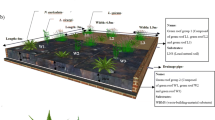
Abstract
Green roof promises to become an increasingly important option for building owners and community planners because it can address many of the challenges facing urban residents. The success of the roof depends on the specific build-up of the green roof, therefore, special attention was focused on the identification and application of more environmentally friendly materials in green roofs. However, except the substrate, very few studies have denoted the potential to use reused materials for drainage layers, despite its important role in determining thermal and hydraulic performance of green roofs. This study analyzes the scientific literature on the use of innovative materials from the recovery/recycling of products for the drainage layer and propose the use of low-density polyethylene (LDPE) granules coming from the recycling of waste films used in agriculture for greenhouse roofing and mulching as innovative and sustainable drainage material in green roofs. In addition, the proposal concerns the possibility to enclose the plastic granular material into micro-perforated bags made of recycled polyethylene and to use the soil coming from washing of agricultural films as substrate in green roofs. This proposal will be further investigated by laboratory assessment on the thermo-physical properties of several polyethylene granules and by experimental set-up having the goal of assessing the thermal performance of different green roof technologies, in order to represent a suitable alternative to materials commercially used from an environmental, economic, and social point of view.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Detommaso, M., Cascone, S., Gagliano, A., Nocera, F., Sciuto, G.: Cool roofs with variable thermal insulation: UHI mitigation and energy savings for several Italian cities. In: Littlewood, J., Howlett, R.J., Capozzoli, A., Jain, L.C. (eds.) Sustainability in Energy and Buildings. SIST, vol. 163, pp. 481–492. Springer, Singapore (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-32-9868-2_41
Oke, T.R., Mills, G., Christen, A., Voogt, J.A.: Urban Climates. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2017). https://doi.org/10.1017/9781139016476
Evola, G., Cascone, S., Sciuto, G., Parisi, C.B.: Performance comparison between building insulating materials made of straw bales and EPS for timber walls. In: IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/609/7/072020
Jim, C.Y., Chen, W.Y.: Bioreceptivity of buildings for spontaneous arboreal flora in compact city environment. Urban For. Urban Green. 10, 19–28 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ufug.2010.11.001
Vijayaraghavan, K.: Green roofs: a critical review on the role of components, benefits, limitations and trends. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 57, 740–752 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.12.119
Koroxenidis, E., Theodosiou, T.: Comparative environmental and economic evaluation of green roofs under Mediterranean climate conditions – extensive green roofs a potentially preferable solution. J. Clean. Prod. 311 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.127563
Vila, A., Pérez, G., Solé, C., Fernández, A.I., Cabeza, L.F.: Use of rubber crumbs as drainage layer in experimental green roofs. Build. Environ. 48, 101–106 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2011.08.010
Pérez, G., Vila, A., Rincón, L., Solé, C., Cabeza, L.F.: Use of rubber crumbs as drainage layer in green roofs as potential energy improvement material. Appl. Energy 97, 347–354 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2011.11.051
Rincón, L., Coma, J., Pérez, G., Castell, A., Boer, D., Cabeza, L.F.: Environmental performance of recycled rubber as drainage layer in extensive green roofs. A comparative Life Cycle Assessment. Build. Environ. 74, 22–30 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2014.01.001
Coma, J., Pérez, G., Castell, A., Solé, C., Cabeza, L.F.: Green roofs as passive system for energy savings in buildings during the cooling period: use of rubber crumbs as drainage layer. Energ. Effi. 7(5), 841–849 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12053-014-9262-x
Kazemi, M., Courard, L.: Modelling thermal and humidity transfers within green roof systems: effect of rubber crumbs and volcanic gravel. Adv. Build. Energy Res. 1–26 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/17512549.2020.1858961
Kazemi, M., Courard, L., Hubert, J.: Heat transfer measurement within green roof with incinerated municipal solid waste aggregates. Sustainability 13 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/su13137115
Kazemi, M., Courard, L.: Modelling hygrothermal conditions of unsaturated substrate and drainage layers for the thermal resistance assessment of green roof: effect of coarse recycled materials. Energy Build. 250, 111315 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2021.111315
Kazemi, M., Courard, L., Hubert, J.: Coarse recycled materials for the drainage and substrate layers of green roof system in dry condition: parametric study and thermal heat transfer. J. Build. Eng. 45, 103487 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2021.103487
Nagase, A.: Novel application and reused materials for extensive green roof substrates and drainage layers in Japan – plant growth and moisture uptake implementation. Ecol. Eng. 153, 105898 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2020.105898
Naranjo, A., Colonia, A., Mesa, J., Maury-Ramírez, A.: Evaluation of semi-intensive green roofs with drainage layers made out of recycled and reused materials. Coatings 10, 525 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/COATINGS10060525
Pushkar, S.: Modeling the substitution of natural materials with industrial byproducts in green roofs using life cycle assessments. J. Clean. Prod. 227, 652–661 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.04.237
Cascone, S., Ingrao, C., Valenti, F., Porto, S.M.C.: Energy and environmental assessment of plastic granule production from recycled greenhouse covering films in a circular economy perspective. J. Environ. Manag. 254, 109796 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109796
Acknowledgement
This research is carried out in collaboration with I.LA.P. s.p.a., a Sicilian company producing granules through the regeneration of low-density polyethylene from the recovery of waste films used in agricultural greenhouses.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Cascone, S. (2022). Drainage Layer in Green Roofs: Proposal for the Use of Agricultural Plastic Waste. In: Calabrò, F., Della Spina, L., Piñeira Mantiñán, M.J. (eds) New Metropolitan Perspectives. NMP 2022. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 482. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-06825-6_177
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-06825-6_177
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-06824-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-06825-6
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)