Abstract
This paper analyzes the academic literature that highlighted the role of digitalization in the implementation of sustainability strategies within organizations. It questions how digital transformation could help organizations to integrate the corporate social responsibility perspective in their structure, their value proposal, business, and management methods (ethics, values…). The main results of the literature review insist on the positive contribution of digital transformation in the implementation and success of corporate social responsibility strategies. Even though the reviewed literature does not give insights into the conditions and implementation processes underlying such positive effect, it highlights the key factors that could positively link digital transformation and the development of corporate social responsibility strategies. These results appear useful both for business practice and future research.
Access provided by Autonomous University of Puebla. Download conference paper PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Keywords
1 Introduction
Everything around us nowadays is based on technology, it is no wonder that our lives revolve around a digital and automated orbit. Let us travel together back in time and remember the initial industrial revolution where they used water and steam to power mechanical production facilities, then came the second industrial revolution where electric power and division of work was utilized for mass production. After that, we all remember the third revolution in industry where the introduction of electronics and information technology enabled a breakthrough that led to the automation of production lines. This is generally referred to as the digital revolution, catalyzed by the development of semiconductors, mainframe computing (1960s), personal computing (1970s and 1980s), and the Internet (1990s).
Today, we are experiencing the fourth industrial revolution. Starting at the turn of the century, it bases on and extends the third digital revolution and it is characterized by a much more ubiquitous and mobile internet, by smaller and more powerful sensors that have become cheaper, by artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning. Similar to other revolutions that took place before, this fourth industrial revolution has the possibility to enhance the global income and expand the standard and quality of life for all populations around the world, while implementing sustainable development goals. Technology has changed and evolved every aspect of our daily lives and made it easier, with various options available, to improve and increase the productivity of our work. We can thus say that the digital transformation is the most essential deliverable of the fourth industrial revolution.
The digital transformation taking place nowadays is leading modern organizations to switch from traditional to digital business models. Progression towards an even more digital world is underway with all industries transforming their traditional operations into digitalized business operations. This transformation process poses challenges and pushes businesses to create awareness among the people working in their organization to undergo new strategies. In order to meet the global climate goals of 2050, the transformation into a circular and thus sustainable economy needs to be accelerated. Such an acceleration is possible through a responsible digitalization. In order to become more socially responsible, a lot of organizations are utilizing their digital and technology innovations to implement strategies characterized by sustainable corporate social decisions. The key success factor for incorporating digital transformation into an effective corporate social responsibility (CSR) is leadership, together with an authentic commitment of leaders and managers within organizations to go through a sustainability-oriented process of change.
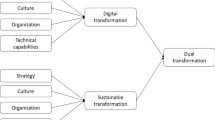
Sustainability within organizations may have many different meanings, such as taking a more ethical approach towards employees, shareholders as well as towards the social and environmental issues. Digital transformation can lead organizations to be socially responsible by supporting the development of sustainable strategies to the benefit of society and the whole economic system. The aim of this paper is to conduct a review of the existing literature to explore digital transformation, its impact on CSR and its contribution to sustainable development through the operationalization of the main CSR principles within organizations.
The paper will be structured as follows: An introduction to the history of digital transformation, review of the conceptual models of digital transformation, review of definitions of sustainable development in literature, overview of CSR within organizations, review of digital transformation and its contribution to CSR, and sustainability within organizations and finally concluding all the above.
2 Literature Review
2.1 Definition of Digital Transformation
In literature, there is not a commonly accepted definition of Digital Transformation (DT). The available definitions show significant variations around the concept of DT that mainly result from the widely spread and diverse academic backgrounds of DT scholars and practitioners. Digital transformation is a relatively new concept in the field of Information technology and business, which has attracted the attention of researchers but at the same time is lacking consensus on a unified definition. Researchers have adapted different approaches to define DT. Some tackled it from a business process point of view and others from a technological perspective. However, many researchers have conceptualized DT as a business strategy and not only as a technological process. Digital transformation is thus related to a revolution impacting the overall work environment (including strategy, management, and people) [1]. On a similar note, digital transformation is referred to as a continuous process characterized by different digital phases and going through a complete redesign to achieve new digital customer experience and enhanced digital value propositions [2].
