Abstract
Angiotensin II, synthesized by the cleavage of angiotensinogen to angiotensin I by renin and then conversion to angiotensin II by the angiotensin-converting enzyme, is the main effector peptide of the renin-angiotensin system. Transmembrane angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), the enzyme that metabolizes angiotensin II, is the host receptor for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). SARS-CoV-2, which binds to transmembrane angiotensin-converting enzyme 2, affects angiotensin II levels by causing an imbalance in the renin-angiotensin system.
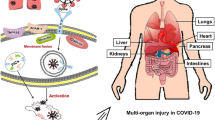
Angiotensin II triggers inflammation, coagulopathy, vasculopathy, fibrosis, oxidative stress, and thrombosis through the angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AT1R). Angiotensin II is thought to contribute to pneumonia, sepsis, acute respiratory distress syndrome, diffuse thrombosis, and multi-organ damage in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).
Studies conducted in the preclinical and early period of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic on severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) shared findings that serum angiotensin II levels increased. However, recent studies have shown an increase in circulating soluble ACE2 levels and a decrease in serum angiotensin II levels in COVID-19.
Despite conflicting results, the majority of studies have shown that decreased serum angiotensin II levels are associated with the severity, prognosis, and mortality of COVID-19.
In this chapter, the relationship between COVID-19 and angiotensin II and the renin-angiotensin system was discussed in light of scientific studies conducted during the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACE:
-
Angiotensin-converting enzyme
- ACE2:
-
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2
- ADAM17:
-
A disintegrin and metalloproteinase 17 domain
- ADH:
-
Antidiuretic hormone
- ALI:
-
Acute lung injury
- Ang:
-
Angiotensin
- AP:
-
Aminopeptidase
- ARDS:
-
Acute respiratory distress syndrome
- AT1R:
-
Angiotensin II type 1 receptor
- AT2R:
-
Angiotensin II type 2 receptor
- AT4R:
-
Angiotensin II type 4 receptor
- COVID-19:
-
Coronavirus disease 2019
- CP:
-
Carboxypeptidase
- MasR:
-
Mas receptor
- MrgD:
-
Mas-related G protein-coupled receptor member
- NEP:
-
Neprilysin
- POP:
-
Prolyloligopeptidase
- RAS:
-
Renin-angiotensin system
- sACE2:
-
Soluble angiotensin-converting enzyme 2
- SARS-CoV:
-
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus
- SARS-CoV-2:
-
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2
- TF:
-
Tissue factor
- TMPRSS2:
-
Human androgen-sensitive transmembrane serine protease type 2
References
Ackermann M, Verleden SE, Kuehnel M, et al. Pulmonary vascular Endothelialitis, thrombosis, and angiogenesis in Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:120–8.
Alam A, Sovic W, Gill J, et al. Angiotensin II: a review of current literature. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2022;36:1180–7.
Annoni F, Orbegozo D, Rahmania L, et al. Angiotensin-converting enzymes in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Intensive Care Med. 2019;45:1159–60.
Bánhegyi V, Enyedi A, Fülöp GÁ, et al. Human tissue angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) activity is regulated by genetic polymorphisms, posttranslational modifications, endogenous inhibitors and secretion in the serum. Lungs and Heart Cells. 2021;10:1708.
Beyerstedt S, Casaro EB, Rangel ÉB. COVID-19: angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) expression and tissue susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2021;40:905–19.
Bhargava M, Wendt CH. Biomarkers in acute lung injury. Transl Res. 2012;159:205–17.
Biberoğlu S, İpekci A, İkizceli İ, et al. Role of plasma angiotensin II and angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 levels on prognosis and mortality in hypertensive patients with COVID-19. Biomark Med. 2021;15:1581–8.
Bolay H, Karadas Ö, Oztürk B, et al. HMGB1, NLRP3, IL-6 and ACE2 levels are elevated in COVID-19 with headache: a window to the infection-related headache mechanism. J Headache Pain. 2021;22:94.
Bullock GR, Steyaert I, Bilbe G, et al. Distribution of type-1 and type-2 angiotensin receptors in the normal human lung and in lungs from patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Histochem Cell Biol. 2001;115:117–24.
