Abstract
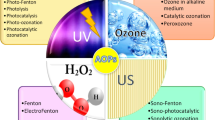
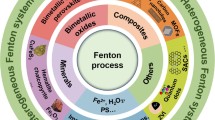
Advanced oxidative processes (AOPs) are technologies in which an oxidizing agent degrades organic molecules until their total mineralization. Therefore, this makes AOPs a promising alternative in the treatment of industrial effluents. The AOPs that most stand out are catalytic processes due to the efficient use of the oxidizing agent and the complete conversion of the pollutant into carbon dioxide and water. Studies related to the use of catalysts aim at optimizing their performance. Optimization strategies include maximization of the contact area, the functional groups, and the active sites. The particle size and porosity of the catalysts are characteristics that influence the efficiency of heterogeneous systems. Scientific research in this area focuses efforts on synthesis methods and the improvement of existing catalysts. Some of the solids with the best characteristics for catalysis are nanocatalysts, which have particle sizes of less than 300 nm and rough surfaces that allow full contact between the molecules of the degradation system. Advances in research signify that there is currently a great diversity of nanocatalysts with varied characteristics and purposes, thus making the identification, classification, and study of the behavior of these materials complicated. This chapter presents the advances in the development of nanocatalysts, classification according to the most relevant characteristics, an analysis of the synthesis process, and uses in the treatment of industrial effluents. Another aspect analyzed is the composition of the substituent groups in the active sites of nanocatalysts, such as amino and hydroxyl groups, characteristic of biogenic processes. Finally, the chapter discusses the perspectives of heterogeneous catalysis with nanomaterials, the challenges to be faced, and consideration to increase the efficiency of the degradation processes.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abolghassem S, Molaei S, Javanshir S (2019) Preparation of α-chitin-based nanocomposite as an effective biocatalyst for microwave aided domino reaction. Heliyon 5:e02036. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02036
Adyani SH, Soleimani E (2019) Green synthesis of Ag/Fe3O4/RGO nanocomposites by Punica Granatum peel extract: catalytic activity for reduction of organic pollutants. Int J Hydrog Energy 44:2711–2730. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.12.012
Ahmed T, Noman M, Shahid M et al (2020) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles transformed synthetic textile dye into less toxic intermediate molecules through LC-MS analysis and treated the actual wastewater. Environ Res 191:110142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.110142
Alle M, Lee S-H, Kim J-C (2020) Ultrafast synthesis of gold nanoparticles on cellulose nanocrystals via microwave irradiation and their dyes-degradation catalytic activity. J Mater Sci Technol 41:168–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2019.11.003
Ameri A, Shakibaie M, Ameri A et al (2016) Photocatalytic decolorization of bromothymol blue using biogenic selenium nanoparticles synthesized by terrestrial actinomycete Streptomyces griseobrunneus strain FSHH12. Desalin Water Treat 57:21552–21563. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2015.1124349
Atalay S, Ersöz G (2016) Review on catalysis in advanced oxidation processes. In: Atalay S, Ersöz G (eds) Novel catalysts in advanced oxidation of organic pollutants. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 35–58. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-28950-2_4
Atarod M, Nasrollahzadeh M, Sajadi SM (2016) Euphorbia heterophylla leaf extract mediated green synthesis of Ag/TiO2 nanocomposite and investigation of its excellent catalytic activity for reduction of variety of dyes in water. J Colloid Interface Sci 462:272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2015.09.073
Barabadi H, Honary S, Ali Mohammadi M et al (2017) Green chemical synthesis of gold nanoparticles by using Penicillium aculeatum and their scolicidal activity against hydatid cyst protoscolices of Echinococcus granulosus. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:5800–5810. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-8291-8
Baran T, Sargin I (2020) Green synthesis of a palladium nanocatalyst anchored on magnetic lignin-chitosan beads for synthesis of biaryls and aryl halide cyanation. Int J Biol Macromol 155:814–822. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.04.003
Bhuiyan MSR, Miah MY, Paul SC et al (2020) Green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticle using Carica papaya leaf extract: application for photocatalytic degradation of remazol yellow RR dye and antibacterial activity. Heliyon 6:e04603. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04603
Bibi I, Nazar N, Ata S et al (2019) Green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles using pomegranate seeds extract and photocatalytic activity evaluation for the degradation of textile dye. J Mater Res Technol 8:6115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2019.10.006
Bishoyi A, Sahoo CR, Sahoo A, Padhy RN (2020) Bio-synthesis of silver nanoparticles with the brackish water blue-green alga Oscillatoria princeps and antibacterial assessment. Appl Nanosci 11:389. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-020-01593-7