Between 1990 and 2000, for example, digitalization enabled payments to be done online and not only physically in the store like the old traditional way. In the following decade from 2000 till 2010, smart devices started emerging and, together with the expansion of social media platforms, they transformed the retail way of how customers and businesses deal with each other. Educational courses started becoming digital, online payments such as those taking place on PayPal have increased, and online banking and commerce have taken off to become the normal way of doing business. Nowadays, thanks to new communication and mobile technologies, a massive amount of customers’ data can be collected online and leveraged to advertise more effectively by tailoring advertising to fit customers’ specific needs. Table 1 illustrates the chronological history of digital transformation.
Digitalization is considered as one of the primary impetus of today’s development that is linked to achieving higher competitiveness by improving the economic, social, and environmental aspects in life [3]. DT is a process used to enhance the performance of organizations, by improving their use of technologies to transform customer relationships, modify internal processes, and capitalizing on new value propositions [4]. On another note, Mazzone highlighted that DT is a continuous digital evolution of the organization, a redesign of business models that introduces new process ideas on a strategic level [5]. To sum up, the different definitions of digital transformation depict a networking of businesses and customers across all value-added chain segments, which include the application of new technologies and appropriate skills and analysis to evolve business models and processes, ultimately leading to an increased performance of organizations [2]. The benefits and positive impacts of DT on business and the economy as a whole highlight that DT is a new form of change that can enable technology to transform existing business [6].
Digitalization from the notion of technology alone may not yield results. However, if coupled with strong strategic leadership, technology can transform firms into digitally mature organizations, which outperform those that are not digitally mature [7]. A lot of organizations lack leadership even if they possess digital capabilities to transform their processes; this lack of leadership prevents organizations to strategize and develop in the right direction. In a McKinsey report of 2017 [8], DT is defined as a process of reinvention. It is not related to the process of digitizing a product or process, it is rather a redesign of processes or an enhancement that generates for instance new customer experience using technology platforms. It is strategy, not technology, that steers DT in the right direction. Thus, in order for organizations to gain value out of the transformation, they should adopt a carefully coordinated digital approach across four areas: first of all, organizations should grasp what is the real value of digitalization; then, they should redesign their structure and processes to target more profitable yet economical changes; third, they would need to back such changes with effective partnerships; and finally, organizations should make sure to evaluate the risk when going through this process of change. If organizations are to respect the sustainable development goals, this implies that organizations act as good citizens and not only work for generating profits. Such an approach needs to become an imperative for the DT process [8] and can only be enabled by an established strategic leadership.
Nwaiwu’s literature review highlighted that there is a lack of connection or application between practice-oriented and academic-based research related to the subject of digital business transformation [4]. This implies that future research should emphasize this gap to ensure that the academic research is practiced by organizations adopting digital transformation. His research findings point out that digital transformation for organizations does not refer to the adoption of technology as this alone does not efficiently transform the organization. Further research reconfirmed that digital business transformation relates to a strategy that has to be aligned with the overall corporate strategy of an organization [4]. On the same note, a new philosophy of digital transformation highlights the appeal of digital entrepreneuring, defined by Gunasilan as “Technopreneurship,” a new concept to strengthen organizations by enabling collaborative digital entrepreneurial ventures [9]. In other words, the researcher emphasized that when startup organizations collaborate with developed organizations, they capitalize on their digital transformation by combining their internal capabilities with external ones and thus maximizing their efficiency. Collaboration in digital transformation can build innovation-oriented partnerships that can extend the best capabilities of both organizations [9].
