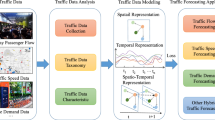
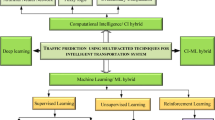
Abstract
Rapid economic development has brought with it an increase in traffic demand and, as a result, serious traffic problems (e.g., congestion, air pollution, and road accidents). Intelligent transport systems (ITS) can significantly improve the efficiency and sustainability of traffic networks by reducing all these problems. Traffic forecasting is an essential component of ITS applications. By providing timely and accurate real-time traffic information for traffic drivers, which can be used for better decision-making and quick actions, think about the future development of real smart transportation in smart cities. Traffic flow forecasting is still an open challenge. Many methods that deal with this problem have been tried out in the empirical literature, but there is still a lot of room for improvement. A comprehensive overview of the development of traffic flow forecasting models is provided in the form of model-driven and data-driven approaches. Through this literature review, which describes the historical evolution of forecasting models, we can identify key trends in forecasting: (1) adjustments and extensions of model-driven to deal with real phenomena; (2) advances in data-driven techniques; (3) the explosion of big data; (4) the convergence of many methods toward machine learning (ML); and (5) the development of hybrid models coupling the advantages of different models.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhao, Y.: Vehicle location and navigation systems (1997)
Qi, L.: Research on intelligent transportation system technologies and applications. In: 2008 Workshop on Power Electronics and Intelligent Transportation System, pp. 529–531. IEEE (2008). https://doi.org/10.1109/PEITS.2008.124
Fantin Irudaya Raj, E., Appadurai, M.: Internet of things-based smart transportation system for smart cities. In: Intelligent Systems for Social Good: Theory and Practice, pp. 39–50. Springer (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-0770-8_4
Zhu, L., Yu, F.R., Wang, Y., Ning, B., Tang, T.: Big data analytics in intelligent transportation systems: a survey. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 20, 383–398. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2018.2815678
Rani, P., Sharma, R.: Intelligent transportation system for internet of vehicles based vehicular networks for smart cities. Comput. Electr. Eng. 105, 108543 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compeleceng.2022.108543
Paul, A., Chilamkurti, N., Daniel, A., Rho, S.: Intelligent transportation systems. Intell. Veh. Netw. Commun. Fundam. Archit. Solut. Romer. B Ed. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-809266-8.00002-8
Vlahogianni, E.I., Golias, J.C., Karlaftis, M.G.: Short-term traffic forecasting: overview of objectives and methods. Transp. Rev. 24, 533–557 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1080/0144164042000195072
Zhang, S., Lin, K.-P.: Short-term traffic flow forecasting based on data-driven model. Mathematics 8, 152 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/math8020152
Kerner, B.S.: Congested traffic flow: observations and theory. Transp. Res. Rec. 1678, 160–167 (1999). https://doi.org/10.3141/1678-20
Guerrero-Ibáñez, J., Zeadally, S., Contreras-Castillo, J.: Sensor technologies for intelligent transportation systems. Sensors 18, 1212 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3390/s18041212
Ren, C., Chai, C., Yin, C., Ji, H., Cheng, X., Gao, G., Zhang, H.: Short-term traffic flow prediction: a method of combined deep learnings. J. Adv. Transp. 2021, 1–15 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/9928073
Vlahogianni, E.I., Karlaftis, M.G., Golias, J.C.: Short-term traffic forecasting: where we are and where we’re going. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 43, 3–19 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trc.2014.01.005
Hoogendoorn, S.P., Bovy, P.H.: State-of-the-art of vehicular traffic flow modelling. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part I J. Syst. Control Eng. 215, 283–303 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1177/095965180121500402
Cascetta, E.: Transportation Systems Engineering: Theory and Methods. Springer Science & Business Media (2013)
van Wageningen-Kessels, F., Van Lint, H., Vuik, K., Hoogendoorn, S.: Genealogy of traffic flow models. EURO J. Transp. Logist. 4, 445–473 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13676-014-0045-5
