Abstract
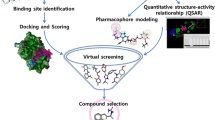
Cheminformatics has the major research factors that lead to the importance of similarity measurements for drugs and increase the chemical compound on databases search. The previous method is used for predicting the design of drugs and is comparatively efficient and less weak. Drug design is the process for finding new medications depended on the collected knowledge about a biological target. This chapter introduces several Metaheuristics Algorithms (MA), and Machine Learning (ML) techniques are used to design and discover new drug compounds in Cheminformatics. The balance of exploration and exploitation processes of MA’s are convenient for selecting the significant features as preprocessing to ML step for accomplishing high classification accuracy to the active chemical compound. In consequence, the results of the drug designed aim an optimal compound and enhanced the chemical descriptor.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
11 October 2021
The original version of the book was published with incorrect affiliation for the author M. Hassaballah. Affiliation has been updated with correct affiliation for the following chapters:
References
P. Willett, Chemoinformatics (2016)
A. Lavecchia, Machine-learning approaches in drug discovery: methods and applications. Drug Discov. Today 20(3), 318–331 (2015)
T. Katsila, G.A. Spyroulias, G.P. Patrinos, M.-T. Matsoukas, Computational approaches in target identification and drug discovery. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 14, 177–184 (2016)
A.U. Khan et al., Descriptors and their selection methods in qsar analysis: paradigm for drug design. Drug Discov. Today 21(8), 1291–1302 (2016)
S. Yuan, H.S. Chan, S. Filipek, H. Vogel, Pymol and inkscape bridge the data and the data visualization. Structure 24(12), 2041–2042 (2016)
S. Forli, R. Huey, M.E. Pique, M.F. Sanner, D.S. Goodsell, A.J. Olson, Computational protein-ligand docking and virtual drug screening with the autodock suite. Nat. Protocols 11(5), 905 (2016)
M. García-Torres, F. Gómez-Vela, B. Melián-Batista, J.M. Moreno-Vega, High-dimensional feature selection via feature grouping: A variable neighborhood search approach. Inf. Sci. 326, 102–118 (2016)
E.H. Houssein, M. Younan, A.E. Hassanien, Nature-inspired algorithms: a comprehensive review. Hybrid Computational Intelligence: Research and Applications, p. 1 (2019)
N. Siddique, H. Adeli, Nature-inspired chemical reaction optimisation algorithms. Cogn. Comput. 9(4), 411–422 (2017)
A.E. Hassanien, M. Kilany, E.H. Houssein, H. AlQaheri, Intelligent human emotion recognition based on elephant herding optimization tuned support vector regression. Biomed. Sig. Process. Control 45, 182–191 (2018)
E.H. Houssein, A.A. Ewees, M.A. ElAziz, Improving twin support vector machine based on hybrid swarm optimizer for heartbeat classification. Pattern Recogn. Image Anal. 28(2), 243–253 (2018)
A. Tharwat, Y.S. Moemen, A.E. Hassanien, Classification of toxicity effects of biotransformed hepatic drugs using whale optimized support vector machines. J. Biomed. Inf. 68, 132–149 (2017)
C.C. Aquino, S.H. Fox, Clinical spectrum of levodopa-induced complications. Mov. Disord. 30(1), 80–89 (2015)
J.-P. Renaud, C.-W. Chung, U.H. Danielson, U. Egner, M. Hennig, R.E. Hubbard, H. Nar, Biophysics in drug discovery: impact, challenges and opportunities. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 15(10), 679 (2016)
J. Gasteiger, Chemoinformatics: achievements and challenges, a personal view. Molecules 21(2), 151 (2016)
M.D. Eastgate, M.A. Schmidt, K.R. Fandrick, On the design of complex drug candidate syntheses in the pharmaceutical industry. Nat. Rev. Chem. 1(2), 0016 (2017)
S.K. Burley, H.M. Berman, C. Bhikadiya, C. Bi, L. Chen, L. Di Costanzo, C. Christie, K. Dalenberg, J.M. Duarte, S. Dutta et al., Rcsb protein data bank: biological macromolecular structures enabling research and education in fundamental biology, biomedicine, biotechnology and energy. Nucleic Acids Res. 47(D1), D464–D474 (2018)
