Abstract
The chapter discusses the knowledge of halal food invention, the concept of innovation, firms’ innovation, and performance. In practice, halal food invention is for the benefit of stakeholders, firm innovation, and profitability. It provides more knowledge regarding the halal value creation effects on halal food consumption of consumers or consumers’ halal food purchasing behaviour. Further, it enables marketers to develop strategies to promote halal-certified food products and increase their engagement with consumers.
Access provided by Autonomous University of Puebla. Download chapter PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Keywords
1 Introduction
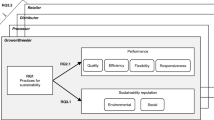
Halal is a dynamic business with global demand contributing to sustainable socio-economic growth in Islamic and non-Islamic nations. These active global halal markets require firms to find new strategies and resources to innovate and obtain superior performance and sustained competitive advantage (Karia & Asaari, 2016a). Innovation is vital for small and medium food enterprise survival, performance, and growth. Halal product and process innovation create firms’ innovation capability, driving a firm’s profitability and competitive advantage to meet massive consumer demands. As a result, such halal food invention promises the success of firms’ innovation capability, suggesting halal-certified products can positively affect firm innovation and performance (Fig. 1). The chapter discusses the knowledge of halal food invention, the concept of innovation, firms’ innovation, and performance. In practice, halal food invention is for the benefit of stakeholders, firm innovation, and profitability. It provides more knowledge regarding the halal value creation effects on halal food consumption of consumers or consumers’ halal food purchasing behaviour. Further, it enables marketers to develop strategies to promote halal-certified food products and increase their engagement with consumers.
2 Knowledge of Halal Food Invention
Muslims can focus on helping people and societies by inventing new knowledge and ideas regarding halal food wisdom that, consequently, leads to the growth and development of spiritual intelligence (Ismail & Karia, 2017). There is a substantial relationship between halal food and the ways humans manage and govern the world.
“Halal food is a powerful force that possesses the capability of perfect chemical reaction for quantum communication by intelligent electrons (messenger particles) to transpire what will enhance our consciousness to its highest levels of intelligence” (Ismail & Karia, 2017, p. 10). The authors state that the spirituality and metaphysics of halal food is not a theory; it is the neuroscience and quantum mechanics of the human body in its micronutrient state. Spirituality reflects the harmony in self and a holistic understanding between spirit and body that enables a sense of inner calm and connection to others in a meta-physical mind, vital to human well-being (Ratten et al., 2017).
This can be contemplated by the verse, “By the fig and the olive; and the Mount Sinai”, Surah At-Tin verse 1. When God takes an oath on something, it possesses an intrinsic value for humankind. The olive strengthens your immune system, while the fig is rich in serotonin which provides us with feelings of bliss/happiness and other great benefits, along with the proper chemical reaction to transpire within the body and the brain. Mount Sinai is where Prophet Musa a.s. communicates with God (the highest level of consciousness). God is speaking to us that living food can provide immense nutritional impact upon the body to help humans raise their level of awareness.
O’ mankind! eat of what is in the earth lawful and good; and do not follow the footsteps of Satan. Surely he is a manifest foe for you. (Al-Quran, Surah Al-Baqarah 2: 168)
Believers! Eat of the pure things wherewith We have provided you for sustenance and give thanks to Allah if it is Him that you serve. (Al-Quran, Surah Al-Baqarah 2: 172)
Eat of the things which Allah hath provided for you, lawful and good; but fear Allah, in Whom ye believe. (Al-Quran, Surah Al-Maaidah 5: 88)
So eat of the sustenance which Allah has provided for you, lawful and good; and be grateful for the favors of Allah, if it is He Whom ye serve. (Al-Quran, Surah Al-Nahl 16: 114)
These recitations of the Quran promote the eating of halal food for those who seek the blessing of Allah, while also prohibiting them from consuming anything that is harmful to a body (haram). The word “lawful” and “pure” as terms used for halal are the mechanisms for human beings’ spiritual intelligence consciousness. Halal food has a significantly influential connection with the human body-mind-soul. What we eat is what our body gets; thus, halal food directly affects our body, which thereby affects our mind. A pure body affects the mind, which significantly impacts a true believer and the institution of their soul, which is crucial in order to worship God appropriately.