Lana, I., Del Ser, J., Velez, M., Vlahogianni, E.I.: Road traffic forecasting: recent advances and new challenges. IEEE Intell. Transp. Syst. Mag. 10, 93–109 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/MITS.2018.2806634
Zhang, J., Wang, F.-Y., Wang, K., et al.: Data-driven intelligent transportation systems: a survey. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 12, 1624–1639 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2011.2158001
Wu, Y., Tan, H., Qin, L., Ran, B., Jiang, Z.: A hybrid deep learning based traffic flow prediction method and its understanding. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 90, 166–180 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trc.2018.03.001
Kashifi, M.T., Al-Turki, M., Sharify, A.W.: Deep hybrid learning framework for spatiotemporal crash prediction using big traffic data. Int. J. Transp. Sci. Technol. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijtst.2022.07.003
Wang, Y., Yu, X., Guo, J., Papamichail, I., Papageorgiou, M., Zhang, L., Sun, J., et al.: Macroscopic traffic flow modelling of large-scale freeway networks with field data verification: state-of-the-art review, benchmarking framework, and case studies using METANET. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 145, 103904 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trc.2022.103904
Treiber, M., Kesting, A.: Traffic Flow Dynamics: Data, Models and Simulation. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-32460-4
Seo, T., Bayen, A.M., Kusakabe, T., Asakura, Y.: Traffic state estimation on highway: a comprehensive survey. Annu. Rev. Control 43, 128–151 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arcontrol.2017.03.005
Greenshields, B.D., Thompson, J.T., Dickinson, H.C., Swinton, R.S.: The Photographic Method of Studying Traffic Behavior. Note on p. 382 (1933)
Chen, C.P., Zhang, C.-Y.: Data-intensive applications, challenges, techniques and technologies: a survey on Big Data. Inf. Sci. 275, 314–347 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2014.01.015
Hofleitner, A., Herring, R., Bayen, A.: Arterial travel time forecast with streaming data: a hybrid approach of flow modeling and machine learning. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 46, 1097–1122 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trb.2012.03.006
Mohammadian, S., Zheng, Z., Haque, M., Bhaskar, A.: Continuum Modelling of Freeway Traffic Flows in the Era of Connected and Automated Vehicles: A Critical Perspective and Research Needs (2021). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2111.04955
Lighthill, M.J., Whitham, G.B.: On kinematic waves II. A theory of traffic flow on long crowded roads. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Sci. 229, 317–345 (1955). https://doi.org/10.1098/rspa.1955.0089
Richards, P.I.: Shock waves on the highway. Oper. Res. 4, 42–51 (1956). https://doi.org/10.1287/opre.4.1.42
Barceló J, Casas J (2005) Dynamic network simulation with AIMSUN. In: Simulation Approaches in Transportation Analysis: Recent Advances and Challenges, pp. 57–98.https://doi.org/10.1007/0-387-24109-4_3
Payne, H.J.: Model of freeway traffic and control. Math. Model Public Syst., 51–61 (1971)
Daganzo, C.F.: The cell transmission model: a dynamic representation of highway traffic consistent with the hydrodynamic theory. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 28, 269–287 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1016/0191-2615(94)90002-7
Daganzo, C.F.: The cell transmission model, Part II: network traffic. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 29, 79–93 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1016/0191-2615(94)00022-Rt
Wang, Y., Papageorgiou, M., Messmer, A.: Renaissance–a unified macroscopic model-based approach to real-time freeway network traffic surveillance. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 14, 190–212 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trc.2006.06.001
Nagel, K., Wagner, P., Woesler, R.: Still flowing: approaches to traffic flow and traffic jam modeling. Oper. Res. 51, 681–710 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1287/opre.51.5.681.16755
Bando, M., Hasebe, K., Nakayama, A., Shibata, A., Sugiyama, Y.: Dynamical model of traffic congestion and numerical simulation. Phys. Rev. E 51, 1035 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.51.1035
Jiang, R., Wu, Q., Zhu, Z.: Full velocity difference model for a car-following theory. Phys. Rev. E 64, 017101 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.64.017101
