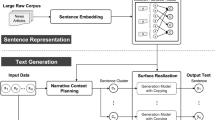
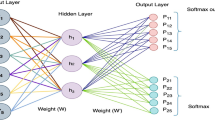
Abstract
Decoding the world of artificial intelligence and its usage in the current intelligence landscape enhance bottom-up growth in building resilient global business. The areas of artificial intelligence (AI) concerned with human-to-machine and machine-to-human interaction. The Next Wave in AI-driven speech is Natural Language Generation (NLG). Natural Language Generation (NLG) is the use of artificial intelligence (AI) programming to produce written or spoken narrative from a dataset. NLG is related to computational linguistics, natural language processing (NLP) and natural language understanding (NLU). NLG research often focuses on building computer programs that provide data points with context. Sophisticated NLG software has the ability to mine large quantities of numerical data, identify patterns and share that information in a way that is easy for humans to understand. The speed of NLG software is especially useful for producing news and other time-sensitive stories on the internet. At its best, NLG output can be published verbatim as web content. The goal of Natural language generation (NLG) is to use AI to produce written or spoken narrative from a dataset. Therefore, this study aims to study how NLG enables machines and humans to communicate seamlessly, simulating human to human conversations and using NLG how organizations are building new customer experiences, monetizing information assets, introducing new offerings and streamlining operational costs. Therefore, the coverage of this chapter will answer to the industrialists and new start-ups. What can NLG do for business? and what are the future applications of NLG?
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. Adamopoulou, M. Lefteris, Chatbots: history, technology, and applications. Mach. Learn. Appl. 2, 100006 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mlwa.2020.100006
A. Choudhury, Analytics India magazine: Top Natural Language Generation Platforms in 2021 (2021). https://analyticsindiamag.com/top-natural-language-generation-platforms-in-2021/
J. Bateman, M. Zock, Natural language generation. Oxford Handbooks Online (2012). https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordhb/9780199276349.013.00
A.J. Cawsey, B.L. Webber, R.B. Jones, Natural language generation in health care. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 4(6), 473–482 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1136/jamia.1997.0040473
R. Dale, Natural language generation: the commercial state of the art in 2020. Nat. Lang. Eng. 26(4), 481–487 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1017/s135132492000025x
O. Dušek, J. Novikova, V. Rieser, Evaluating the state-of-the-art of end-to-end natural language generation: the E2E NLG challenge. Comput. Speech Lang. 59, 123–156 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csl.2019.06.009
E. Reiter, Natural language generation, in A. Clark, C. Fox, S. Lappin (eds.), Handbook of Computational Linguistics and Natural Language Processing, John Wiley & Sons 574–598 (2010)
E. Reiter, R. Dale, Building natural language generation systems (Studies in Natural Language Processing) Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, 1st edition (9 March 2006)
A. Mykowiecka, Natural-language generation—an overview. Int. J. Man Mach. Stud. 34(4), 497–511 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1016/0020-7373(91)90032-3
E.Reiter, R. Dale, Building applied natural-language generation systems. J. Nat.-Lang. Eng. 3, 57–87 (1997)
R. Sivarethinamohan, S. Sujatha, Unraveling the potential of artificial intelligence-driven blockchain technology in environment management, in G. Manik, S. Kalia, S.K. Sahoo, T.K. Sharma, O.P. Verma (eds) Advances in mechanical engineering. Lecture notes in mechanical engineering. Springer, Singapore (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-0942-8_66
R. Sivarethinamohan, D. Yuvaraj, S. Shanmuga Priya, S. Sujatha, Captivating profitable applications of artificial intelligence in agriculture management, in P. Vasant, I. Zelinka, GW Weber (eds) Intelligent computing and optimization. ICO 2020. Advances in intelligent systems and computing, vol. 1324. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-68154-8_73
M.O. Topal, A. Bas, I.V. Heerden, Exploring transformers in natural language generation: GPT, BERT, and XLNet (2021). ArXiv, abs/2102.08036
K. Van Deemter, E. Reiter, H. Horacek, Formal issues in natural language generation. Res Lang Comput 4, 1–7 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11168-006-9008-9
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Sivarethinamohan, R., Sujatha, S. (2022). Nurturing the Rudiments and Use Cases of Ongoing Natural Language Generation for a Future Profitable Business More Profitable. In: Fernandes, S.L., Sharma, T.K. (eds) Artificial Intelligence in Industrial Applications. Learning and Analytics in Intelligent Systems, vol 25. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-85383-9_10
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-85383-9_10
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-85382-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-85383-9
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)