Muslims should not simply consume foods permissible by Islamic dietary law; they should learn why it is important and promote the invention of halal products to the world by emphasizing the missing ingredient of its spiritual values and exploring how the human body interacts with halal food. Scholars and industry have acknowledged the slaughtering effects of spirituality much better than the physical method. Pure halal food can process intelligent thought and impact human civilization with the highest intrinsic value and social-religious structure. Such particle physics and scientific findings of the most subtle consciousness of matter endorse the Holy Quran’s spiritual significance and challenge modern science’s perception of the spiritual sciences. The Quran, thus, encourages innovation, new knowledge, new practices, or good practices while strictly prohibiting evil practices or inventions that are harmful to people and the planet (animals and environment).
Islam welcomes innovations or new knowledge if they conform to Islam; hence, Islam encourages the innovativeness of products or services which are shariah-compliant businesses. It is a form of ibadah (worship) in enterprises, operations, and all related services. Ibadah, in any form, like inventing or consuming halal food, will bring positive effects to akhlaq because people who serve ibadah will train themselves to obey the principles of shariah as outlined by the Quran (al-Hijr 15: 99; al-Kahfi 18: 107–108; al-Ankabut 29: 45). Islam teaches that the function of ibadah is to shape akhlaq and to soften manners. A strong aqidah can drive a person to fulfil their responsibility as a Muslim by performing ibadah to Allah. Islam thus encourages prosperity through venture into business following the Holy Quran and the prophet’s Hadith (Ramadani et al., 2015).
3 The Concept of Halal Food Invention
Innovation refers to halal-certified food, halal product and process innovation, a new invention that leads to the growth and development of spiritual intelligence (individual performance), firm performance, and competitiveness. God commands us to eat halal food because our body reacts to the food we eat, thereby suggesting that halal food has a positive impact on our body, affecting our minds. Therefore, food that we consume has a certain degree of spiritual purity that stimulates positive and spiritual energies, subsequently enhancing human civilization.
Halal value creation under Islamic thought conveys a firm’s responsible business practices and practical systems in terms of four Islamic values:
-
1.
Aqidah—faith and belief that halal food offers benefits
-
2.
Akhlak—behaviour, ethics, and morality to obtain halal food certification and offer halal-certified food to customers
-
3.
Shariah law—an act to establish the halal standard, halal assurance system for halal certification requirements
-
4.
Allah blessing—divine compassion
Aqidah signifies a strong faith, agreement, and intention (qasad) that could control every act or intent of an individual in life, which shapes the framework of moral and ethical behaviour (akhlak) of a person (Ismail et al., 2011). Akhlak is a positive human behaviour in Islam or visibility of positive acts, the practice of virtue, morality, and manners in Islamic theology and philosophy (Ismail et al., 2011). Shariah comprises laws prescribed by Allah so that humans hold dearly to Him in fulfilling their duties as a servant of God, as a person, and as someone with duties or responsibilities to nature, the environment, surroundings, and life as a whole (Din, 1985; Kamali, 2010). Those who declare themselves to be a believer but neglect either three of these values are not accountable in business and to themselves.
Halal certification acknowledges that the product or service is shariah compliant and follows the Islamic guidelines; this is represented by documentation, a logo, trademark, label, or Trustmark. It ensures the products or services uphold halal standards determined by JAKIM, the halal regulations and enforcement, a global benchmark, as safe, quality assured, hygienic, wholesome, pure, trustworthy, nutritious, healthy, brand image, and reputable. The objective of halal certification is to continuously increase the certainty of halal and quality of the products or services (cleanliness and purity—tayyib), firms’ profitability and competitiveness and environmental preservation (Karia & Asaari, 2016b, 2016c), and the Islamic values in the welfare of human beings (communal obligation), sustenance (rizq), and, ultimately, Allah’s blessing (barakah) and compassion (Rahmah) to improve all Muslims’ connection, devotion, and submission to Allah s.w.t. (Firdaus, 2020; Karia & Asaari, 2016b). Therefore, the halal logo or halal brand appeals to Muslim and non-Muslim consumers because of the high confidence in the product’s safety, quality, and purity which is widely recognized and accepted globally.