Rakha, H., Crowther, B.: Comparison of Greenshields, Pipes, and Van Aerde car-following and traffic stream models. Transp. Res. Rec. 1802, 248–262 (2002)
Minderhoud, M.M.: Supported Driving: Impacts on Motorway Traffic Flow (1999)
Prigogine, I., Herman, R., Schechter, R.S.: Kinetic theory of vehicular traffic. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern., 295–295 (1972)
Solomatine, D., See, L.M., Abrahart, R.J.: Data-driven modelling: concepts, approaches and experiences. Pract. Hydroinformatics, 17–30 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-79881-1_2
Cheslow, M., Hatcher, S.G., Patel, V.M.: An initial evaluation of alternative intelligent vehicle highway systems architectures (1992)
Anand, N.C., Scoglio, C., Natarajan, B.: GARCH—non-linear time series model for traffic modeling and prediction. In: NOMS 2008–2008 IEEE Network Operations and Management Symposium, pp. 694–697. IEEE (2008). https://doi.org/10.1109/NOMS.2008.4575191
Li, Y., Yu, R., Shahabi, C., Liu, Y.: Diffusion convolutional recurrent neural network: Data-driven traffic forecasting (2017). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1707.01926
Ma, T., Zhou, Z., Abdulhai, B.: Nonlinear multivariate time–space threshold vector error correction model for short term traffic state prediction. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 76, 27–47 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trb.2015.02.008
Chen, X., Li, L., Shi, Q.: Stochastic Evolutions of Dynamic Traffic Flow: Modeling and Applications. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-44572-3
Qi, T., Chen, L., Li, G., Li, Y., Wang, C.: FedAGCN: a traffic flow prediction framework based on federated learning and Asynchronous Graph Convolutional Network. Appl. Soft Comput. 138, 110175 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2023.110175
Chen, C., Wang, Y., Li, L., Hu, J., Zhang, Z.: The retrieval of intra-day trend and its influence on traffic prediction. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 22, 103–118 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trc.2011.12.006
Kamarianakis, Y., Shen, W., Wynter, L.: Real-time road traffic forecasting using regime-switching space-time models and adaptive LASSO. Appl. Stoch. Models Bus. Ind. 28, 297–315 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1002/asmb.1937
Chen, Q., Song, Y., Zhao, J.: Short-term traffic flow prediction based on improved wavelet neural network. Neural Comput. Appl. 33, 8181–8190 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-020-04932-5
Zhang, H., Wang, X., Cao, J., Tang, M., Guo, Y.: A hybrid short-term traffic flow forecasting model based on time series multifractal characteristics. Appl. Intell. 48, 2429–2440 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-017-1095-9
Abdulhai, B., Porwal, H., Recker, W.: Short term freeway traffic flow prediction using genetically-optimized time-delay-based neural networks (1999)
Ishak, S., Al-Deek, H.: Performance evaluation of short-term time-series traffic prediction model. J. Transp. Eng. 128, 490–498 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-947X(2002)128:6(490)
Dochy, T.: Arbres de régression et réseaux de neurones appliqués à la prévision de trafic routier. These de doctorat, Paris 9 (1995)
Van Lint, J.W.C.: Reliable travel time prediction for freeways. Netherlands TRAIL Research School (2004)
Vlahogianni, E., Karlaftis, M.: Temporal aggregation in traffic data: implications for statistical characteristics and model choice. Transp. Lett. 3, 37–49 (2011). https://doi.org/10.3328/TL.2011.03.01.37-49
Vlahogianni, E.I., Karlaftis, M.G., Golias, J.C.: Short-term traffic forecasting: where we are and where we’re going. Transp. Res. Part C 1, 3–19 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trc.2014.01.005
Guo, J., Williams, B.M., Smith, B.L.: Data collection time intervals for stochastic short-term traffic flow forecasting. Transp. Res. Rec. 2024, 18–26 (2007)
Jiang, X., Adeli, H.: Wavelet packet-autocorrelation function method for traffic flow pattern analysis. Comput. Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 19, 324–337 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8667.2004.00360.x
Guo, F.: Short-Term Traffic Prediction Under Normal and Abnormal Conditions. Imperial College London (2013)
Smith, B.L.: Forecasting freeway traffic flow for intelligent transportation systems application. Transp. Res. Part A 1, 61 (1997)