The potential of DT to achieve the sustainable development goals in the economy has been explored in literature [10]. It is an important area to look into and understand how DT can contribute to the success of SDGs from a local perspective. DT could help organizations become more efficient in adopting a sustainable strategy aligned with their overall strategy. ElMassah and Mohieldin highlighted that decentralized economies or governance structures yield successful transformation as they involve local communities to be part of the decision making. Digital transformation can contribute to the accomplishment of sustainability if complete transparency and thus free exchange of information is ensured [10]. This ensures that sustainability can be accomplished successfully locally which in turn will ensure the global success. On top of that, in order to have a successful implementation of digital transformation within organizations, there must be a change of organizational culture and thus of people’s awareness working in the business [1].
Table 2 summarizes all the above-mentioned conceptualizations of digital transformation from the perspective and approach of different researchers.
2.2 Review of the Conceptual Frameworks or Theories on Digital Transformation
This section analyzes the relevant theories that have been developed by different scholars on digital transformation and their application within the organizational context [4]. Some of these theories are relevant and empirically tested, whereas some others lack the applicability of the theory within companies.
The frameworks that looked at digital transformation from a technological and strategic perspective include the “Six Keys to Success” framework proposed by Kavadia et al. (2016), “The Digital Reinvention” framework by Berman et al. (2016), the “Digital Transformation Model” proposed by Matt et al. (2015), the “Technology Acceptance Model (TAM)” proposed in 1989 by Davis, and the “Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT) model” proposed by Venkatesh et al. (2003). Table 3 summarizes the findings of the relevant frameworks discussed in digital transformation and presents a comparison of the selected frameworks.
The above review of the theoretical frameworks, whether their approach is academic or business oriented, helps in understanding the parameters used to support organizations during their digital transformation journey [4]. The “Six keys to Success” and the “Digital Reinvention” frameworks highlighted the dimensions that are key to success for organizations going through a digital transformation. However, these frameworks present some limitations as they could not link these dimensions to the performance of organizations. Focused on the general business model they failed to link the technology development with the organization itself. Therefore, they are considered as business tools for organizations to understand “how to” transform, but not complete in terms of achieving digital business transformation.
TAM and UTAUT frameworks looked at the technology adoption from a narrow point of view: the “personal” rather than the overall point of view. Therefore, they lack the depth to analyze how different organizations are transformed by digitalization. This confirms that digital transformation represents rather an organizational strategy, and not only an intention and behavior analysis aiming at technology adoption. Despite the above-mentioned limitations, most frameworks capture that people’s technology acceptance and leadership are key factors to enable a successful digital transformation within organizations.
The result of this review of frameworks suggests that future research should investigate on DT by combining business and academic frameworks to achieve clear empirical evidence concerning the impact of DT on organizations.
2.3 Definition of Sustainable Development
The United Nations defined sustainable development (SD) as “development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs” [11]. The idea behind this definition is to develop while preserving resources from depleting in the future, which explains the difference between being environmentally friendly and being sustainable. In 2015, the member countries of the UN nations approved a new plan for sustainability that should yield results by 2030. They decided on 17 goals that promote sustainability development to ensure a better and safer world for the people and planet.
Sustainability was argued in research as a source for competitive advantage [12]. The ultimate goal of SD is the long-term stability of the economy and environment; and this is only attainable through the integration and acknowledgment of economic, environmental, and social concerns throughout the decision-making process [13, 14]. The aim of the sustainable development goals is to ensure a good equilibrium between needs of the economy, environmental, and social aspects, which allows to preserve resources for the present and upcoming generations. Avoiding the over consumption of natural resources while ensuring not to exploit these resources is key to achieving a healthy and balanced environment that is as well socially efficient [15]. These goals, set by the UN and agreed upon by 193 countries, represent the starting point of a transforming process into a longer sustainable world to fight poverty and attain sustainable development within the next 15 years [16].