Cao Y, Liu Y, Shang J, et al. Ang-(1-7) treatment attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced early pulmonary fibrosis. Lab Investig. 2019;99:1770–83.
Catarata MJ, Ribeiro R, Oliveira MJ, et al. Renin-angiotensin system in lung tumor and microenvironment interactions. Cancers (Basel). 2020;12:1457.
Celi A, Cianchetti S, Dell’Omo G, et al. Angiotensin II, tissue factor and the thrombotic paradox of hypertension. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2010;8:1723–9.
Chow JH, Mazzeffi MA, McCurdy MT. Angiotensin II for the treatment of COVID-19-related vasodilatory shock. Anesth Analg. 2020;131:102–5.
Coppo M, Boddi M, Bandinelli M, et al. Angiotensin II upregulates renin-angiotensin system in human isolated T lymphocytes. Regul Pept. 2008;151:1–6.
Dean AQ, Bozza WP, Twomey JD, et al. The fight against COVID-19: striking a balance in the renin-angiotensin system. Drug Discov Today. 2021;26:2214–20.
Donoghue M, Hsieh F, Baronas E, et al. A novel angiotensin converting enzyme-related carboxypeptidase (ACE2) converts angiotensin I to angiotensin 1-9. Circ Res. 2000;87:E1–9.
Eleuteri D, Montini L, Cutuli SL, et al. Renin-angiotensin system dysregulation in critically ill patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome due to COVID-19: a preliminary report. Crit Care. 2021;25(1):91.
Ferrão FM, Lara LS, Lowe J. Renin-angiotensin system in the kidney: what is new? World J Nephrol. 2014;3:64–76.
Files DC, Gibbs KW, Schaich CL, et al. A pilot study to assess the circulating renin-angiotensin system in COVID-19 acute respiratory failure. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2021;321:L213–8.
Fisher NDL. Overview of the renin-angiotensin system. In: Bakris GL, Forman JP. UpToDate. 2022. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/overview-of-the-renin-angiotensin-system. Accessed 22 Apr 2022.
Fountain JH, Lappin SL. Physiology, renin angiotensin system. [Updated 2021 Jul 22]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470410. Accessed 20 Apr 2022.
Garvin MR, Alvarez C, Miller JI, et al. A mechanistic model and therapeutic interventions for COVID-19 involving a RAS-mediated bradykinin storm. elife. 2020;9:e59177.
Gerard L, Lecocq M, Bouzin C, et al. Increased angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 and loss of alveolar type II cells in COVID-19-related acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2021;204:1024–34.
Gheblawi M, Wang K, Viveiros A, et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2: SARS-CoV-2 receptor and regulator of the renin-angiotensin system: celebrating the 20th anniversary of the discovery of ACE2. Circ Res. 2020;126:1456–74.
Guo YR, Cao QD, Hong ZS, et al. The origin, transmission and clinical therapies on coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak-an update on the status. Mil Med Res. 2020;7:11.
Henry BM, Benoit S, Lippi G, et al. Letter to the editor – circulating plasma levels of angiotensin ii and aldosterone in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a preliminary report. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2020;63:702–3.
Heurich A, Hofmann-Winkler H, Gierer S, et al. TMPRSS2 and ADAM17 cleave ACE2 differentially and only proteolysis by TMPRSS2 augments entry driven by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus spike protein. J Virol. 2014;88:1293–307.
Hoch NE, Guzik TJ, Chen W, et al. Regulation of T-cell function by endogenously produced angiotensin II. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2009;296:R208–16.
Hoffmann M, Kleine-Weber H, Schroeder S, et al. SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor. Cell. 2020;181:271–280.e8.
Hrenak J, Simko F. Renin–angiotensin system: an important player in the pathogenesis of acute respiratory distress syndrome. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:8038.
Huang F, Guo J, Zou Z, et al. Angiotensin II plasma levels are linked to disease severity and predict fatal outcomes in H7N9-infected patients. Nat Commun. 2014;5:3595.