Williams, B.M., Durvasula, P.K., Brown, D.E.: Urban freeway traffic flow prediction: application of seasonal autoregressive integrated moving average and exponential smoothing models. Transp. Res. Rec. 1644, 132–141 (1998). https://doi.org/10.3141/1644-14
Williams, B.M., Hoel, L.A.: Modeling and forecasting vehicular traffic flow as a seasonal Arima process: theoretical basis and empirical results. J. Transp. Eng. 129, 664–672 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-947X(2003)129:6(664)
Bates, J.M., Granger, C.W.: The combination of forecasts. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 20, 451–468 (1969). https://doi.org/10.1057/jors.1969.103
Lu, S., Zhang, Q., Chen, G., Seng, D.: A combined method for short-term traffic flow prediction based on recurrent neural network. Alex. Eng. J. 60, 87–94 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aej.2020.06.008
Zheng, W., Lee, D.-H., Shi, Q.: Short-term freeway traffic flow prediction: Bayesian combined neural network approach. J. Transp. Eng. 132, 114–121 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-947X(2006)132:2(114)
Abdi, J., Moshiri, B.: Application of temporal difference learning rules in short-term traffic flow prediction. Expert Syst. 32, 49–64 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1111/exsy.12055
Chen, Q., Song, Y., Zhao, J.: Short-term traffic flow prediction based on improved wavelet neural network. Neural Comput. Appl., 1–10 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-020-04932-5
Choi, T.-M., Yu, Y., Au, K.-F.: A hybrid SARIMA wavelet transform method for sales forecasting. Decis. Support Syst. 51, 130–140 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dss.2010.12.002
Diao, Z., Zhang, D., Wang, X., et al.: A hybrid model for short-term traffic volume prediction in massive transportation systems. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 20, 935–946 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2018.2841800
Hossain, J.: A Hybrid Approach of Traffic Flow Prediction Using Wavelet Transform and Fuzzy Logic, p. 75 (2017)
Karlaftis, M.G., Vlahogianni, E.I.: Statistical methods versus neural networks in transportation research: differences, similarities and some insights. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 19, 387–399 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trc.2010.10.004
Ma, T., Antoniou, C., Toledo, T.: Hybrid machine learning algorithm and statistical time series model for network-wide traffic forecast. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 111, 352–372 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trc.2019.12.022
Wang, J., Shi, Q.: Short-term traffic speed forecasting hybrid model based on Chaos-Wavelet Analysis-Support Vector Machine theory. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 27, 219–232 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trc.2012.08.004
Wei, Y., Chen, M.-C.: Forecasting the short-term metro passenger flow with empirical mode decomposition and neural networks. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 21, 148–162 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trc.2011.06.009
Zhang, G.P.: Time series forecasting using a hybrid ARIMA and neural network model. Neurocomputing 50, 159–175 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-2312(01)00702-0
Kirby, H.R., Watson, S.M., Dougherty, M.S.: Should we use neural networks or statistical models for short-term motorway traffic forecasting? Int. J. Forecast. 13, 43–50 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-2070(96)00699-1
Smith, B.L., Demetsky, M.J.: Traffic flow forecasting: comparison of modeling approaches. J. Transp. Eng. 123, 261–266 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-947X(1997)123:4(261)
Oh, S., Byon, Y.-J., Jang, K., Yeo, H.: Short-term travel-time prediction on highway: a review of the data-driven approach. Transp. Rev. 35, 4–32 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1080/01441647.2014.992496
Van Hinsbergen, C.P., Van Lint, J.W., Sanders, F.M.: Short term traffic prediction models. In: Proceedings of the 14TH World Congress on Intelligent Transport Systems its Held Beijing, Oct 2007 (2007)
Yang, H.-F., Dillon, T.S., Chang, E., Phoebe Chen, Y.-P.: Optimized configuration of exponential smoothing and extreme learning machine for traffic flow forecasting. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 15, 23–34 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2018.2876907
Ahmed, M.S., Cook, A.R.: Analysis of freeway traffic time-series data by using Box-Jenkins techniques. Transp. Res. Rec. (1979)