An invention of halal products can be based on the significant benefits to profit (economy), people (society), and planet (environment) (Karia & Asaari, 2016b, 2016c). The following 4Ps’ benefits are as follows:
-
1.
Product or process (zero defect, shariah compliant)—provide halal (lawful) and tayyib (clean) food products, halal-certified products; quality, nutritional, and safe products; tasty, healthy, more hygienic, original, and with animal welfare, than haram foods.
-
2.
Profit (maximizing firm and public interest)—halal-certified products enable firms to gain better and long-term success.
-
3.
People—halal food consumption leads to human beings’ spiritual intelligence, promoting mental alertness, life thought and learning, physical-emotional-spiritual health, job performance, and satisfaction.
-
4.
Planet (maximizing benefits to the environment and animal welfare)—consumption of halal food promotes environmental and sustainable performance.
Product innovation involves creating halal goods or services consumed by customers, whereby process innovation improves the creation or delivery of halal products or services. It evolutes from the halal product invented and obtained as a halal-certified product to halal market products adopted by more people (Muslims and non-Muslims). Firms adopt or focus on halal product development by capturing opportunities such as the following:
-
1.
Understanding the customer—ahead of halal market trends about the halal food wisdom.
-
2.
Economic change—increasingly more people are willing to pay for halal in the long run.
-
3.
Sociological and demographic change—increasing halal lifestyle, increasingly more people demand halal-certified products or services.
-
4.
Technological change—technologies improve the quality of halal products and enable halal products to be reached everywhere.
-
5.
Political and legal change—new trade agreement, tariffs, government requirements, and halal as mandatory.
-
6.
Other changes—paradigm shifts create new opportunities for market practice, professional standards, suppliers, and distributors.
The potential to invent halal products or create valuable knowledge determines innovation capability comprising product innovation—radical innovation focuses on the invention of a new product—and process innovation, refers to a new method or process making a product. The refinement or minor adaptation of current products and processes considers incremental innovation. Firms can strive to innovate through an innovation strategy:
-
1.
Product-based—design a new halal-certified food
-
2.
Halal-based—apply new technologies in halal product or process innovation
-
3.
Opportunity-based—adopt halal implementation and achieve success through potential halal business, mimic halal adoption success from competitors
4 Attributes of Halal Food Consumption
Halal product invention is the critical factor that offers better business performance and sustainability. Through halal value creation, firms can diversify and become the first firm leader creatively thinking of a new customer/segment or a new customer/segment’s wants and needs. In practice, halal products are favoured by an enormous number of Muslim and non-Muslim customers, which thereby provides great potential for business. If customers believe they get a better product from the invention of a halal product or process, rather than non-halal, its revenue will increase.
Halal value creation is an Islamic value-driven rather than profit- or customer-driven approach. In a product-based approach, Islamic values refer to the importance of halal products or services that benefit customers, such as quality, safety, purity, healthy, and nutrition. The halal value creation in food is added value created for customers. Consequently, from the producer-based approach, only Islam has clear guidelines on managing products and process innovation. Manufacturing plants must follow new halal standard procedures and process improvements to obtain halal certification. The halal assurance system promises the halal integrity of the product and process innovation that yields consumer confidence and satisfaction. Both innovations are interdependent and require managing both core and enablers to realize competitiveness through new or improved products or manufacturing processes of halal implementation.
In the user-based approach, halal embraces all attributes of life, which brings us to a halal lifestyle that leads to halal food consumption. Lifestyle reflects any values or standards that maintained on a routine basis or espoused and chosen in life by adoption, adaptation, obligation, or stimulation. Many attributes like food safety, nutrition, quality food trust, healthy food and clean, religion (Bonne et al., 2008), and dietary habits influence people’s choice of halal food consumption (Arsil et al., 2018). However, the halal value is the main factor influencing halal food consumption (Muhamed et al., 2019), followed by other consumer values (Khan & Mohsin, 2017; Maehle et al., 2015) and consumer behaviour (Billah et al., 2020).