Ipekci A, Biberoglu S, Ikizceli I, et al. ACE2 and ANGII levels in patients with COVID-19 based on thoracic tomography findings and PCR test results. J Infect Dev Ctries. 2022;16:427–34.
Jia HP, Look DC, Hickey M, et al. Infection of human airway epithelia by SARS coronavirus is associated with ACE2 expression and localization. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2006;581:479–84.
Karthika T, Joseph J, Das VRA, et al. SARS-CoV-2 cellular entry is independent of the ACE2 cytoplasmic domain signaling. Cell. 2021;10:1814.
Kintscher U, Slagman A, Domenig O, et al. Plasma angiotensin peptide profiling and ACE (angiotensin-converting enzyme)-2 activity in COVID-19 patients treated with pharmacological blockers of the renin-angiotensin system. Hypertension. 2020;76:e34–6.
Kragstrup TW, Singh HS, Grundberg I, et al. Plasma ACE2 predicts outcome of COVID-19 in hospitalized patients. PLoS One. 2021;16:e0252799.
Krenn K, Tretter V, Kraft F, et al. The Renin-Angiotensin System as a Component of Biotrauma in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Front Physiol. 2022;12:806062.
Kuba K, Imai Y, Rao S, et al. Lessons from SARS: control of acute lung failure by the SARS receptor ACE2. J Mol Med (Berl). 2006;84:814–20.
Kutz A, Conen A, Gregoriano C, et al. Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system peptide profiles in patients with COVID-19. Eur J Endocrinol. 2021;184:543–52.
Lambert DW, Yarski M, Warner FJ, et al. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha convertase (ADAM17) mediates regulated ectodomain shedding of the severe-acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus (SARS-CoV) receptor, angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 (ACE2). J Biol Chem. 2005;280:30113–9.
Li W, Moore MJ, Vasilieva N, et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 is a functional receptor for the SARS coronavirus. Nature. 2003;426:450–4.
Li Y, Zhou W, Yang L, et al. Physiological and pathological regulation of ACE2, the SARS-CoV-2 receptor. Pharmacol Res. 2020;157:104833.
Li Y, Schneider AM, Mehta A, et al. SARS-CoV-2 viremia is associated with distinct proteomic pathways and predicts COVID-19 outcomes. J Clin Invest. 2021;131:e148635.
Liu Y, Yang Y, Zhang C, et al. Clinical and biochemical indexes from 2019-nCoV infected patients linked to viral loads and lung injury. Sci China Life Sci. 2020;63:364–74.
Lundström A, Ziegler L, Havervall S, et al. Soluble angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 is transiently elevated in COVID-19 and correlates with specific inflammatory and endothelial markers. J Med Virol. 2021;93:5908–16.
Marshall RP, Gohlke P, Chambers RC, et al. Angiotensin II and the fibroproliferative response to acute lung injury. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2004;286:L156–64.
Mascolo A, Scavone C, Rafaniello C, et al. Renin-angiotensin system and coronavirus disease 2019: a narrative review. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2020;7:143.
Mascolo A, Scavone C, Rafaniello C, et al. The role of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in the heart and lung: focus on COVID-19. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:667254.
Miesbach W. Pathological role of angiotensin II in severe COVID-19. TH Open. 2020;4:e138–44.
Montiel V, Lobysheva I, Gérard L, et al. Oxidative stress-induced endothelial dysfunction and decreased vascular nitric oxide in COVID-19 patients. EBioMedicine. 2022;77:103893.
Morris DL, Sanghavi D, Kahwaji CI. Angiotensin II. [Updated 2021 Jul 25]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK499912/
Nagy B Jr, Fejes Z, Szentkereszty Z, et al. A dramatic rise in serum ACE2 activity in a critically ill COVID-19 patient. Int J Infect Dis. 2021;103:412–4.
Nie W, Zang Y, Chen J, et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme I/D polymorphism is associated with pneumonia risk: a meta-analysis. J Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone Syst. 2014;15:585–92.
Orfanos SE, Armaganidis A, Glynos C, et al. Pulmonary capillary endothelium-bound angiotensin-converting enzyme activity in acute lung injury. Circulation. 2000;102:2011–8.