Hamed, M.M., Al-Masaeid, H.R., Said, Z.M.B.: Short-term prediction of traffic volume in urban arterials. J. Transp. Eng. 121, 249–254 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-947X(1995)121:3(249)
Smith, B.L., Williams, B.M., Keith, O.R.: Comparison of parametric and nonparametric models for traffic flow forecasting. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 10, 303–321 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0968-090X(02)00009-8
Chan, K.Y., Dillon, T.S., Singh, J., Chang, E.: Traffic flow forecasting neural networks based on exponential smoothing method. In: 2011 6th IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications, pp. 376–381. IEEE (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIEA.2011.5975612
Kalman, R.E.: A new approach to linear filtering and prediction problems. J. Basic Eng. 82, 35–45 (1960). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.3662552
Okutani, I., Stephanedes, Y.J.: Dynamic prediction of traffic volume through Kalman filtering theory. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 18, 1–11 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1016/0191-2615(84)90002-X
Kumar, S.V.: Traffic flow prediction using kalman filtering technique. Procedia Eng. 187, 582–587 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2017.04.417
Box, G.E.: GM Jenkins Time Series Analysis: Forecasting and Control. San Franc Holdan-Day (1970)
Rojas, I., Valenzuela, O., Rojas, F., Guillén, A., Herrera, L.J., Pomares, H., Pasadas, M., et al.: Soft-computing techniques and ARMA model for time series prediction. Neurocomputing 71, 519–537 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2007.07.018
Box, G.E., Jenkins, G.M., Reinsel, G.C., Ljung, G.M.: Time Series Analysis, Forecasting and Control-Segunda Edição. Prentice Hall San Francisco (1976)
Brockwell, P.J., Davis, R.A.: Introduction to Time Series and Forecasting. Springer (2002).https://doi.org/10.1007/0-387-21657-X_8
Chung, E., Rosalion, N.: Short term traffic flow prediction. In: Australasian Transport Research Forum (ATRF), 24th, 2001, Hobart, Tasmania, Australia (2001)
Kumar, S.V., Vanajakshi, L.: Short-term traffic flow prediction using seasonal ARIMA model with limited input data. Eur. Transp. Res. Rev. 7, 1–9 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12544-015-0170-8
Zhang, Y., Liu, Y.: Comparison of parametric and nonparametric techniques for non-peak traffic forecasting. World Acad. Sci. Eng. Technol. 51, 8–14 (2009). https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.1329472
Raza, A., Zhong, M.: Hybrid artificial neural network and locally weighted regression models for lane-based short-term urban traffic flow forecasting. Transp. Plan Technol. 41, 901–917 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1080/03081060.2018.1526988
Cortes, C., Vapnik, V.: Support-vector networks. Mach. Learn. 20, 273–297 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00994018
Castro-Neto, M., Jeong, Y. S., Jeong, M. K., & Han, L. D.: Online-SVR for short-term traffic flow prediction under typical and atypical traffic conditions. Expert systems with applications, 36(3), 6164–6173.(2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2008.07.069
Haykin, S.: Neural Networks: A Comprehensive Foundation. Prentice Hall PTR (1998).https://doi.org/10.1017/S0269888998214044
Haykin, S.: Neural Networks: A Comprehensive Foundation. Prentice Hall PTR (1994)
Abiodun, O.I., Jantan, A., Omolara, A.E., et al.: State-of-the-art in artificial neural network applications: a survey. Heliyon 4, e00938 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2018.e00938
Zhang, G., Eddy Patuwo, B.Y., Hu, M.: Forecasting with artificial neural networks: the state of the art. Int. J. Forecast. 14, 35–62 (1998)https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-2070(97)00044-7
Sharda, R., Patil, R.B.: Connectionist approach to time series prediction: an empirical test. J. Intell. Manuf. 3, 317–323 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01577272
Smith, B.L., Demetsky, M.J.: Short-term traffic flow prediction models-a comparison of neural network and nonparametric regression approaches. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, vol. 2, pp. 1706–1709 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICSMC.1994.400094
Yasdi, R.: Prediction of road traffic using a neural network approach. Neural Comput. Appl. 8, 135–142 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s005210050015
