Abstract
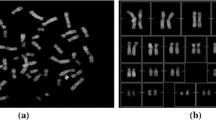
Chromosomal diseases diagnostics is based on identifying chromosomes and detecting abnormalities in them. It is a sophisticated procedure that is performed manually or partially automated, therefore is prone to human error. Automation of such diagnostics is a complex multistage task that presents many challenges. One of such challenges is chromosome feature extraction and classification. Categorizing chromosomes is necessary for determining a diagnosis. This problem has been previously covered by research papers, but there is no complete solution by now. Moreover, the vast majority of proposals rely on Machine Learning (ML) and Neural Networks (NN). Usage of ML-powered solutions may pose a problem due to difficulty of dataset collection - medical data may be diverse, heterogeneous and hard to collect because of its sensitive nature. Given paper presents a proposal of chromosome feature extraction and categorization without NN. It uses Computer Vision (CV) techniques for chromosome feature extraction: medial axis is extracted from a chromosome to identify its direction, and than chromosome bands (colored segments that make up distinct chromosome pattern) are identified along the axis. Having transformed chromosome image into a discrete piece of data, it is passed to a proposed multiple-criteria decision-making algorithm. This algorithm is designed to categorize chromosomes without learning dataset, instead making use of ideogram (schematic reference chromosome) data. The algorithm is focused on processing a chromosome as a set of segments, where each segment can be recognized by a special predicate. A predefined combination of such predicates should allow recognizing chromosome type.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tiwari, P., Gupta, M.M.: Study of lethal congenital malformations at a tertiary-care referral centre in North India. Cureus 12(4) (2020). https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.7502
Boyle, B., Addor, M.C., Arriola, L., et al.: Estimating global burden of disease due to congenital anomaly: an analysis of European data. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 103(1), F22–F28 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1136/archdischild-2016-311845
Moallem, P., Karimizadeh, A., Yazdchi, M.: Using shape information and dark paths for automatic recognition of touching and overlapping chromosomes in G-band images. MECS, Int. J. Image Graph. Sig. Process. 5, 22–28 (2013). https://doi.org/10.5815/ijigsp.2013.05.03
O’Connor, C.: Karyotyping for chromosomal abnormalities. Nat. Educ. 1(1), 27 (2008)
Nandakumar, R., Jayanthi, K.B.: Feature extraction for the classification of human chromosomes from G-band images using wavelets. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. (IJERT) ICEECT 8(17), 67–72 (2020)
Moradi, M., Setarehdan, K.: New features for automatic classification of human chromosomes: a feasibility study. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 27(1), 19–28 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2005.06.011
Oppenheim, A.V., Schafer, R.: Image and Signal Processing and Analysis. Pearson (2015)
Aldroubi, A., Unser, M.: Wavelets in Medicine and Biology. CRC Press, Boca Raton (1996)
Huret, J.L., Ahmad, M., Arsaban, M., et al.: Atlas of genetics and cytogenetics in oncology and haematology. Nucleic Acids Res. (2013) 41(D1) (2013). https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks1082
O’Connor, C.: Chromosome mapping: idiograms. Nat. Educ. 1(1), 107 (2008)
Nagpal, A., Gabrani, G.: Python for data analytics, scientific and technical applications. In: 2019 Amity International Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AICAI), pp. 140–145 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/AICAI.2019.8701341
Harris, C.R., Millman, K.J., van der Walt, S.J., et al.: Array programming with NumPy. Nature 585(7825), 357–362 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2649-2
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Pysarchuk, O., Mironov, Y. (2022). Chromosome Feature Extraction and Ideogram-Powered Chromosome Categorization. In: Hu, Z., Dychka, I., Petoukhov, S., He, M. (eds) Advances in Computer Science for Engineering and Education. ICCSEEA 2022. Lecture Notes on Data Engineering and Communications Technologies, vol 134. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-04812-8_36
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-04812-8_36
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-04811-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-04812-8
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)