of an arachnoid sheath. Scanning electron microscopy. Magnification × 150 (From Reina et al. [1]; with permission)
Trabecular arachnoid. Detail of an arachnoid sheath without spinal nerve root. Scanning electron microscopy. Magnification × 100 (From Reina et al. [6]; with permission)
Trabecular arachnoid. Detail of an arachnoid sheath. Scanning electron microscopy. Magnification × 150 (From Reina et al. [6]; with permission)
Trabecular arachnoid. Detail of an arachnoid sheath. Scanning electron microscopy. Magnification × 150 (From Reina et al. [6]; with permission)
Trabecular arachnoid. Detail of anterior and posterior spinal nerve root enclosed by its arachnoid sheath. Scanning electron microscopy. Magnification × 30 (From Reina et al. [1]; with permission)
Trabecular arachnoid. Vessel within subarachnoid space surrounded by arachnoid trabecular structure. Scanning electron microscopy. Magnification × 120 (From Reina et al. [4]; with permission)
Trabecular arachnoid. (a, b) Detail of inner portion of trabecular arachnoid close to arachnoid layer. Transmission electron microscopy. Magnification: a, ×15,000; b, ×25,000 (b from Reina et al. [7]; with permission)
Trabecular arachnoid. (a, b) Detail of trabecular arachnoid. Transmission electron microscopy. Magnification: a, ×40,000; b, ×120,000 (a from Reina et al. [7]; with permission)
References
Reina MA, López A, De Andrés JA. Hypothesis concerning the anatomical basis of cauda equina syndrome and transient nerve root irritation after spinal anesthesia. Rev Esp Anestesiol Reanim. 1999;46:99–105.
Reina MA, Machés F, López A, De Andrés JA. The ultrastructure of the spinal arachnoid in humans and its impact on spinal anesthesia, cauda equina syndrome and transient neurological syndrome. Tech Reg Anesth Pain Management. 2008;12:153–60.
Reina MA, De Andrés JA, López A. Anatomía: implicaciones en la práctica de las técnicas de conducción espinal. In: Torres LM, editor. Tratado de anestesia y reanimación. Madrid: Arán; 2001. p. 1135–55.
Reina MA, De Andrés JA, López A. Subarachnoid and epidural anesthesia. In: Raj P, editor. Textbook of regional anesthesia. New York: Churchill Livingstone; 2002. p. 307–24.
Reina MA, López A, Machés F, de Leon-Casasola O, De Andrés JA. Electron microscopy and the expansion of regional anesthesia knowledge. Tech Reg Anesth Pain Management. 2002;6:165–71.
Reina MA, Villanueva MC, López A. Human spinal trabecular arachnoid, pia mater and spinal anesthesia. Rev Arg Anestesiol. 2008;66:111–33.
Reina MA, Prats-Galino A, Sola RG, Puigdellívol-Sánchez A, Arriazu Navarro R, De Andrés JA. Structure of the arachnoid layer of the human spinal meninges: a barrier that regulates dural sac permeability. Rev Esp Anestesiol Reanim. 2010;57:486–92.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Reina, M.A., López, A., De Andrés, J.A. (2015). Ultrastructure of Human Spinal Trabecular Arachnoid. In: Reina, M., De Andrés, J., Hadzic, A., Prats-Galino, A., Sala-Blanch, X., van Zundert, A. (eds) Atlas of Functional Anatomy for Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-09522-6_24
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-09522-6_24
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-09521-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-09522-6
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)