Vlahogianni, E.I., Karlaftis, M.G., Golias, J.C.: Optimized and meta-optimized neural networks for short-term traffic flow prediction: a genetic approach. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 13, 211–234 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trc.2005.04.007
Mrad, S., Mraihi, R.: Short term prediction of hourly traffic volume using neural network in interurban freeway. In: 2019 International Colloquium on Logistics and Supply Chain Management (LOGISTIQUA), pp. 1–5 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/LOGISTIQUA.2019.8907310
Song, C., Lee, H., Kang, C., Lee, W., Kim, Y.B., Cha, S.W.: Traffic speed prediction under weekday using convolutional neural networks concepts. In: 2017 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), pp. 1293–1298 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/IVS.2017.7995890
Sawah, M.S., Taie, S.A., Ibrahim, M.H., Hussein, S.A.: An accurate traffic flow prediction using long-short term memory and gated recurrent unit networks. Bull. Electr. Eng. Inform. 12, 1806–1816 (2023). https://doi.org/10.11591/eei.v12i3.5080
Kumar, A., Sunitha, R.: MuSeFFF: multi-stage feature fusion framework for traffic prediction. Intell. Syst. Appl., 200–227 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iswa.2023.200227
Méndez, M., Merayo, M.G., Núñez, M.: Long-term traffic flow forecasting using a hybrid CNN-BiLSTM model. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 121, 106041 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2023.106041
Kim, K.: Financial time series forecasting using support vector machines. Neurocomputing 55, 307–319 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-2312(03)00372-2
Ren, Y., Xie, K.: Transfer knowledge between sub-regions for traffic prediction using deep learning method. In: Intelligent Data Engineering and Automated Learning–IDEAL 2019: 20th International Conference, Manchester, UK, November 14–16, 2019, Proceedings, Part I 20, pp. 208–219. Springer (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-33607-3_23
Majumdar, S., Subhani, M.M., Roullier, B., Anjum, A., Zhu, R.: Congestion prediction for smart sustainable cities using IoT and machine learning approaches. Sustain. Cities Soc. 64, 102500 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2020.102500
Subramaniyan, A.B., Wang, C., Shao, Y., Li, W., Wang, H., Zhang, G., Ma, T.: Hybrid recurrent neural network modeling for traffic delay prediction at signalized intersections along an urban arterial. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. (2022).https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2022.3201880
Khashei, M., Bijari, M.: A novel hybridization of artificial neural networks and ARIMA models for time series forecasting. Appl. Soft Comput. 11, 2664–2675 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2010.10.015
Zeng, D., Xu, J., Gu, J., Liu, L., Xu, G.: Short term traffic flow prediction using hybrid ARIMA and ANN models. In: 2008 Workshop on Power Electronics and Intelligent Transportation System, pp. 621–625 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1109/PEITS.2008.135
Luo, X., Niu, L., Zhang, S.: An algorithm for traffic flow prediction based on improved SARIMA and GA. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 22, 4107–4115 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-018-0429-4
Ouyang, L., Zhu, F., Xiong, G., Zhao, H., Wang, F., Liu, T.: Short-term traffic flow forecasting based on wavelet transform and neural network. In: 2017 IEEE 20th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), pp. 1–6 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/ITSC.2017.8317895
Mousavizadeh Kashi, S.O., Akbarzadeh, M.: A framework for short-term traffic flow forecasting using the combination of wavelet transformation and artificial neural networks. J. Intell. Transp. Syst. 23, 60–71 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1080/15472450.2018.1493929
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Mrad, S., Mraihi, R. (2023). An Overview of Model-Driven and Data-Driven Forecasting Methods for Smart Transportation. In: Rivera, G., Cruz-Reyes, L., Dorronsoro, B., Rosete, A. (eds) Data Analytics and Computational Intelligence: Novel Models, Algorithms and Applications. Studies in Big Data, vol 132. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-38325-0_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-38325-0_8
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-38324-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-38325-0
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)