The consumption of halal foods, products, and services is compulsory for all Muslims. Halal certified food means the whole cycle from the source, production, process, transformation, cooking, serving, packaging, selling, and buying. Nevertheless, halal food consumption or consumer purchasing behaviour towards halal-certified food depends on total customer satisfaction. Regardless of religiosity, Muslim and non-Muslim consumers who consume halal food obtain complete satisfaction through their confidence in knowledge, experience, and belief. The values propagated by religion might influence consumers irrespective of a person’s religiosity (Dana, 2009).
Here, halal food is about more than religious identity; it encompasses how food can stimulate growth of the body, mind, and soul. The three fundamental consumption values that determine complete customer satisfaction are as follows:
-
1.
Halal value—the decision to purchase reflects the product/service’s compliance to Islam, halal logo, or halal certification by, e.g., quality, safety, purity, nutrient, hygiene, and wholesome for food and trust, dedication, honesty, timeliness, and discipline for service.
-
2.
Epistemic value—knowledge confidence level determines buying halal products, obtaining product knowledge or a substantial amount of information about halal products before making a purchase.
-
3.
Emotional value—a belief that halal food has a significant impact on body-mind-soul, thereby stimulating a person to consume halal food.
There are many studies concerning halal food consumption; however, purchasing factors towards halal food can be categorized into three distinct consumption values (Table 1).
5 Small and Medium Food Enterprises’ (SMFEs) Innovation
The entire concept of halal is fundamental to Islam and acceptable to all producers for quality, safety, and trust. Non-Muslims consume halal foods and embrace halal standards as the most comprehensive and excellent food quality standards that increase global halal food markets. The advantage of SMFEs is that small, flexible, close to customers, and independent entrepreneurs are the source of innovation. Indeed, small firms bring innovation to the market more quickly than large businesses. In product innovation, small business is advantageous due to more excellent proximity to and high interaction with customers. SMFEs of inventions are also users; therefore, the user is closer to the innovation developer. Therefore, SMFEs are good at the implementation of new halal-certified products brought to the market. They are most likely to be better in the application, development, and introduction to the market.
The world’s population and the number of Muslims increase in size every year, signifying the potential growth of the global halal market and demands of halal food products, both inside and outside Islamic nations. Malaysia has become the most prominent halal exporter to China, Singapore, the USA, and Japan. Indonesia and the Netherlands are also highly notable importers; the rest are Middle Eastern and European countries. The massive demands for halal in non-Muslim countries indicate high consumer confidence levels and trust towards consuming Malaysian halal-certified food.
Halal food has been recognized locally and internationally, regardless of religiosity, and brings a vast amount of potential business. Given the colossal market potential of halal foods, Malaysia should be the leader of halal commodities. Despite SMFEs being significant contributors to the growth of the halal food industry and economy, SMFEs’ constraints, low production volume, and availability are often incomparable to meet the high demands of halal foods. Therefore, halal SMFEs’ competitiveness continuously challenges Malaysian halal export performance. An SMFE’s enablers of halal food implementations empower its ability to exploit innovation capability in an innovation context.
Innovation requires organizations to be open to new knowledge, product processes, technologies, and routines, thereby enabling and enhancing firms’ growth in dynamic and competitive environments. It is a critical success factor for the survival, growth, and development of SMFEs. It becomes a worthwhile strategic capability of SMFEs fostering business success and competitive advantage in markets. Halal assurance systems directly affect both the process and product innovation that, in turn, impacts performance outcomes.
The creation of competitive advantage concerning the halal certification of SMFEs depends on their acquisition of resources and capabilities, rather than ownership, per se. Resources and assets are firms’ inputs to generate economic value. Capabilities are the skills, knowledge, and abilities that firms strengthen to enhance performance and competitiveness over time. Capabilities often reflect core competencies of firms’ competitive advantage by creating complex coordination of different activities and technologies that are difficult for competitors to imitate—for instance, a core capability in persuading customers by integrating marketing, advertising, and customer service. Resource and capability of technology, physical, knowledge, relational, and organizational are main inputs acquired for innovation. However, competitive advantage takes value only when resources are valuable, rare, non-substitutable, difficult to imitate, and durable. Knowledge and organizational capability are socially complex, and difficult for competitors to replicate and purchase; hence they become the source of competitive advantage.