Bolbanabad EM, Ashengroph M, Darvishi F, Darvishi F (2020) Development and evaluation of different strategies for the clean synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Yarrowia lipolytica and their antibacterial activity. Process Biochem 94:319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2020.03.024
Bonardd S, Saldías C, Ramírez O et al (2019) A novel environmentally friendly method in solid phase for in situ synthesis of chitosan-gold bionanocomposites with catalytic applications. Carbohydr Polym 207:533–541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.12.009
Castro L, Li J, González F et al (2020) Green synthesis of tellurium nanoparticles by tellurate and tellurite reduction using Aeromonas hydrophila under different aeration conditions. Hydrometallurgy 196:105415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2020.105415
Chand K, Cao D, Fouad DED et al (2020) Green synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic application of silver nanoparticles synthesized by various plant extracts. Arab J Chem 13:8248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2020.01.009
Da Silva ES, Prevot V, Forano C et al (2014) Heterogeneous photocatalytic degradation of pesticides using decatungstate intercalated macroporous layered double hydroxides. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:11218–11227. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2971-z
Desai MP, Patil RV, Harke SS, Pawar KD (2020) Bacterium mediated facile and green method for optimized biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles for simple and visual detection of two metal ions. J Clust Sci 32:341. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-020-01793-9
Díaz-Rodríguez D, Palacios-Antón ME, Santana RMDR et al (2020) Comparative study of the degradation of the diclofenac drug using photo-peroxidation and heterogeneous photocatalysis with UV-C and solar radiation. Water Air Soil Pollut 231:147. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04497-y
do Nascimento GE, Cavalcanti VOM, Santana RMR et al (2020) Degradation of a sunset yellow and tartrazine dye mixture: optimization using statistical design and empirical mathematical modeling. Water Air Soil Pollut 231:254. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04547-5
Dobrucka R (2019) Facile synthesis of trimetallic nanoparticles Au/CuO/ZnO using Vitex agnus-castus extract and their activity in degradation of organic dyes. Int J Environ Anal Chem 101:2046–2057. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2019.1691543
Ebrahimzadeh M, Mortazavi-Derazkola S, Zazouli MA (2019) Eco-friendly green synthesis and characterization of novel Fe3O4/SiO2/Cu2O–Ag nanocomposites using Crataegus pentagyna fruit extract for photocatalytic degradation of organic contaminants. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 30:10994. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-01440-8
Ekennia A, Uduagwu DN, Nwaji NN et al (2020) Green synthesis of biogenic zinc oxide nanoflower as dual agent for photodegradation of an organic dye and tyrosinase inhibitor. J Inorg Organomet Polym Mater 31:886. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-020-01729-w
Fadlalla MI, Senthil Kumar P, Selvam V, Ganesh Babu S (2019) Recent advances in nanomaterials for wastewater treatment. In: Naushad M, Rajendran S, Gracia F (eds) Advanced nanostructured materials for environmental remediation. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 21–58. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-04477-0_2
Fang X, Wang Y, Wang Z et al (2019) Microorganism assisted synthesized nanoparticles for catalytic applications. Energies 12:190. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12010190
Fazlzadeh M, Rahmani K, Zarei A et al (2017) A novel green synthesis of zero valent iron nanoparticles (NZVI) using three plant extracts and their efficient application for removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions. Adv Powder Technol 28:122. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APT.2016.09.003
Francis PK, Sivadasan S, Avarachan A, Gopinath A (2020) A novel green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using seaweed Lobophora variegata and its potential application in the reduction of nitrophenols. Particulate Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1080/02726351.2018.1547340
Giler-Molina JM, Zambrano-Intriago LA, Quiroz-Fernández LS et al (2020) Degradation of Oxytetracycline in aqueous solutions: application of homogeneous and heterogeneous advanced oxidative processes. Sustainability 12:8807. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12218807
Hamedi S, Shojaosadati SA (2019) Rapid and green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Diospyros lotus extract: evaluation of their biological and catalytic activities. Polyhedron. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.POLY.2019.07.010
Hemmati S, Heravi MM, Karmakar B, Veisi H (2020) Green fabrication of reduced graphene oxide decorated with Ag nanoparticles (rGO/Ag NPs) nanocomposite: a reusable catalyst for the degradation of environmental pollutants in aqueous medium. J Mol Liq 319:114302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.114302
Jadoun S, Arif R, Jangid NK, Meena RK (2020) Green synthesis of nanoparticles using plant extracts: a review. Environ Chem Lett 19:355. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-020-01074-x