M.A. Toropova, A.M. Veselinović, J.B. Veselinović, D.B. Stojanović, A.A. Toropov, Qsar modeling of the antimicrobial activity of peptides as a mathematical function of a sequence of amino acids. Comput. Biol. Chem. 59, 126–130 (2015)
V.H. Masand, V. Rastija, Pydescriptor: a new pymol plugin for calculating thousands of easily understandable molecular descriptors. Chemometr. Intell. Lab. Syst. 169, 12–18 (2017)
P. Prajapat, S. Agarwal, G. Talesara, Significance of computer aided drug design and 3d qsar in modern drug discovery. J. Med. Org. Chem. 1(1), 1 (2017)
A.G. Hussien, A.E. Hassanien, E.H. Houssein, Swarming behaviour of salps algorithm for predicting chemical compound activities, in 2017 Eighth International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Information Systems (ICICIS) (IEEE, 2017) pp. 315–320
L. Rutkowski, M. Korytkowski, R. Scherer, R. Tadeusiewicz, L.A. Zadeh, J.M. Zurada, Artificial Intelligence and Soft Computing: Proceedings of 16th International Conference, ICAISC 2017, vol. 10246, Zakopane, Poland, 11–15 June 2017 (Springer, 2017)
A. Maseleno, N. Sabani, M. Huda, R. Ahmad, K.A. Jasmi, B. Basiron, Demystifying learning analytics in personalised learning. Int. J. Eng. Technol. 7(3), 1124–1129 (2018)
F. Han, C. Yang, Y.-Q. Wu, J.-S. Zhu, Q.-H. Ling, Y.-Q. Song, D.-S. Huang, A gene selection method for microarray data based on binary pso encoding gene-to-class sensitivity information. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 14(1), 85–96 (2017)
R. Rodríguez-Perez, M. Vogt, J. Bajorath, Support vector machine classification and regression prioritize different structural features for binary compound activity and potency value prediction. ACS Omega 2(10), 6371–6379 (2017)
K. Sörensen, M. Sevaux, F. Glover, A history of metaheuristics, in Handbook of heuristics (2018), pp. 1–18
K. Hussain, M.N.M. Salleh, S. Cheng, Y. Shi, Metaheuristic research: a comprehensive survey. Artif. Intell. Rev. 52(4), 2191–2233 (2019)
M. Ghaemi, M.-R. Feizi-Derakhshi, Feature selection using forest optimization algorithm. Pattern Recogn. 60, 121–129 (2016)
M. Ghosh, R. Guha, R. Sarkar, A. Abraham, A wrapper-filter feature selection technique based on ant colony optimization, in Neural Computing and Applications (2019), pp. 1–19
I. Aljarah, A.-Z. AlaM, H. Faris, M.A. Hassonah, S. Mirjalili, H. Saadeh, Simultaneous feature selection and support vector machine optimization using the grasshopper optimization algorithm. Cogn. Comput. 10(3), 478–495 (2018)
R.V. Devi, S.S. Sathya, M.S. Coumar, Evolutionary algorithms for de novo drug design-a survey. Appl. Soft Comput. 27, 543–552 (2015)
B. Jia, A.R. Raphenya, B. Alcock, N. Waglechner, P. Guo, K.K. Tsang, B.A. Lago, B.M. Dave, S. Pereira, A.N. Sharma et al., Card 2017: expansion and model-centric curation of the comprehensive antibiotic resistance database. Nucleic Acids Res. p. gkw1004 (2016)
S.C.W. Peh, J.L. Hong, Bacteria foraging optimization for drug design, in International Conference on Computational Science and Its Applications (Springer, 2016), pp. 322–331
R. Chen, X. Liu, S. Jin, J. Lin, J. Liu, Machine learning for drug-target interaction prediction. Molecules 23(9), 2208 (2018)
P.-A. Grenier, L. Brun, D. Villemin, Chemoinformatics and stereoisomerism: a stereo graph kernel together with three new extensions. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 87, 222–230 (2017)
J.K. Yella, S. Yaddanapudi, Y. Wang, A.G. Jegga, Changing trends in computational drug repositioning. Pharmaceuticals 11(2), 57 (2018)
A.M. Dar, S. Mir, Molecular docking: approaches, types, applications and basic challenges. J. Anal. Bioanal. Tech. 8(2), 356 (2017)
N.S. Pagadala, K. Syed, J. Tuszynski, Software for molecular docking: a review. Biophys. Rev. 9(2), 91–102 (2017)
Y. Ma, H.-L. Li, X.-B. Chen, W.-Y. Jin, H. Zhou, R.-L. Wang, 3d qsar pharmacophore based virtual screening for identification of potential inhibitors for cdc25b. Comput. Biol. Chem. 73, 1–12 (2018)
I.L. Ruiz, M.A. Gomez-Nieto, Advantages of relative versus absolute data for the development of quantitative structure-activity relationship classification models. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 57(11), 2776–2788 (2017)
