Abstract
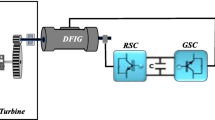
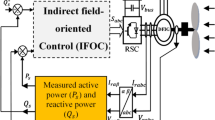
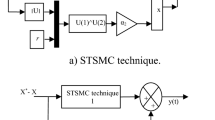
This work presents a nonlinear control strategy called Super Twisting Sliding Mode Control (STSMC). It is applied to Wind Energy Conversion System (WECS), the main goal is to control the active and reactive stator powers of the Doubly Fed Induction Generator (DFIG) and the wind turbine speed generated by the Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT).
Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) is used to tune the parameters of five sliding surfaces, by selecting an objective function. The proposed PSO-STSMC approach reduces powers and currents ripples while maintaining the Sliding Mode Control (SMC) advantages such as robustness. Simulation results show the effectiveness of the proposed strategy in reducing the chattering phenomenon.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abad, G., López, J., Rodríguez, M., Marroyo, L., Iwanski, G.: Introduction to a wind energy generation system, in Doubly Fed Induction Machine. In: Modeling and Control for Wind Energy Generation Applications, pp. 1–85. IEEE (2011)
Kelkoul, B., Boumediene, A.: Stability analysis and study between classical sliding mode control (SMC) and super twisting algorithm (STA) for doubly fed induction generator (DFIG) under wind turbine. Energy 214, 118871 (2021)
Sami, I., Ullah, S., Ali, Z., Ullah, N., Ro, J.-S.: A super twisting fractional order terminal sliding mode control for DFIG-based wind energy conversion system. Energies 13, 2158 (2020)
Bouyekni, A., Taleb, R., Boudjema, Z., Kahal, H.: A second-order continuous sliding mode based on DPC for wind-turbine-driven DFIG. Elektrotehniški Vestnik 85, 29–36 (2018)
Tria, F.Z., Srairi, K., Benchouia, M.T., Benbouzid, M.E.H.: An integral sliding mode controller with super-twisting algorithm for direct power control of wind generator based on a doubly fed induction generator. Int. J. Syst. Assur. Eng. Manag. 8(4), 762–769 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-017-0597-5
Benbouhenni, H., Boudjema, Z., Belaidi, A.: DPC based on ANFIS super-twisting sliding mode algorithm of a doubly-fed induction generator for wind energy system. J. Européen des Systèmes Automatisés 53, 69–80 (2019)
Belabbas, B., Allaoui, T., Tadjine, M., Denai, M.: Comparative study of back-stepping controller and super twisting sliding mode controller for indirect power control of wind generator. Int. J. Syst. Assur. Eng. Manag. 10, 1–12 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-019-00905-7
Yahdou, A., Djilali, A.B., Boudjema, Z., Mehedi, F.: Using adaptive second order sliding mode to improve power control of a counter-rotating wind turbine under grid disturbances. Eur. J. Electr. Eng. 22, 427–434 (2020)
Panathula, C.B., Shtessel, Y.: Practical stability margins in continuous higher order sliding mode control systems. J. Franklin Inst. 357, 106–120 (2020)
Boudjehem, D., Boudjehem, B.: Improved heterogeneous particle swarm optimization. J. Inf. Optim. Sci. 38, 481–499 (2017)
Sai Rayala, S., Ashok Kumar, N.: Particle Swarm Optimization for robot target tracking application. Mater. Today Proc. 33, 3600–3603 (2020)
Bounar, N., Labdai, S., Boulkroune, A.: PSO–GSA based fuzzy sliding mode controller for DFIG-based wind turbine. ISA Trans. 85, 177–188 (2019)
Soufi, Y., Kahla, S., Bechouat, M.: Particle swarm optimization based sliding mode control of variable speed wind energy conversion system. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 41, 20956–20963 (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Gasmi, H., Mendaci, S., Kantas, W. (2022). Wind Energy Conversion System Controlled by Particle Swarm Optimization Super Twisting Sliding Mode Control Equipped with Doubly Fed Induction Generator. In: Hatti, M. (eds) Artificial Intelligence and Heuristics for Smart Energy Efficiency in Smart Cities. IC-AIRES 2021. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 361. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-92038-8_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-92038-8_8
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-92037-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-92038-8
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)