The three elements that are essential to the sustainable development goals can be classified as environmental, economic, and social elements. These elements may introduce complications in balancing their objective and success. The question is which aspect will take precedence and if two are conflicting, which of these elements can be successfully measured in terms of success or failure [14]. For example, an economical goal can be moving energy to non-polluting sources, which may contradict social goals as the poor will probably not be able to afford it and the burden on them will increase. Therefore, the goals that contribute efficiently to society, economy, and environment should complement and not contradict each other to reach and build sustainability in the world. Researchers stressed that for all the sustainable goals to be achieved equally and fairly, global governance systems must be designed for the effective integration of all three elements [13]. This supports the argument that digital transformation can play a major important role in achieving the implementation of sustainable development strategy. On a similar note, other research defined sustainability as a choice of selection, rather a mindset to respect the overall environment and the social goals [16]. This further supports the idea that the three elements—economic, environmental, and social—are the fundamental pillars of sustainability. On the other hand, other research argued that production and consumption (economic theory) need to transform in order to achieve sustainability [17]. Therefore, sustainability is understood as the accommodation of the economic needs, in addition to the social, and to the environmental requirements of the present time and of the future generations.
Literature had studied the relationship between sustainability and financial performance [18]. Pyka confirmed that sustainability strategy served as a support factor enhancing the effect of managerial capability on financial performance. This positive correlation confirmed that employing or adopting a digital business strategy will enhance the financial performance of the organization. Sustainability has become an important part of business operations. On another note, further research emphasized that there is a lack of attention towards the implementation of sustainability strategies within the overall business strategy of an organization [19]. Ukko et al. highlighted the factors required to ensure a successful implementation of an efficient corporate sustainability strategy. This includes having a proper organizational structure that is driven by a strong leadership. These new strategies should take into consideration cost reduction and optimization of processes by improving efficiency. Therefore, another definition that was introduced by Ukko et al. for sustainability is the fact that it is a strategy that needs to be developed by integrating the sustainable development principles mentioned in literature into business operations [19].
Moreover, the relation between sustainability and organizations was discussed by Engert and Baumgartner in the context of organizational strategies [20]. Organizations should shift their thinking from a competitive strategy to incorporate a sustainable strategy. Competitive strategies within organization definitely yield profit to shareholders, however sustainable strategies yield gains to stakeholders by increasing partnerships to improve competitiveness. Sustainability within organizations is an important topic that consist in finding a balance between generating profits while ensuring the safety of the other people and the planet. Therefore, for organizations to do so and become sustainable thinkers, they must undergo a shift in their economic or financial mindset and evolve it into a more social and economically sustainable mindset. This shift does not happen over a day or so, this is part of a continuous and long-term process of change, led by managers and leaders inside the organization and aimed at ensuring the adoption and implementation of sustainable strategies. The authors’ research emphasized the conflict or contradiction that organizations face nowadays between the financial-economical view and the sustainable view [20]. They further highlighted the importance of educating leaders and managers about sustainability. Managers or leaders need to be aware that they are accountable for making sound decisions beneficial to all stakeholders. Sustainable strategies within organizations are not only based on the management approach as an economical practice but rather on a social approach (culture and people).
2.4 Definition of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) Within Organizations
When we refer to a “corporate entity,” we are simply pointing to an organization or corporation which exist to generate profit and maximize this profit. However, there is an increased pressure nowadays on organizations to act as a good citizen to the society and environment [20]. The legitimization of achieving corporate success has been depicted in a lot of research as possible if organizations adopt Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) within its organization’s strategy. Therefore, the concept of Kumar of CSR was originated from the concept of organizations leaving an impact of social, economic, and environmental nature [1]. Orbik and Zozulakova stated that the problem of CSR was apparent in the 1980s where organizations in the US used monopoly practices which led European companies to lose business. This is when CSR started emerging to protect organizations from the exploitation of their practices, that can cause an economic and social cost.
