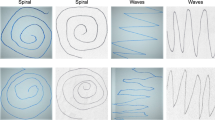
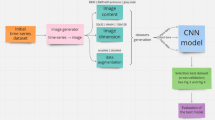
Abstract
This work presented a brief of the most recent technologies that tried to early diagnose Parkinson’s Disease (PD). Early diagnosis of PD can help to detect its symptoms and evolution which increases the chances of treatment because there’s no treatment for PD. So, we compiled several papers published in some well-established databases, all of which have almost the same diagnosis phases: preprocessing and classification and a few papers applied augmentation before classification. Each one has been mentioned to identify its objective, methodology, and results. Our brief showed that most papers used different approaches that use machine learning mechanisms to perform the automatic PD diagnosis. The main contribution of this paper is to propose an analyzed survey for the most recent proposed computer-assisted diagnosis systems mainly from 2018 to 2021, and how they can affect while handling the PD identification issue, and there are two experiments done using HandPD and NewHandPD datasets: the first experiment done using hybrid classification approach based on both SVM and PCA, while the second done using our modified CNN architecture, the modification done by changing of the number of filters: using 30 convolutional layers instead of 10, 50 pooling layers instead of 20 and 250 neurons at dense layer instead of 100. HandPD gave us the best accuracy using our modified CNN by 100.00% which is much better compared with “hybrid classification approach” mentioned above & “CNN model classification based”.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Man, J.H.K., Groenink, L., Caiazzo, M.: Cell reprogramming approaches in geneand cell-based therapies for Parkinson’s disease. Corel 286, 114–124 (2018)
Broeder, S., Nackaerts, E., Nieuwboer, A., Smits-Engelsman, B.C.M., Swinnen, S.P., Heremans, E.: The effects of dual tasking on handwriting in patients with parkinson’s disease s. Neuroscience 263, 193–202 (2014)
Drotar, P., Mekyska, J., Rektorova, I., Masarova, L., Smekal, Z., Faundez-Zanuy, M.: A New Modality for Quantitative Evaluation of Parkinson’s Disease: In-Air Movement, 978–1–4799–3163–7/13/$31.00 ©2013 IEEE
Smekal, Z., Mekyska, J., Rektorova, I., Faundez-Zanuy, M.: Analysis of Neurological Disorders Based on Digital Processing of Speech and Handwritten Text, 978–1–4673–6143–9/13/$31.00 ©2013 IEEE
Rosenblum, S., Samuel, M., Zlotnik, S., Erikh, I., Schlesinger, I.: Handwriting as an Objective Tool for Parkinson’s Disease Diagnosis. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg (2013)
Drotar, P., Mekyska, J., Rektorova, I., Masarova, L., Smekal, Z., Faundez-Zanuy, M.: Analysis of In-Air Movement in Handwriting: A novel Marker For Parkinson’s Disease, Elsevier Ireland Ltd, 2014 0169–2607/©
Akyol, K.: A study on the diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease using digitized wacom graphics tablet dataset. Int. J. Inf. Technol. Comput. Sci. 12(12), 45–51 (2017)
Tucha, O., et al.: Kinematic analysis of dopaminergic effects on skilled handwriting movements in Parkinson’s disease. J. Neural Transm. 113(5), 609–623 (2006)
Letanneux, A., Danna, J., Velay, J.-L., Viallet, F., Pinto, S.: From micrographia to Parkinson’s disease dysgraphia. Mov. Disord. 29(12), 1467–1475 (2014)
Lang, A.E., Lozano, A.M.: Parkinson’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 339(15), 1044–1053 (1998)
Ponsen, M.M., Daffertshofer, A., Wolters, E.C., Beek, P.J., Berendse, H.W.: Impairment of complex upper limb motor function in de novo Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 14(3), 199–204 (2008)
Van Gemmert, A., Teulings, H.L., Contreras-Vidal, J.L., Stelmach, G.E.: Parkinsons disease and the control of size and speed in handwriting. Neuropsychologia 37(6), 685–694 (1999)
Diaz, M., Moetesum, M., Siddiqi, I., Vessio, G.: Sequence-based dynamic handwriting analysis for Parkinson’s disease detection with one-dimensional convolutions and BiGRUs. Expert Syst. Appl. 168, 114405 (2021)