I. Ponzoni, V. Sebastián-Pérez, C. Requena-Triguero, C. Roca, M.J. Martínez, F. Cravero, M.F. Díaz, J.A. Páez, R.G. Arrayás, J. Adrio et al., Hybridizing feature selection and feature learning approaches in qsar modeling for drug discovery. Sci. Rep. 7(1), 2403 (2017)
M.H. Fatemi, A. Heidari, S. Gharaghani, Qsar prediction of hiv-1 protease inhibitory activities using docking derived molecular descriptors. J. Theor. Biol. 369, 13–22 (2015)
Y.S. Is, S. Durdagi, B. Aksoydan, M. Yurtsever, Proposing novel mao-b hit inhibitors using multidimensional molecular modeling approaches and application of binary qsar models for prediction of their therapeutic activity, pharmacokinetic and toxicity properties. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 9(7), 1768–1782 (2018)
R. Satpathy, Quantitative structure-activity modelling of toxic compounds, in Nanotechnology, Food Security and Water Treatment (Springer, 2018), pp. 313–331
A. Del Rio, G. Varchi, Molecular design of compounds targeting histone methyltransferases, in Epi-Informatics (Elsevier, 2016), pp. 257–272
E. Di Muzio, D. Toti, F. Polticelli, Dockingapp: a user friendly interface for facilitated docking simulations with autodock vina. J. Comput.-Aided Mol. Des. 31(2), 213–218 (2017)
Z. Wang, H. Sun, X. Yao, D. Li, L. Xu, Y. Li, S. Tian, T. Hou, Comprehensive evaluation of ten docking programs on a diverse set of protein-ligand complexes: the prediction accuracy of sampling power and scoring power. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 18(180), 12964–12975 (2016)
M.C. Ng, S. Fong, S.W. Siu, Psovina: The hybrid particle swarm optimization algorithm for protein-ligand docking. J. Bioinform. Comput. Biol. 13(03), 1541007 (2015)
Y. Liu, L. Zhao, W. Li, D. Zhao, M. Song, Y. Yang, Fipsdock: a new molecular docking technique driven by fully informed swarm optimization algorithm. J. Comput. Chem. 34(1), 67–75 (2013)
H. Lin, S. Siu, A hybrid cuckoo search and differential evolution approach to protein-ligand docking. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19(10), 3181 (2018)
B. Jiménez-García, J. Roel-Touris, M. Romero-Durana, M. Vidal, D. Jiménez-González, J. Fernández-Recio, Lightdock: a new multi-scale approach to protein-protein docking. Bioinformatics 34(1), 49–55 (2017)
T.R. Law, J. Hancox, S.A. Wright, S. Jarvis, An algorithm for computing short-range forces in molecular dynamics simulations with non-uniform particle densities. J. Parallel Distrib. Comput. 130, 1–11 (2019)
A. Kumar, G. Srivastava, A.S. Negi, A. Sharma, Docking, molecular dynamics, binding energy-mm-pbsa studies of naphthofuran derivatives to identify potential dual inhibitors against bace-1 and gsk-3\(\beta \). J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 37(2), 275–290 (2019)
D. Prada-Gracia, S. Huerta-Yépez, L.M. Moreno-Vargas, Application of computational methods for anticancer drug discovery, design, and optimization. Boletín Médico Del Hospital Infantil de México (English Edition) 73(6), 411–423 (2016)
C. Anusha, Z. Halidha, T. Radha, M. Balaji, Identification of insilico drugs and drug docking studies on hypothyroidism and inferility disorders in human. Int. J. Novel Trends Pharm. Sci. 5(3), 42–54 (2015)
S. Mirjalili, The ant lion optimizer. Adv. Eng. Softw. 83, 80–98 (2015)
M.A. Elaziz, Y.S. Moemen, A.E. Hassanien, S. Xiong, Quantitative structure-activity relationship model for hcvns5b inhibitors based on an antlion optimizer-adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system. Sci. Rep. 8(1), 1506 (2018)
Y.-C. Lo, S.E. Rensi, W. Torng, R.B. Altman, Machine learning in chemoinformatics and drug discovery. Drug Discov. Today 23(8), 1538–1546 (2018)
A.H.A. El-Atta, A.E. Hassanien, Two-class support vector machine with new kernel function based on paths of features for predicting chemical activity. Inf. Sci. 403, 42–54 (2017)
M.J. Martínez, M. Razuc, I. Ponzoni, Modesus: a machine learning tool for selection of molecular descriptors in qsar studies applied to molecular informatics, in BioMed Research International, vol. 2019 (2019)