Several research studies highlighted the positive impact of introducing CSR strategies and practices within organizations. Researchers addressed the necessity of CSR and digital transformation as main factors to achieve organizational competitiveness [1], including the improvement of financial performance for the organization, a better reputation for the business, improved employee motivation, enrichment of brand image, decreasing operating costs, and increased sustainability for the environment and society. This helps to differentiate an organization from its competitors. These CSR-driven benefits favor the goodwill of the organizations as well as that of our society as a whole.
On the same note, other research highlighted that organizations should act in an ethical and sensible way towards society and environment and that this is not a differentiation strategy within their organization, it is rather a normal strategy to obtain legitimacy [21]. Kumar examined the concept of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) as a strategic business decision that maintains a balance between the social, environmental, and economic benefits of stakeholders and shareholders. CSR was always understood as beneficial from a social point of view by doing good deeds and sponsorships to the society. It was rather a philanthropic concept. However, a proper CSR strategy should be mirroring the organizational overall strategy. It is about realizing a competitive advantage in the society that can enhance sales while cutting operational costs by improving the supply-chain both economically and socially. CSR is described as a responsibility of the shareholders and directors of the organization onwards employees, shareholders, stakeholders, and also the environment and society [21]. In 2005, the concept of CSR became more prevalent towards the concept of business. It stated the major six principles that are supposed to guide organizations in doing business through legitimate and fair practices to promote governance and ethics. Adhering to these six principles would certainly constitute the social responsibility of a company. Briefly, these six principles of CSR are listed below as follows:
-
1.
“Businesses should have a proper conduct in line with Ethics, Transparency and Accountability.”
-
2.
“Businesses should provide goods and services that are safe and contribute to sustainability throughout their life cycle.”
-
3.
“Businesses should protect the well-being of all employees.”
-
4.
“Businesses should respect and promote human rights.”
-
5.
“Businesses should respect, protect, and make efforts to restore the environment.”
-
6.
“Businesses, when engaged in influencing public and regulatory policy, should do so in a responsible manner.”
Organizations should evolve their strategy and undergo a redesign of their processes in order to re-align and adopt a sustainable culture [21]. Palma et al. pointed out that managers play a fundamental role in integrating a sustainable approach in the organization’s strategy, in order to make it ecologically and socially acceptable by society. It is imperative to keep the socio-economic environment embedded within the organizational strategy [9]. The authors stressed out the importance of a proper implementation of corporate social responsibility strategies within organizations to survive the worldwide competitive struggle. They analyzed an effective approach to assess the competitive advantage of the organization by considering the practices of the organization in building its competitive strategy. These competitive indicators are the People, Profits, Planet, and Partnership. Their research confirmed that the integration of the corporate social practices of the organization in the development of sustainable strategies is essential.
Moreover, a study conducted in Bangladesh on the entrepreneur’s personal social responsibility (PSR) has confirmed that the entrepreneurs’ PSR has a positive effect on the longevity and credibility of the CSR of their organizations [22]. The important element in establishing a reputable CSR lies in the intangible asset of organizations which is their people or what is called the human capital [22]. Basically, if a person’s behavior is based on good values and ethics and the person tends to take responsibility on a personal level towards society, this will definitely reflect positively on and improve the quality of CSR. In other words, personal social responsibility has a positive effect on CSR.
3 Digital Transformation and Its Contribution to Corporate Social Responsibility as a Sustainability Strategy Within Organizations
Sustainability concerns have forced organizations to reconsider their strategies to incorporate the social well-being of the society and the organization. In order for organizations to implement effective sustainability-focused strategies, they have to consider a process of change. This is not about product change or change of a specific service that an organization offers; it is about creating new strategies and a full transformation of the organization’s business process.