Kamran, I., Naz, S., Razzak, I., Imran, M.: Handwriting dynamics assessment using deep neural network for early identification of Parkinson’s disease. Futur. Gener. Comput. Syst. 117, 234–244 (2021)
Kamble, M., Shrivastava, P., Jain, M.: Digitized spiral drawing classification for Parkinson’s disease diagnosis. Measurement: Sensors 16, 100047 (2021)
Gupta, U., Bansal, H., Joshi, D.: An improved sex-specific and age-dependent classification model for Parkinson’s diagnosis using handwriting measurement. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 189, 105305 (2020)
Shoujiang, X., Pan, Z.: A novel ensemble of random forest for assisting diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease on small handwritten dynamics dataset. Int. J. Med. Informatics 144, 104283 (2020)
Taleb, C., Likforman-Sulem, L., Khachab, M., Mokbel, C.: Feature Selection for an Improved Parkinson’s Disease Identification Based on Handwriting
Parziale, A., Senatore, R., Della Cioppa, A., Marcelli, A.: Cartesian genetic programming for diagnosis of Parkinson disease through handwriting analysis: Performance vs. interpretability issues. Artificial Intelligence in Medicine 111, 101984 (2021)
Goel, N., Khanna, A., Gupta, D., Gupta, N.: Detection of Parkinson’s disease using machine learning techniques for voice and handwriting features. International Conference on Innovative Computing and Communications, pp. 631–643
Ali, L., Zhu, C., Zhao, H., Zhang, Z., Liu, Y.: An integrated system for unbiased parkinson’s disease detection from handwritten drawings. In: Zhang, J.F., Chen, C.M., Chu, S.C., Kountchev, R. (eds) Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing. Smart Innovation, Systems and Technologies, 268 (2022). Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-8048-9_1
Seedat, N., Aharonson, V., Schlesinger, I.: Automated Machine Vision Enabled Detection of Movement Disorders from Hand Drawn Spirals (2020). arXiv:2006.12121v1cs.CV
Al-Wahishi, A., Belal, N., Ghanem, N.: Diagnosis of Parkinson’s Disease by Deep Learning Techniques Using Handwriting Dataset. SIRS 2020: Advances in Signal Processing and Intelligent Recognition Systems, pp. 131–143
Pereira, C.R., et al.: Handwritten dynamics assessment through convolutional neural networks: an application to Parkinson’s disease identification. Artificial Intelligence in Med. 87, 67–77 (2018)
Diaz, M., Ferrer, M.A., Impedovo, D., Pirlo, G., Vessio, G.: Dynamically enhanced static handwriting representation for Parkinson’s disease detection. Pattern Recognition Letters 128, 204–210 (2019)
Moetesum, M., Siddiqi, I., Vincent, N., Cloppet, F.: Assessing visual attributes of handwriting for prediction of neurological disorders—a case study on Parkinson’s disease. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 121, 19–27 (2019)
Ali, L., Zhu, C., Golilarz, N.A., Javeed, A., Zhou, M., Liu, Y.: Reliable Parkinson’s disease detection by analyzing handwritten drawings: construction of an unbiased cascaded learning system based on feature selection and adaptive boosting model. Digital Object Identifier https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2932037
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Sultan, M., Hamed, G., Tantawi, M., Tolba, M.F. (2023). Early Diagnosis of Parkinson’s Disease Using Hand Drawings Images. In: Hassanien, A., Rizk, R.Y., Pamucar, D., Darwish, A., Chang, KC. (eds) Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Systems and Informatics 2023. AISI 2023. Lecture Notes on Data Engineering and Communications Technologies, vol 184. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-43247-7_36
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-43247-7_36
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-43246-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-43247-7
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)