SMFEs must perceive environmental factors (market dynamism, competitive hostility) in halal competitive environments and develop halal innovation strategies to enhance business performance. They must innovate and develop new knowledge, skills, and abilities by exploiting existing products and services. Successful firms’ innovation capability must possess innovation enablers/factors, namely, leadership, organizational culture, open innovation, competent management, external knowledge utilization capabilities, networking capabilities, and resource exploitation capabilities to adapt and align with the rapidly changing environment. To achieve superior performance, SMFEs should consider environmental stability and certainty to facilitate the relationship between innovation strategies and performance.
Understanding the innovation capability of halal food creation for the benefit of firms and stakeholders can enhance SMFE performance and competitiveness. In halal, innovation capability is about firms’ ability to create halal-certified food products. The transformation of innovation factors or enablers such as top management leadership, entrepreneurial orientation, and external network transformation challenges SMFEs’ innovation capability. Top management is the most crucial resource of SMFEs responsible for strategic operation decisions to their innovativeness. SMFEs’ owners or managers play a significant role in implementing halal. The upper echelon theory (Hambrick & Mason, 1984) explains the values and cognitive ability of top management which influence organizational outcomes. Karia (2021) confirms that the entrepreneur’s attributes of emotional intelligence comprised of self-confidence, self-innovation, self-inspiration, and self-vision affect entrepreneurial performance. The most influential factors are self-vision—manager’s ideas lead to actions and decisions for success—and self-innovation, the manager’s creativity to find a new process or product innovation.
Both internal and external forces influence halal food invention. Internal forces like business benefits, halal integrity, corporate image and reputation, social responsibility, entrepreneurship, organizational commitment, marketing function, operations strategies, and organizational readiness enable manufacturers to adopt halal product invention. The external forces include competitive force, demand/customer force, market expansion, and government regulation and support, which positively stimulate SMFEs towards halal implementation. The mediating effects of internal factors and moderating effects of external factors can positively impact innovation and performance. For instance, in the implementation of halal, the perceived benefit is the most influential factor of SMFEs halal food products to enhancing their business performance. The halal assurance system is a holistic concept that maintaining halal integrity is crucial to the halal product and process innovation success. Organizational readiness to adopt new policies, standards, and practices of halal affects SMFE investment in halal food implementation. Competitive forces can facilitate the effects of internal factors on halal food implementation to be robust and durable.
In SMFEs, limited knowledge and external contact area are relative to SMFEs’ innovation and diffusion challenges and barriers. Therefore, innovation factors such as research and development (R&D), technology applications, and training and education are significant variables for both halal product and process innovation. Insufficient organizational resources or lack of management capabilities can hinder innovation capability. Further, firms can establish an external network or intermediary to accelerate their innovation capability by engaging with the entire halal food industry players from raw material suppliers to inbound and outbound halal logistics and supply chains.
6 Innovation and Performance of SMFEs
The knowledge-based view (Grant, 1996, 2002) regards knowledge as the most strategic source of firm growth and explains that applying knowledge for halal value creation of a new halal product or process leads to organizational innovation which, in turn, improves firm productivity, growth, and performance. Heterogeneous knowledge bases and capabilities are difficult to imitate and socially complex; therefore, they generate sustained competitive advantage and superior performance. When knowledge becomes more tacit, it is more difficult to transfer and relatively costly.
Food manufacturers adopt halal to gain a competitive advantage in the global halal market, which directly enhances consumers trust in the product as halal standards reflect quality and integrity. Therefore, innovation anticipates variations in performance outcomes. Firm performance measures and financial and non-financial business performance, respectively, refer to objective and subjective measurement. Innovation capability in the product, process, services, skills, organization, and marketing positively connects with new product performance, brand performance, and overall firm performance.