Research emphasized that managers should benefit from the digital transformation by utilizing technology to evolve their internal processes and value propositions [15]. Emas focused on the implementation of digital transformation within the overall organization that also sustains their responsibility to remain socially and economically efficient towards the society. Three blocks of digital transformation including an evolvement of the organization’s customer experience, operational processes, and its overall business model have stressed the importance of leadership within this transformation to accomplish an effective CSR strategy.
A lot of organizations are utilizing IT capabilities and systems to enhance customer experience by the understanding of customers and by building effective cost structures that positively affect society. For example, restaurants adjust their price structures to fit the demand of people due to weather or inventory or proximity to closing times. Other examples include insurance companies and banks that redeveloped their cost structures to be more socially acceptable. All this is possible thanks to the IT-driven business analytics they use to understand their customers better. This leads to CSR and sustainability by opening to radical reinventions in seeking new sustainable sources of income. These adjustments or the concept of building a new reinvention of the fundamental business can yield real benefits and represents an important phase to drive organizations into digital transformation.
Digital transformation or reinvention does not refer to taking an existing product and digitalizing it by introducing an e-commerce site or digitizing a customer experience [13]. A new concept or approach for organizations as a tool to support them in developing their economic, social, and environmental competitiveness in order to achieve their CSR strategies has been discussed in literature [21]. With the help of IT systems, organizations should develop specialized CSR teams to implement CSR strategies that formulate policies for their social corporate programs. These programs have clear objectives that run with the purpose of achieving social well-being and are aligned with the objectives and strategies of the overall business. The programs are led by decision makers and employees that can make this process effective within the organization [21]. In other words, these CSR programs can be linked with the development of communities, aligning with educational or health projects in the community, thus contributing to improve societies and the overall environment.
Other researchers drew some similarities and differences between the concept of business processes reengineering (BPR), which complements CSR strategies, and digital transformation [2]. Their research reconfirmed the contribution of what digital transformation can add to the development of CSR or sustainable development strategies of organizations. Their research designed a roadmap as an approach to the DT of business models. The last stage, which they called digital implementation, concerns the reengineering of an organization’s strategy to redesign the digital customer experience and develop a digital value-creation network by integrating partners [2]. They proved that DT refers to a continual process and not just to technology enablement, which confirms research addressing DT as a tool to achieve CSR as a sustainability strategy within organizations [2, 21].
Other research looked into the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) on a local level and how DT can affect the achievement of these goals [22]. The commitment of world leaders towards the adoption of such goals in 2015 put pressure and challenged every country to localize the SDGs. Considering these national and global efforts towards sustainable development, including the process of localizing these efforts, technology and innovation play an important role to achieve or facilitate sustainability [10]. ElMassah and Mohieldin examined several case studies of DT application in 7 countries, considering also the progress towards localizing the SDGs. Their findings confirmed that digital transformation improves the process of localizing SDGs. Big Data and e-governance can facilitate the effective implementation of sustainable development through the localization of the SDGs [10].
On the same note, similar research studied the impact of digitalization on the development of sustainability in societies and confirmed that the level of digitalization can improve the sustainable economic development on a country level [12]. Porter et al. confirmed that as the digitalization level increases, the economic development level also increases through higher competitiveness, innovativeness, and entrepreneurial activities. This is reflected in a higher GDP in the more digitalized countries. Additionally, their research concluded that the social aspect of the country is also positively influenced by the digitalization. However, the ecological environment is neglected showing a negative impact of digitalization. The authors explained that the cultural dimensions or other differences between nations may influence the process of digitalization.
Digital transformation does not only base on a technical capability, it rather depends on a managerial and operational capability that leads to a successful sustainable development in the organization [18]. This is because digital transformation implies a redesign of business processes taking into consideration the sustainability strategy, and this requires not only technical capabilities but also experienced managerial and organizational capabilities to succeed. Research showed that sustainable development is positively correlated with financial performance. Therefore, this is a confirmation that digital transformation supports and improves the sustainability development strategies of organizations by means of capable managers leading the transformation and redesigning business processes. However, research that empirically analyzes the effect of DT on sustainability within organizations is still poor [18].
