Abstract
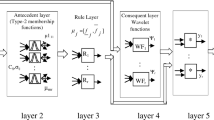
Residential buildings use a significant part of the total energy of the countries. The utilisation of energy is defined by consumer occupancy, construction materials used in buildings. The timely changes of these factors lead to vague and imprecise representations of energy consumption prediction. Fuzzy logic is a more suitable approach for modelling this problem. In this paper, type-2 fuzzy wavelet neural networks (T2-FWNN) is proposed for modelling the energy consumption prediction of residential buildings. The system implements type-2 fuzzy reasoning using wavelet neural network technology. A gradient descent algorithm using a cross-validation approach has been applied for the construction of T2-FWNN system. The learning of T2-FWNN system is based on an adaptive procedure that adjusts learning rates for stabilisation of training. The constructed system is used for the prediction of energy demand in residential buildings of Northern Cyprus. The presented comparative results prove the effectiveness of the constructed T2-FWNN model and the suitability of the T2-FWNN in the prediction of energy demand.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amasyali, K., El-Gohary, N.M.: A review of data-driven building energy consumption prediction studies. Renew. Sustain. Energ. Rev. 81, 1192–1205 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.04.095
Tsanas, A., Xifara, A.: Accurate quantitative estimation of energy performance of residential buildings using statistical machine learning tools. Energy .ings 49, 560–567 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2012.03.003
Simulation Research Group, Lawrence Berkley National Lab, Overview of DOE 2.2 (1998). http://ww.doe2.com/
Crawley, D.B., et al.: EnergyPlus: creating a new-generation building energy simulation program, Energ. Build. 33(4), 319–331 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-7788(00)00114-6
Strachan, P.A., Kokogiannakis, G., Macdonald, I.A.: History and development of validation with the ESP-r simulation program. Build. Environ. 43(4), 601–609 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2006.06.025
Yan, D., Xia, J., Tang, W., Song, F., Hang, X.Z., Jiang, Y.: DeST—an integrated building simulation toolkit part I: fundamentals. Build. Simul. 1(2), 95–110 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12273-008-8118-8
Fumo, N.: A review on the basics of building energy estimation. Renew. Sustain. Energ. Rev. 31, 53–60 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2013.11.040
Kumar, R., Aggarwal, R., Sharma, J.: Energy analysis of a building using artificial neural network: a review. Energ. Build. 65, 352–360 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2013.06.007
Li, Q., Meng, Q., Cai, J., Yoshino, H., Mochida, A.: Applying support vector machine to predict hourly cooling load in the building. Appl. Energ. 86, 2249–2256 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2008.11.035
Hong, W.C.: Electric load forecasting by support vector model. Appl. Math. Model 33(5), 2444–2454 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2008.07.010
Abiyev, R.H.: Fuzzy wavelet neural network for prediction of electricity consumption. AIEDAM: Artif. Intell. Eng. Des. Anal. Manuf. 23(2), 109–118 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1017/S0890060409000018
Abiyev, R., Abiyev, V.H., Ardil, C: Electricity consumption prediction model using neuro-fuzzy system. World Acad. Sci. Eng. Technol. 8 (2005)
Zadeh, L.H.: The concept of linguistic variable and its application to approximate reasoning. Inf. Sci. 8, 199–249 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1016/0020-0255(75)90036-5
Mendel, J.M.: Uncertain Rule-Based Fuzzy Logic System: Introduction and New Directions, 2nd edn, 684 p. Springer, Cham (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-51370-6
Karnik, N.N., Mendel, J.M.: Application of Type-2 fuzzy logic systems to forecasting of time-series. Inf. Sci. 120, 89–111 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0020-0255(99)00067-5
Abiyev, R.H.: A Type-2 fuzzy wavelet neural network for time series prediction. In: García-Pedrajas, N., Herrera, F., Fyfe, C., Benítez, J.M., Ali, M. (eds.) IEA/AIE 2010. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 6098, pp. 518–527. Springer, Heidelberg (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-13033-5_53
Abiyev, R.H., Kaynak, O., Alshanableh, T., Mamedov, F.: A Type-2 neuro-fuzzy system based on clustering and gradient techniques applied to system identification and channel equalization. Appl. Soft Comput. 11(1), 1396–1406 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2010.04.011
Abiyev, R.H., Kaynak, O.: Type-2 fuzzy neural structure for identification and control of time-varying plants. IEEE T. Ind. Electron 57(12), 4147–4159 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2010.2043036
Abiyev, R.H., Kaynak, O., Kayacan, E.: A type-2 fuzzy wavelet neural network for system identification and control. J. Franklin Inst.-Eng. Appl. Math. 350(7), 1658–1685 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfranklin
Kayacan, E., Oniz, Y., Aras, A.C., Kaynak, O., Abiyev, R.: A servo system control with time-varying and nonlinear load conditions using Type-2 TSK fuzzy neural system. Appl. Soft Comput. 11(8), 5735–5744 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2011.03.008
Abiyev, R.H: Credit rating using Type-2 fuzzy neural networks. Math. Probl. Eng. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/460916
Thuillard, M.: Wavelets in Softcomputing. World Scientific Press, Singapore (2001)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Abiyev, R., Abizada, S. (2023). Prediction of Energy Consumption in Residential Buildings Using Type-2 Fuzzy Wavelet Neural Network. In: Aliev, R.A., Kacprzyk, J., Pedrycz, W., Jamshidi, M., Babanli, M.B., Sadikoglu, F. (eds) 15th International Conference on Applications of Fuzzy Systems, Soft Computing and Artificial Intelligence Tools – ICAFS-2022. ICAFS 2022. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 610. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-25252-5_46
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-25252-5_46
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-25251-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-25252-5
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)