Jafarinejad S (2019) Cost-effective catalytic materials for AOP treatment units. In: Gil A, Galeano LA, Vicente MÁ (eds) Applications of advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) in drinking water treatment. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 309–343
Jayabalan J, Mani G, Krishnan N et al (2019) Green biogenic synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Pseudomonas putida culture and its In vitro antibacterial and anti-biofilm activity. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2019.101327
Jayarambabu N, Akshaykranth A, Rao TV et al (2020) Green synthesis of Cu nanoparticles using Curcuma longa extract and their application in antimicrobial activity. Mater Lett. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2019.126813
Kalantari E, Khalilzadeh MA, Zareyee D, Shokouhimehr M (2020) Catalytic degradation of organic dyes using green synthesized Fe3O4-cellulose-copper nanocomposites. J Mol Struct 1218:128488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2020.128488
Karimipourfard D, Eslamloueyan R, Mehranbod N (2019) Novel heterogeneous degradation of mature landfill leachate using persulfate and magnetic CuFe2O4/RGO nanocatalyst. Process Saf Environ Prot 131:212–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2019.09.009
Khan A, Liao Z, Liu Y et al (2017) Synergistic degradation of phenols using peroxymonosulfate activated by CuO-Co3O4@MnO2 nanocatalyst. J Hazard Mater 329:262–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.01.029
Khodadadi B, Bordbar M, Nasrollahzadeh M (2017) Green synthesis of Pd nanoparticles at Apricot kernel shell substrate using Salvia hydrangea extract: catalytic activity for reduction of organic dyes. J Colloid Interface Sci 490:1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2016.11.032
Li S, Niu Y, Chen H, He P (2021) Complete genome sequence of an Arctic Ocean bacterium Shewanella sp. Arc9-LZ with capacity of synthesizing silver nanoparticles in darkness. Mar Genomics 56:100808. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.margen.2020.100808
Lian S, Diko CS, Yan Y et al (2019) Characterization of biogenic selenium nanoparticles derived from cell-free extracts of a novel yeast Magnusiomyces ingens. 3 Biotech 9:1. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-019-1748-y
Lu J, Ali H, Hurh J et al (2019) The assessment of photocatalytic activity of zinc oxide nanoparticles from the roots of Codonopsis lanceolata synthesized by one-pot green synthesis method. Optik 184:82. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJLEO.2019.03.050
Morshed MN, Al Azad S, Deb H et al (2020) Titania-loaded cellulose-based functional hybrid nanomaterial for photocatalytic degradation of toxic aromatic dye in water. J Water Process Eng 33:101062. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2019.101062
Mulongo-Masamba R, El Hazzat M, El Hamidi A et al (2019) New functional β-chitin/calcium phosphate as promising support of copper nanocatalyst for the reductive degradation of methylene blue. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16:8117–8128. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-019-02353-z
Napoleão DC, Zaidan LEMC, Rodríguez-Díaz JM et al (2018) Use of the photo-Fenton process to discover the degradation of drugs present in water from the Wastewater Treatment Plants of the pharmaceutical industry. Afinidad 75:23–31. https://raco.cat/index.php/afinidad/article/view/335959
Nasiri A, Tamaddon F, Mosslemin MH, Faraji M (2019) A microwave assisted method to synthesize nanoCoFe2O4@methyl cellulose as a novel metal-organic framework for antibiotic degradation. MethodsX 6:1557–1563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mex.2019.06.017
Noman M, Shahid M, Ahmed T et al (2019) Use of biogenic copper nanoparticles synthesized from a native Escherichia sp. as photocatalysts for azo dye degradation and treatment of textile effluents. Environ Pollut. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113514
Oruç Z, Ergüt M, Uzunoğlu D, Özer A (2019) Green synthesis of biomass-derived activated carbon/Fe-Zn bimetallic nanoparticles from lemon (Citrus limon (L.) Burm. f.) wastes for heterogeneous Fenton-like decolorization of Reactive Red 2. J Environ Chem Eng. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JECE.2019.103231
Pal S, Singh PN, Verma A et al (2020) Visible light photo-Fenton catalytic properties of starch functionalized iron oxyhydroxide nanocomposites. Environ Nanotechnol Monit Manag 14:100311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2020.100311
Pei X, Li Y, Deng Y et al (2021) Chitin microsphere supported Pd nanoparticles as an efficient and recoverable catalyst for CO oxidation and Heck coupling reaction. Carbohydr Polym 251:117020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.117020
Rachna, Rani M, Shanker U (2021) Synergistic effects of zinc oxide coupled copper hexacyanoferrate nanocomposite: robust visible-light driven dye degradation. J Colloid Interface Sci 584:67–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2020.09.079
Rafiee F, Rezaie Karder F (2020) Bio-crosslinking of chitosan with oxidized starch, its functionalization with amino acid and magnetization: as a green magnetic support for silver immobilization and its catalytic activity investigation. Int J Biol Macromol 146:1124–1132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.09.238