Therefore, in order to achieve a successful digital transformation within organizations, a sustainable CSR strategy coupled with an effective leadership able to align the organizational strategy with a sustainable approach is needed. Corporate Leadership seems to be a critical component for creating a sustaining value in organizations. Table 4 summarizes the role of DT in CSR to ensure sustainability development within organizations along with the essential components needed to drive this transformation effectively.
4 Conclusion
The review of the various conceptual and theoretical frameworks relevant to digital transformation within organizations has depicted a lack of adequate research towards the implementation of sustainability strategy within the organization’s business strategy, or what is referred to as the Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) and its contribution to digital transformation. The theoretical frameworks of TAM and UTAUT have addressed the technology adoption and user behavior intention towards technology from a “person” point of view and not from an “organizational” point of view. Technology has developed rapidly in today’s environment where industries and organizations are highly impacted by this transformation. Countries around the world as well as major industries have noticed that their natural resources have been exploited in order to keep up with the rapid economic growth that is happening all around the world. Therefore, organizations should benefit from the digital transformation by utilizing technology as a strategy to evolve their internal processes and enhance their value propositions in order to become more sustainable socially and economically.
This paper analyzed the business and theoretical frameworks and looked into the existing academic literature to look for a logic and introduce a research-based analysis to find a proper fit of corporate social and digital transformation. CSR and digital transformation are relatively new concepts that are reshaping the relationship between technology and organizational strategy. Corporate Digital Responsibility (CDR) is the new approach of organizations that reinforces the corporate social responsibility by adapting to the impact of technological and digital transformation. DT can serve as a framework for understanding how the digital reinvention or evolution can also evolve towards a sustainable development. It impacts the sustainability aspects of doing business. DT is the primary step in helping leaders in the economy and in the organizations achieve a better digital sustainable world with un-depleting resources for the future.
Today everything is dependent on the capabilities of technology. In business nowadays, the major revolution is to switch from traditional to digital business models to maximize competitiveness. Digital transformation is one of the important developments in the business world. Its contribution to organizations for achieving a successful and sustainable development depends on the managerial capabilities and not only on the technical capabilities of organizations. It is important that the overall organizational strategies ensure proper alignment with its technical capability and includes the knowledge and competencies to integrate and redesign their business processes by taking into consideration the sustainability strategy or what we call the corporate social responsibility strategy of organizations. DT processes need experienced managerial and organizational capability to succeed.
Therefore, organizations should benefit from digital transformation if they evolve their strategy and transform their processes by showing CDR and implementing a Corporate Social Responsibility strategy that calls for a digital but sustainable culture. In order to accomplish that, managers and leaders in organizations play a fundamental role in transforming the organization into a sustainable entity. Leadership is an essential organizational trait for the success of such transformation, as it is critical for creating and sustaining the appropriate values within the organization. Thus, the success of DT depends not only on the IT capabilities, but also and especially on the right combination of other factors such as proper managerial and leadership skills as well as organizational thinking and commitment within the organization. For future research, it is important to explore the notion of corporate leadership and its relation to the success of digital transformation implementation. There is not sufficient academic studies linking DT and leadership. It is advisable to research these dimensions further to explore the relationship between digital transformation success and leadership effect on CSR within organizations. The limitation in this literature review is that most of the research studies looked at and concentrated only on qualitative studies and did not apply any qualitative analysis which could result in more significant information that is related to the topic. Therefore, for future research, we could know more about the digitalization transformation process and successful implementation to learn more in depth about successful strategies that organizations follow to encourage digital transformation implementation and know more about what kind of real experiences they have passed through to implement DT.
References
Orbik, Z., & Zozuľaková, V. (2019). Corporate social and digital responsibility. Management Systems in Production Engineering, 27, 79–83.