Ozkan S, Cakmak F, Konukoglu D, et al. Efficacy of serum angiotensin II levels in prognosis of patients with coronavirus disease 2019. Crit Care Med. 2021;49:e613–23.
Patel VB, Zhong JC, Grant MB, et al. Role of the ACE2/Angiotensin 1-7 axis of the renin-angiotensin system in heart failure. Circ Res. 2016;118:1313–26.
Patel SK, Juno JA, Lee WS, et al. Plasma ACE2 activity is persistently elevated following SARS-CoV-2 infection: implications for COVID-19 pathogenesis and consequences. Eur Respir J. 2021;57:2003730.
Puurunen MK, Hwang SJ, Larson MG, et al. ADP platelet Hyperreactivity predicts cardiovascular disease in the FHS (Framingham heart study). J Am Heart Assoc. 2018;7:e008522.
Rahman MM, Hasan M, Ahmed A. Potential detrimental role of soluble ACE2 in severe COVID-19 comorbid patients. Rev Med Virol. 2021;31:1–12.
Ramchand J, Patel SK, Srivastava PM, et al. Elevated plasma angiotensin converting enzyme 2 activity is an independent predictor of major adverse cardiac events in patients with obstructive coronary artery disease. PLoS One. 2018;13:e0198144.
Reddy R, Asante I, Liu S, et al. Circulating angiotensin peptides levels in acute respiratory distress syndrome correlate with clinical outcomes: a pilot study. PLoS One. 2019;14:e0213096.
Reindl-Schwaighofer R, Hödlmoser S, Eskandary F, et al. ACE2 elevation in severe COVID-19. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2021;203:1191–6.
Rieder M, Wirth L, Pollmeier L, et al. Serum ACE2, angiotensin II, and aldosterone levels are unchanged in patients with COVID-19. Am J Hypertens. 2021;34(3):278–81.
Ruiz-Ortega M, Lorenzo O, Suzuki Y, et al. Proinflammatory actions of angiotensins. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2001;10:321–9.
Shah A. Novel coronavirus-induced NLRP3 Inflammasome activation: a potential drug target in the treatment of COVID-19. Front Immunol. 2020;11:1021.
Shylesh CMS, Arya VS, Kanthlal SK, et al. Renin-angiotensin system modulators in COVID-19 patients with hypertension: friend or foe? Clin Exp Hypertens. 2022;44:1–10.
Silva MG, Falcoff NL, Corradi GR, et al. Renin-angiotensin system blockade on angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 and TMPRSS2 in human type II pneumocytes. Life Sci. 2022;293:120324.
Skurk T, Lee YM, Hauner H. Angiotensin II and its metabolites stimulate PAI-1 protein release from human adipocytes in primary culture. Hypertension. 2001;37:1336–40.
Sodhi CP, Wohlford-Lenane C, Yamaguchi Y, et al. Attenuation of pulmonary ACE2 activity impairs inactivation of des-Arg9 bradykinin/BKB1R axis and facilitates LPS-induced neutrophil infiltration. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2018;314:L17–31.
Sodhi CP, Nguyen J, Yamaguchi Y, et al. A dynamic variation of pulmonary ACE2 is required to modulate neutrophilic inflammation in response to Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung infection in mice. J Immunol. 2019;203:3000–12.
Soro-Paavonen A, Gordin D, Forsblom C, et al. Circulating ACE2 activity is increased in patients with type 1 diabetes and vascular complications. J Hypertens. 2012;30:375–83.
South AM, Diz DI, Chappell MC. COVID-19, ACE2, and the cardiovascular consequences. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2020;318:H1084–90.
Sungnak W, Huang N, Bécavin C, et al. SARS-CoV-2 entry factors are highly expressed in nasal epithelial cells together with innate immune genes. Nat Med. 2020;26:681–7.
Triposkiadis F, Starling RC, Xanthopoulos A, et al. The counter regulatory Axis of the lung renin-angiotensin system in severe COVID-19: pathophysiology and clinical implications. Heart Lung Circ. 2021;30:786–94.