Innovation strategies such as the invention of new processes, the creation of halal products and services, the utilization of new opportunities within a new halal market, and new distribution channels are related to SMFE performance. Product and process innovation can positively impact innovation capabilities and, in turn, contribute to enhancing firm growth and productivity. Resources and capabilities are sources of competitive advantage through innovation, but they must be durable and untransferable across firms to achieve sustained competitiveness. Therefore, they have direct effects on innovation performance and indirect positive effects on innovation capability.
In general, halal food product invention can determine operational performance, financial performance, and market performance. Due to the initial costs of halal implementation, together with the barriers, SMFEs find it challenging to gain economic and market performance. In addition, operational performance improvement can increase financial and market performance and further mediate the halal implementation and financial and market performance relationship. For instance, attributes of innovation capability like leadership, organizational structure, and knowledge capability may not effectively contribute to economic and market performance but, directly, encourage operational business and export performance. Innovation capability plays a mediating role in the knowledge capability-innovation performance relationship. Knowledge capability anticipates innovation capability that, in turn, influences innovation performance.
7 Conclusions and Future Research Directions
Despite many acknowledging halal food and innovation, little knowledge about halal food possesses the perfect chemical reaction for transpiring human consciousness to the highest intelligence level. This halal food invention becomes global demand contributing to sustainable socio-economic growth in Islamic and non-Islamic nations. Due to SMFEs’ significant role in the halal economy and export performance, halal product innovation should be of the highest interest. Despite the many constraints, SMFEs are often successful innovators. Their natural attributes become an advantage for them to facilitate innovation and move faster than larger firms, thus gaining entrepreneurial success for a more extended period. In addition, SMFEs can benefit prominently from halal product and process innovation. For instance, by offering halal products, SMFEs compete on uniqueness and avoid price competition, creating new demand, thereby facilitating firm growth. Therefore, introducing innovative halal products becomes an opportunity for SMFEs to remain competitive as customers value the uniqueness of halal. However, the successful development and introduction of halal products require SMFEs’ resources and capabilities to gain innovation capability and generate the benefits of innovation. There is theoretical and empirical proof of the positive effects of the invention. The global case of the leading manufacturer, Nestlé, and restaurants such as McDonald’s, Starbucks, and Pizza Hut shows the positive impact of halal products on the potential growth of the international halal business and halal industry.
This chapter contributes to halal food fundamental in the context of SMFE innovation capability and competitiveness. It exposes halal food invention knowledge of halal food-body interconnectedness that consuming halal food stimulates positive spiritual intelligence for the growth and development of human civilization. The focus on halal reflection on product-based, manufacturer-based, and user-based has constructed the concept of halal food invention. This chapter operationalizes halal food consumption in terms of halal, epistemic, and emotional value to gain total customer satisfaction. Halal SMFEs should have strong innovation capability for halal product invention to obtain and sustain business, growth, and competitive advantage. This provides food manufacturers and marketers with helpful knowledge and guidance to attract consumer confidence and satisfaction and increase halal food consumption.
Some directions for future research address the gaps of scarce papers for antecedents and outcomes of halal product invention, factors and outcomes of halal innovation capability, the halal food knowledge, and its consequences that have considerably no research. In general, previous studies acknowledge the positive effect of innovation on the performance of SMEs. How innovation enables superior performance remains scant; hence, future research should unearth the mechanisms of how firms achieve the benefits of halal product invention. Thus, there is a need for more research to explain how SMFEs transform halal dynamic capability into innovation capability and manage the innovation process. Future research should provide empirical research on the halal product invention-performance relationships and factors that impact such relationships.
References
Arsil, P., Tey, Y. S., Brindal, M., Phua, C. U., & Liana, D. (2018). Personal values underlying halal food consumption: Evidence from Indonesia and Malaysia. British Food Journal, 120(11), 2524–2538.
Billah, A., Rahman, M. A., & Hossain, M. T. (2020). Factors influencing Muslim and non-Muslim consumers’ consumption behavior: A case study on halal food. Journal of Foodservice Business Research, 23(4), 324–349.