Schallmo, D., Williams, C., & Boardman, L. (2017). Digital transformation of business models—Best practice, enablers, and roadmap. International Journal of Innovation Management, 21, 1740014.
(2018). Digitalization and society’s sustainable development—Measures and implications. Zbornik radova Ekonomskog fakulteta u Rijeci: časopis za ekonomsku teoriju i praksu/Proceedings of Rijeka Faculty of Economics: Journal of Economics and Business, 36.
Nwaiwu, F. (2018). Review and comparison of conceptual frameworks on digital business transformation. Journal of Competitiveness, 10, 86–100.
Mazzone, D. (2014). Digital or death: Digital transformation—The only choice for business to survive smash and conquer (1st ed.).
Arroyo Lazo, M. A. (2018). Schwab, Klaus. The fourth industrial revolution. Ginebra: World Economic Forum, 2016, 172 pp. Economía, 41, 194–197.
(2011). Digital business transformation and strategy: What do we know so far? https://www.researchgate.net/publication/322340970_Digital_Business_Transformation_and_Strategy_What_Do_We_Know_So_Far.
(2017). Digital reinvention: Unlocking THE ‘HOW’. McKinsey. https://www.mckinsey.com/business-functions/mckinsey-digital/our-insights/digital-reinvention-unlocking-the-how.
Gunasilan, U. (2019). Entrepreneurship as a driver of the digital transformation. International Review of Management and Marketing, 9, 23–29.
ElMassah, S., & Mohieldin, M. (2020). Digital transformation and localizing the sustainable development goals (SDGs). Ecological Economics, 169, 106490.
(1987). Report of the world commission on environment and development: Our common future. https://digitallibrary.un.org/record/139811.
Porter, M. E., & van Linde, C. (1995). Toward a new conception of the environment-competitiveness relationship. Journal of Economic Perspectives, 9, 97–118.
Dernbach. (2003). Achieving sustainable development: The centrality and multiple facets of integrated decision making. Indiana Journal of Global Legal Studies, 10, 247.
Stoddart, H. (2011). A pocket guide to sustainable development governance. Commonwealth Secretariat.
Emas, R. (2015). The concept of sustainable development: Definition and defining principles. https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/content/documents/5839GSDR%202015_SD_concept_definiton_rev.pdf.
Freyling, V. The importance of all sustainable development goals (SDG).
Harris, J. M. (2004). Global environmental challenges of the twenty-first century: Resources, consumption, and sustainable solutions. Ecological Economics, 50, 315–316.
Pyka, A. (2017). Dedicated innovation systems to support the transformation towards sustainability: Creating income opportunities and employment in the knowledge-based digital bioeconomy. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity, 3.
Ukko, J., Nasiri, M., Saunila, M., & Rantala, T. (2019). Sustainability strategy as a moderator in the relationship between digital business strategy and financial performance. Journal of Cleaner Production, 236, 117626.
Engert, S., & Baumgartner, R. J. (2016). Corporate sustainability strategy—Bridging the gap between formulation and implementation. Journal of Cleaner Production, 113, 822–834.
Palma, L. C., Pedrozo, E. Á., & Alves, N. B. (2019). Sustentabilidade, organizações e formação de gestores: Uma pesquisa exploratória em cursos De administração no Rio Grande do Sul. Revista de Administração da UFSM, 11, 1324–1343.
Kumar, S. (2017). Position and technology of corporate social responsibility in company management. International Journal of Recent Research Aspects, 4(3), 126–131.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Diab, Y., Nasr, I.B. (2023). Digital Transformation and Its Contribution to Corporate Social Responsibility as a Sustainable Development Strategy Within Organizations: A Literature Review. In: Dal Zotto, C., Omidi, A., Aoun, G. (eds) Smart Technologies for Organizations. Lecture Notes in Information Systems and Organisation, vol 60. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-24775-0_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-24775-0_8
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-24774-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-24775-0
eBook Packages: Business and ManagementBusiness and Management (R0)