A. Ghosh, M. Talukdar, U.K. Roy, Stable drug designing by minimizing drug protein interaction energy using pso (2015). arXiv preprint arXiv:1507.08408
M. Zainudin, M. Sulaiman, N. Mustapha, T. Perumal, A. Nazri, R. Mohamed, S. Manaf, Feature selection optimization using hybrid relief-f with self-adaptive differential evolution. Int. J. Intell. Eng. Syst. 10(3), 21–29 (2017)
E.H. Houssein, M.E. Hosney, D. Oliva, W.M. Mohamed, M. Hassaballah, A novel hybrid harris hawks optimization and support vector machines for drug design and discovery. Computers & Chemical Engineering 133, 106656 (2020)
M.J. Martínez, J.S. Dussaut, I. Ponzoni, Biclustering as strategy for improving feature selection in consensus qsar modeling. Electron. Notes Discrete Math. 69, 117–124 (2018)
R.I.D. Putra, A.L. Maulana, A.G. Saputro, Study on building machine learning model to predict biodegradable-ready materials, in AIP Conference Proceedings, vol. 2088 (AIP Publishing, 2019), pp. 60003–600010
A. Dutta, P. Riba, J. Lladós, A. Fornés, Hierarchical stochastic graphlet embedding for graph-based pattern recognition (2018). arXiv preprint arXiv:1807.02839
G.B. Goh, K. Sakloth, C. Siegel, A. Vishnu, J. Pfaendtner, Multimodal deep neural networks using both engineered and learned representations for biodegradability prediction (2018). arXiv preprint arXiv:1808.04456
G.B. Goh, C. Siegel, A. Vishnu, N. Hodas, Using rule-based labels for weak supervised learning: a chemnet for transferable chemical property prediction, in Proceedings of the 24th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (ACM, 2018), pp. 302–310
J. Atwood, D. Towsley, Diffusion-convolutional neural networks, in Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (2016), pp. 1993–2001
A. Bender, N. Brown, Cheminformatics in drug discovery. ChemMedChem 13(6), 467–469 (2018)
S. Zheng, S. Dharssi, M. Wu, J. Li, Z. Lu, Text mining for drug discovery, in Bioinformatics and Drug Discovery (Springer, 2019), pp. 231–252
S.A. Cashman, D.E. Meyer, A.N. Edelen, W.W. Ingwersen, J.P. Abraham, W.M. Barrett, M.A. Gonzalez, P.M. Randall, G. Ruiz-Mercado, R.L. Smith, Mining available data from the united states environmental protection agency to support rapid life cycle inventory modeling of chemical manufacturing. Environ. Sci. Technol. 50(17), 9013–9025 (2016)
S.K. Burley, H.M. Berman, G.J. Kleywegt, J.L. Markley, H. Nakamura, S. Velankar, Protein data bank (pdb): the single global macromolecular structure archive, in Protein Crystallography (Springer, 2017), pp. 627–641
C.N. Hemalatha, V. Muthukumar, Application of 3d qsar and docking studies in optimization of perylene diimides as anti-cancer agent. Indian J. Pharm. Educ. Res. 52, 666–75 (2018)
S. Xu, J. Fang, and X.-Y. Li, “Weighted laplacian and its theoretical applications,” arXiv preprint arXiv:1911.10311, 2019
N.M. O’Boyle, M. Banck, C.A. James, C. Morley, T. Vandermeersch, G.R. Hutchison, Open babel: An open chemical toolbox. J. Cheminf. 3(1), 33 (2011)
A. Mauri, V. Consonni, M. Pavan, R. Todeschini, Dragon software: an easy approach to molecular descriptor calculations. MATCH Commun. Math. Comput. Chem. 56, 237–248 (2006)
H. Moriwaki, Y.-S. Tian, N. Kawashita, T. Takagi, Mordred: a molecular descriptor calculator. J. Cheminf. 10(1), 4 (2018)
O. Korb, T. Stützle, T.E. Exner, An ant colony optimization approach to flexible protein-ligand docking. Swarm Intell. 1(2), 115–134 (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Houssein, E.H., Hosney, M.E., Oliva, D., Ortega-Sánchez, N., Mohamed, W.M., Hassaballah, M. (2021). Drug Design and Discovery: Theory, Applications, Open Issues and Challenges. In: Oliva, D., Houssein, E.H., Hinojosa, S. (eds) Metaheuristics in Machine Learning: Theory and Applications. Studies in Computational Intelligence, vol 967. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-70542-8_15
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-70542-8_15
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-70541-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-70542-8
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)