Abstract
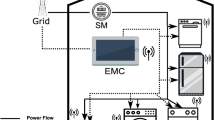
An intelligent home is able to automatically adjust and manage different systems of the building according to a predefined plan to control energy consumption level. In order to manage energy costs, smart appliances can be scheduled to be used at different times of the day. Energy costs may continuously vary over time depending on different factors such as inhabitant behavior, weather conditions, renewable energy generation, etc. Scheduling of smart appliances can be carried out by taking into account the varying behavior of energy costs. Therefore, by considering different factors affecting energy costs and operational constraints, mathematical models can be utilized to optimize the scheduling of energy consumption of different appliances of a smart home. These models for optimizing the scheduling of smart appliances can result in significant energy savings. Therefore, the problem of energy consumption scheduling in smart homes is investigated in this research and some basic integer programming and mixed integer programming models are reviewed and described.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K.C. Sou et al., Scheduling smart home appliances using mixed integer linear programming, in 2011 50th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control and European Control Conference. (2011). IEEE.
F.A. Qayyum et al., Appliance Scheduling Optimization in Smart Home Networks. IEEE Access 3, 2176–2190 (2015)
A. Akbari-Dibavar et al., Smart home energy management using hybrid robust-stochastic optimization. Comput. Ind. Eng. 143, 106425 (2020a)
A. Perera, P. Kamalaruban, Applications of reinforcement learning in energy systems. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 137, 110618 (2021)
A. Ipakchi, F. Albuyeh, Grid of the future. IEEE Power Energy Mag. 7(2), 52–62 (2009)
M. Farrokhifar et al., Real-time based approach for intelligent building energy management using dynamic price policies. Sustain. Cities Soc. 37, 85–92 (2018)
T.T. Kim, H.V. Poor, Scheduling power consumption with price uncertainty. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2(3), 519–527 (2011)
A.P. Sanghvi, Flexible strategies for load/demand management using dynamic pricing. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 4(1), 83–93 (1989)
Z. Hu et al., Review of dynamic pricing programs in the US and Europe: Status quo and policy recommendations. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 42, 743–751 (2015)
A.B. Haney et al., Demand-side Management Strategies and the Residential Sector: Lessons from International Experience. The Future of Electricity Demand: Customers, Citizens and Loads (2010), pp. 337–378.
K. Clement-Nyns, E. Haesen, J. Driesen, The impact of charging plug-in hybrid electric vehicles on a residential distribution grid. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 25(1), 371–380 (2009)
D.L. Bleviss, Transportation is critical to reducing greenhouse gas emissions in the United States. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Energy and Environment 10(2), e390 (2021)
E. Sortomme, M.A. El-Sharkawi, Optimal charging strategies for unidirectional vehicle-to-grid. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2(1), 131–138 (2010)
X. Lu et al., Optimal scheduling of household appliances for smart home energy management considering demand response. Nat. Hazards 88(3), 1639–1653 (2017)
X. Chen, T. Wei, S. Hu, Uncertainty-aware household appliance scheduling considering dynamic electricity pricing in smart home. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 4(2), 932–941 (2013)
M. Rahmani-Andebili, Scheduling deferrable appliances and energy resources of a smart home applying multi-time scale stochastic model predictive control. Sustain. Cities Soc. 32, 338–347 (2017)
S. Zeynali, N. Rostami, A. Ahmadian, A. Elkamel, Two-stage stochastic home energy management strategy considering electric vehicle and battery energy storage system: An ANN-based scenario generation methodology. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assessments 39, 100722 (2020)
C.A. Correa-Florez, A. Gerossier, A. Michiorri, G. Kariniotakis, Stochastic operation of home energy management systems including battery cycling. Appl. Energy 225, 1205–1218 (2018a)
A.S. Gazafroudi, M. Shafie-khah, E. Heydarian-Forushani, A. Hajizadeh, A. Heidari, J.M. Corchado, J.P. Catalão, Two-stage stochastic model for the price-based domestic energy management problem. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 112, 404–416 (2019)
C. Wang, Y. Zhou, B. Jiao, Y. Wang, W. Liu, D. Wang, Robust optimization for load scheduling of a smart home with photovoltaic system. Energy Convers. Manag. 102, 247–257 (2015)
C.A. Correa-Florez, A. Michiorri, G. Kariniotakis, Robust optimization for day-ahead market participation of smart-home aggregators. Appl. Energy 229, 433–445 (2018b)
A. Akbari-Dibavar, S. Nojavan, B. Mohammadi-Ivatloo, K. Zare, Smart home energy management using hybrid robust-stochastic optimization. Comput. Ind. Eng. 143, 106425 (2020b)
A. Mohsenzadeh, M.H. Shariatkhah, M.-R. Haghifam, Applying Fuzzy Techniques to Model Customer Comfort in a Smart Home Control System (2013), pp. 1164–1164
F. Chekired, A. Mahrane, Z. Samara, M. Chikh, A. Guenounou, A. Meflah, Fuzzy logic energy management for a photovoltaic solar home. Energy Procedia 134, 723–730 (2017)
Y. Huang, L. Wang, W. Guo, Q. Kang, Q. Wu, Chance constrained optimization in a home energy management system. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid. 9(1), 252–260 (2016)
K. Garifi, K. Baker, B. Touri, D. Christensen, Stochastic model predictive control for demand response in a home energy management system, in 2018 IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting (PESGM) 2018 Aug 5 (pp. 1–5). IEEE.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this entry
Cite this entry
Momayezi, F., Sabri-Laghaie, K., Ghaffarinasab, N. (2022). Energy Management of Smart Homes by Optimizing Energy Consumption Scheduling. In: Fathi, M., Zio, E., Pardalos, P.M. (eds) Handbook of Smart Energy Systems. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-72322-4_67-1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-72322-4_67-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-72322-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-72322-4
eBook Packages: Springer Reference Economics and FinanceReference Module Humanities and Social SciencesReference Module Business, Economics and Social Sciences