Rafique M, Shafiq F, Gillani S et al (2020) Eco-friendly green and biosynthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles using Citrofortunella microcarpa leaves extract for efficient photocatalytic degradation of Rhodamin B dye form textile wastewater. Optik 208:164053. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2019.164053
Rani M, Rachna, Shanker U (2020) Metal oxide-chitosan based nanocomposites for efficient degradation of carcinogenic PAHs. J Environ Chem Eng 8:103810. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.103810
Ravichandran V, Vasanthi S, Shalini S et al (2019) Green synthesis, characterization, antibacterial, antioxidant and photocatalytic activity of Parkia speciosa leaves extract mediated silver nanoparticles. Res Phys 15:102565. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RINP.2019.102565
Ravikumar K, Sudakaran SV, Ravichandran K et al (2019) Green synthesis of NiFe nano particles using Punica granatum peel extract for tetracycline removal. J Clean Prod. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCLEPRO.2018.11.108
Rehmer A, Scheurell K, Scholz G, Kemnitz E (2017) Sol-gel-synthesis of nanoscopic complex metal fluorides. Nanomaterials 7:362. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7110362
Sadhukhan S, Bhattacharyya A, Rana D et al (2020) Synthesis of RGO/NiO nanocomposites adopting a green approach and its photocatalytic and antibacterial properties. Mater Chem Phys 247:122906. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2020.122906
Salem SS, Fouda A (2021) Green synthesis of metallic nanoparticles and their prospective biotechnological applications: an overview. Biol Trace Elem Res 199:344–370. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-020-02138-3
Saneinezhad S, Bamoharram FF, Mozhdehi AM et al (2020) Functionalized cellulose-preyssler heteropolyacid bio-composite: an engineered and green matrix for selective, fast and in-situ preparation of Pd nanostructures: synthesis, characterization and application. Arab J Chem 13:4644–4660. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2019.10.006
Sharma G, Kumar D, Kumar A et al (2017) Revolution from monometallic to trimetallic nanoparticle composites, various synthesis methods and their applications: a review. Mater Sci Eng C 71:1216–1230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2016.11.002
Shoueir K, El-Sheshtawy H, Misbah M et al (2018) Fenton-like nanocatalyst for photodegradation of methylene blue under visible light activated by hybrid green DNSA@Chitosan@MnFe2O4. Carbohydr Polym 197:17–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.05.076
Tamaddon F, Mosslemin MH, Asadipour A et al (2020) Microwave-assisted preparation of ZnFe2O4@methyl cellulose as a new nano-biomagnetic photocatalyst for photodegradation of metronidazole. Int J Biol Macromol 154:1036–1049. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.03.069
Tran PH, Nguyen HT, Nguyen LHT, Le Doan TH (2021) Chapter 12 – Microwave-assisted for solvent-free organic synthesis. In: Inamuddin, Boddula R, Asiri AM (eds) Green sustainable process for chemical and environmental engineering and science. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 511–538
Vaanamudan A, Sarkar M, Sadhu M, Pamidimukkala PS (2019) Clusters of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles capped with palm shell extract and modified with chitosan: catalytic applications for degradation of cationic and anionic dyes and their binary mixtures. J Environ Chem Eng 7:103244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.103244
Vinay SP, Alharthi FA, Udayabhanu et al (2020) Hydrothermal synthesis of Ag/rGO@CTFE nanocomposite as a promising photocatalyst for degradation action. J Mol Struct 1228:129722. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2020.129722
Yang Y, Ali N, Khan A et al (2021) Chitosan-capped ternary metal selenide nanocatalysts for efficient degradation of Congo red dye in sunlight irradiation. Int J Biol Macromol 167:169–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.11.167
Zaidan LEMC, de Lima Sales RV, de Almeida Salgado JB et al (2017) Photodegradation applied to the treatment of phenol and derived substances catalyzed by TiO2/BiPO4 and biological toxicity analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 24:6002–6012. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5952-y
Zhang S, Xu Y, Zhao D et al (2020) Preparation of magnetic CuFe2O4@Ag@ZIF-8 nanocomposites with highly catalytic activity based on cellulose nanocrystals. Molecules 25:124. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25010124
Zhou Y, Shen J, Bai Y et al (2020) Enhanced degradation of Acid Red 73 by using cellulose-based hydrogel coated Fe3O4 nanocomposite as a Fenton-like catalyst. Int J Biol Macromol 152:242–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.02.200
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this entry
Cite this entry
Fernández-Andrade, K.J., Fernández-Andrade, A.A., Ávila-Toro, B.A., Zambrano-Intriago, L.Á., Baquerizo-Crespo, R.J., Rodríguez-Díaz, J.M. (2023). Nanocatalysts for Advanced Oxidation Processes in Heterogeneous Systems. In: Shanker, U., Hussain, C.M., Rani, M. (eds) Handbook of Green and Sustainable Nanotechnology. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16101-8_10
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16101-8_10
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-16100-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-16101-8
eBook Packages: Chemistry and Materials ScienceReference Module Physical and Materials ScienceReference Module Chemistry, Materials and Physics