Bonne, K., Vermeir, I., & Verbeke, W. (2008). Impact of religion on halal meat consumption decision making in Belgium. Journal of International Food and Agribusiness Marketing, 21(1), 5–26.
Dana, L. P. (2009). Religion as an explanatory variable for entrepreneurship. Entrepreneurship and Innovation, 10(2), 87–99.
Din, H. (1985). Manusia dan Islam. Percetakan Watan Sdn. Bhd.
Firdaus, A. F. (2020). Determinants of halal certification success (HCS) of small medium food enterprises (SMFES) in Penang. PhD Thesis, Universiti Sains Malaysia.
Grant, R. M. (1996). Toward a knowledge-based theory of the firm. Strategic Management Journal, 17, 109–122. https://doi.org/10.1002/smj.4250171110
Grant, R. M. (2002). The knowledge-based view of the firm. In C. W. Choo & N. Bontis (Eds.), The strategic management of intellectual capital and organizational knowledge (pp. 133–148). Oxford University Press.
Hambrick, D. C., & Mason, P. A. (1984). Upper echelons: The organization as a reflection of its top managers. Academy of Management Review, 9, 193–206.
Ismail, S. S. S., & Karia, N. (2017). Probing halal food wisdom to the growth and development of spiritual intelligence. Journal of Contemporary Islamic Studies, 3(1), 15–29.
Ismail, A. M., Othman, M. Y., & Dakir, J. (2011). The development of human Islamic approach. Jurnal Hadhari, 3(2), 103–116.
Kamali, M. H. (2010). The Halal industry from a Shariah perspective. Islam and Civilisational Renewal, 1(4), 595–612.
Karia, N. (2021). A comparative benchmark model for SMEs: Viable entrepreneur emotion intelligence. Bechmarking: An international Journal, 28(3), 813–829.
Karia, N., & Asaari, M. H. A. H. (2016a). Halal business and sustainability: Strategies, resources and capabilities of halal third-party logistics (3PLs). Progress in Industrial Ecology, an International Journal, 10(2–3), 286–300.
Karia, N., & Asaari, M. H. A. H. (2016b). Halal value creation: Its role in adding value and enabling logistics service. Production Planning and Control, 27(9), 677–685.
Karia, N., & Asaari, M. H. A. H. (2016c). Assessing innovation in halal service: An Islamic-based view approach. In S. K. A. Manan, F. A. Rahman, & M. Sahri (Eds.), Contemporary issues and development in the global halal industry—Selected papers from the international halal conference 2014 (pp. 589–597). Springer.
Khan, S. N., & Mohsin, M. (2017). The power of emotional value: Exploring the effects of values on green product consumer choice behavior. Journal of Cleaner Production, 150(May), 65–74.
Maehle, N., Iversen, N., Hem, L., & Otnes, C. (2015). Exploring consumer preferences for hedonic and utilitarian food attributes. British Food Journal, 117(12), 3039–3063.
Muhamed, A. A., Rahman, N. N. A., Hamzah, F. M., Zain, C. R. C. M., & Zailani, S. (2019). The impact of consumption value on consumer behavior: A case study of halal-certified food supplies. British Food Journal, 121(11), 2951–2966.
Ramadani, V., Dana, L., Ratten, V., & Tahiri, S. (2015). The context of Islamic entrepreneurship and business: Concept, principles and perspectives. International Journal of Business and Globalisation, 15(3), 244–261.
Ratten, V., Ramadani, V., Dana, L., & Rashiti, S. G. (2017). Islamic entrepreneurship and management: Future research. In V. Ramadani et al. (Eds.), Entrepreneurship and management in an Islamic context (pp. 227–242). Springer.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Noorliza, K. (2022). Managing Halal Food Knowledge and Innovation: Small and Medium Food Enterprises’ (SMFEs) Performance. In: Alserhan, B.A., Ramadani, V., Zeqiri, J., Dana, LP. (eds) Strategic Islamic Marketing. Contributions to Management Science. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-98160-0_10
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-98160-0_10
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-98159-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-98160-0
eBook Packages: Business and ManagementBusiness and Management (R0)