Abstract
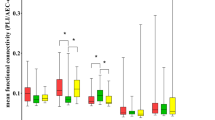
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is an incurable brain disorder which affects especially elderly. Over the years, the analysis of the brain functional connectivity from EEG signals has been exploited for promoting an early diagnosis of AD. Graph theory provides helpful tools to describe complex brain networks. In this work, starting from High-Density EEGs, we estimated the functional connectivity by the Lagged Linear Connectivity (LLC) parameter, for 84 Regions of Interest (ROIs), and analyzed the brain networks properties for three groups of subjects: control subjects (CNT), Mild Cognitive Impairment patients (MCI) and AD patients. We computed three network parameters: the Clustering Coefficient, the Characteristic Path Length and the Randić Index. The results showed that the functional connectivity of MCI and even more of AD patients declines in comparison to healthy people. Moreover, the results deriving from the Randić Index about robustness of brain networks outperform those deriving from the Connection Density Index, commonly used for brain network analysis.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bassett, D.S., Bullmore, E.: Small-world brain networks. Neuroscientist 12(6), 512–523 (2006)
Bastos, A.M., Schoffelen, J.M.: A tutorial review of functional connectivity analysis methods and their interpretational pitfalls. Front. Syst. Neurosc. 9, 175 (2016)
Dattola, S., Mammone, N., Morabito, F.C., Rosaci, D., Sarné, G.M.L., La Foresta, F.: Testing graph robustness indexes for EEG analysis in alzheimer’s disease diagnosis. Electronics 10(12), 1440 (2021)
De Meo, P., Messina, F., Rosaci, D., Sarné, G.M., Vasilakos, A.V.: Estimating graph robustness through the randic index. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 48(11), 3232–3242 (2017)
Freeman, W.J., Holmes, M.D., Burke, B.C., Vanhatalo, S.: Spatial spectra of scalp EEG and EMG from awake humans. Clin. Neurophysiol. 114(6), 1053–1068 (2003)
Gibbons, J., Chakraborti, S.: Nonparametric Statistical Inference Springer (2011)
König, T., Prichep, L., Dierks, T., Hubl, D., Wahlund, L., John, E., Jelic, V.: Decreased eeg synchronization in alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment. Neurobiol. Aging 26(2), 165–171 (2005)
La Foresta, F., Morabito, F.C., Marino, S., Dattola, S.: High-density EEG signal processing based on active-source reconstruction for brain network analysis in alzheimer’s disease. Electronics 8(9), 1031 (2019)
Labate, D., La Foresta, F., Palamara, I., Morabito, G., Bramanti, A., Zhang, Z., Morabito, F.C.: EEG complexity modifications and altered compressibility in mild cognitive impairment and alzheimer’s disease. In: Recent Advances of Neural Network Models and Applications, pp. 163–173. Springer (2014)
Mammone, N., De Salvo, S., Bonanno, L., Ieracitano, C., Marino, S., Marra, A., Bramanti, A., Morabito, F.C.: Brain network analysis of compressive sensed high-density EEG signals in AD and MCI subjects. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 15(1), 527–536 (2019)
Pascual-Marqui, R.D.: Discrete, 3d distributed, linear imaging methods of electric neuronal activity. Part 1: exact, zero error localization (2007). arXiv:0710.3341
Pascual-Marqui, R.D.: Instantaneous and lagged measurements of linear and nonlinear dependence between groups of multivariate time series: frequency decomposition (2007). arXiv:0711.1455
Pascual-Marqui, R.D., Michel, C.M., Lehmann, D.: Low resolution electromagnetic tomography: a new method for localizing electrical activity in the brain. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 18(1), 49–65 (1994)
Pascual-Marqui, R.D., et al.: Standardized low-resolution brain electromagnetic tomography (sloreta): technical details. Methods Find Exp. Clin. Pharmacol. 24(Suppl D), 5–12 (2002)
Phillips, D.J., McGlaughlin, A., Ruth, D., Jager, L.R., Soldan, A., Initiative, A.D.N., et al.: Graph theoretic analysis of structural connectivity across the spectrum of alzheimer’s disease: the importance of graph creation methods. NeuroImage: Clin. 7, 377–390 (2015)
Randic, M.: Characterization of molecular branching. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 97(23), 6609–6615 (1975)
Rossini, P.M., Di Iorio, R., Vecchio, F., Anfossi, M., Babiloni, C., Bozzali, M., Bruni, A.C., Cappa, S.F., Escudero, J., Fraga, F.J., et al.: Early diagnosis of alzheimer’s disease: the role of biomarkers including advanced EEG signal analysis. Report from the IFCN-sponsored panel of experts. Clin. Neurophysiol.131(6), 1287–1310 (2020)
Rubinov, M., Sporns, O.: Complex network measures of brain connectivity: uses and interpretations. Neuroimage 52(3), 1059–1069 (2010)
Sankari, Z., Adeli, H., Adeli, A.: Intrahemispheric, interhemispheric, and distal EEG coherence in alzheimer’s disease. Clin. Neurophysiol. 122(5), 897–906 (2011)
Spitzer, A.R., Cohen, L.G., Fabrikant, J., Hallett, M.: A method for determining optimal interelectrode spacing for cerebral topographic mapping. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 72(4), 355–361 (1989)
Stam, C.J., Jones, B., Nolte, G., Breakspear, M., Scheltens, P.: Small-world networks and functional connectivity in alzheimer’s disease. Cereb. Cortex 17(1), 92–99 (2006)
Tijms, B.M., Wink, A.M., de Haan, W., van der Flier, W.M., Stam, C.J., Scheltens, P., Barkhof, F.: Alzheimer’s disease: connecting findings from graph theoretical studies of brain networks. Neurobiol. Aging 34(8), 2023–2036 (2013)
Wang, G., Ren, D.: Effect of brain-to-skull conductivity ratio on EEG source localization accuracy. BioMed Res. Int. 2013 (2013)
Wang, R., Wang, J., Yu, H., Wei, X., Yang, C., Deng, B.: Decreased coherence and functional connectivity of electroencephalograph in alzheimer’s disease. Chaos: Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 24(3), 033136 (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Dattola, S., La Foresta, F. (2022). Graph Theory Applied to Brain Network Analysis in Alzheimer’s Disease. In: Camacho, D., Rosaci, D., Sarné, G.M.L., Versaci, M. (eds) Intelligent Distributed Computing XIV. IDC 2021. Studies in Computational Intelligence, vol 1026. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-96627-0_33
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-96627-0_33
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-96626-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-96627-0
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)