Unger T. The role of the renin-angiotensin system in the development of cardiovascular disease. Am J Cardiol. 2002;89:3A–9A; discussion 10A.
Valle Martins AL, da Silva FA, Bolais-Ramos L, et al. Increased circulating levels of angiotensin-(1-7) in severely ill COVID-19 patients. ERJ Open Res. 2021;7:00114–2021.
van Lier D, Kox M, Santos K, et al. Increased blood angiotensin converting enzyme 2 activity in critically ill COVID-19 patients. ERJ Open Res. 2021;7:00848–2020.
Vassiliou AG, Zacharis A, Keskinidou C, et al. Soluble angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) is upregulated and soluble endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) is downregulated in COVID-19-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021;14:695.
Wallentin L, Lindbäck J, Eriksson N, et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) levels in relation to risk factors for COVID-19 in two large cohorts of patients with atrial fibrillation. Eur Heart J. 2020;41:4037–46.
Walls AC, Park YJ, Tortorici MA, et al. Structure, function, and antigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein. Cell. 2020;181:281–92.
Wang J, Zhao H, An Y. ACE2 shedding and the role in COVID-19. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022;11:789180.
Wrapp D, Wang N, Corbett KS, et al. Cryo-EM structure of the 2019-nCoV spike in the prefusion conformation. Science. 2020;367:1260–3.
Wu Z, Hu R, Zhang C, et al. Elevation of plasma angiotensin II level is a potential pathogenesis for the critically ill COVID-19 patients. Crit Care. 2020;24:290.
Xavier LL, Neves PFR, Paz LV, et al. Does angiotensin II peak in response to SARS-CoV-2? Front Immunol. 2021;11:577875.
Yan R, Zhang Y, Li Y, et al. Structural basis for the recognition of SARS-CoV-2 by full-length human ACE2. Science. 2020;367:1444–8.
Yang P, Gu H, Zhao Z, et al. Angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) mediates influenza H7N9 virus-induced acute lung injury. Sci Rep. 2014;4:7027.
Yeung ML, Teng JLL, Jia L, et al. Soluble ACE2-mediated cell entry of SARS-CoV-2 via interaction with proteins related to the renin-angiotensin system. Cell. 2021;184:2212–2228.e12.
Zhang H, Penninger JM, Li Y, et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) as a SARS-CoV-2 receptor: molecular mechanisms and potential therapeutic target. Intensive Care Med. 2020;46:586–90.
Zhang Q, Ling S, Hu K, et al. Role of the renin-angiotensin system in NETosis in the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;148:112718.
Zhu Z, Cai T, Fan L, et al. The potential role of serum angiotensin-converting enzyme in coronavirus disease 2019. BMC Infect Dis. 2020;20:883.
Zhuo JL, Ferrao FM, Zheng Y, et al. New frontiers in the intrarenal renin-angiotensin system: a critical review of classical and new paradigms. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2013;4:166.
Ziegler CGK, Allon SJ, Nyquist SK, et al. SARS-CoV-2 receptor ACE2 is an interferon-stimulated gene in human airway epithelial cells and is detected in specific cell subsets across tissues. Cell. 2020;181:1016–1035.e19.
Zipeto D, Palmeira JDF, Argañaraz GA, et al. ACE2/ADAM17/TMPRSS2 interplay may be the Main risk factor for COVID-19. Front Immunol. 2020;11:576745.
Zou Z, Yan Y, Shu Y, et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 protects from lethal avian influenza a H5N1 infections. Nat Commun. 2014;5:3594.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this entry
Cite this entry
Ozkan, S., Ipekci, A. (2022). Serum Angiotensin II as a Biomarker in COVID-19. In: Rajendram, R., Preedy, V.R., Patel, V.B. (eds) Biomarkers in Trauma, Injury and Critical Care. Biomarkers in Disease: Methods, Discoveries and Applications. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87302-8_69-1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87302-8_69-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-87302-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-87302-8
eBook Packages: Springer Reference Biomedicine and Life SciencesReference Module Biomedical and Life Sciences