Abstract
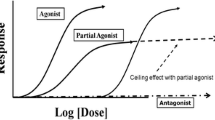
Buprenorphine is an opioid analgesic and a medication used for opioid agonist treatment. Being a partial mu-opioid receptor agonist, it has a greater margin of safety compared to full agonists. Despite the relative safety of buprenorphine, the concomitant use of central nervous system depressant drugs is associated with an increased risk of respiratory depression, intoxication, and death. Injection of buprenorphine and polydrug use are major mortality risk factors. Clonazepam, alprazolam, diazepam, pregabalin, and alcohol are particularly often associated with fatal poisonings. An established user does not favor buprenorphine because of its euphoric effect, but the drug is rather used to manage opioid withdrawal symptoms, while concomitant sedative-hypnotic or illicit drugs may be taken to obtain or augment the opioid high. Perceived underdosing of buprenorphine in opioid agonist treatment is one reason for polydrug use. Prevention measures include encouraging safer consumption habits such as avoiding injection, as well as efforts to reduce concomitant use of alcohol, sedative-hypnotic drugs, and illicit drugs among buprenorphine users.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- alpha-PVP:
-
alpha-pyrrolidinopentiophenone
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- GHB:
-
gamma-hydroxybutyric acid
- MDMA:
-
3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine, ecstasy
- OAT:
-
Opioid agonist treatment
- SSRI:
-
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor
- THC:
-
Tetrahydrocannabinol
References
Alhaddad H, Cisternino S, Decleves X et al (2012) Respiratory toxicity of buprenorphine results from the blockage of P-glycoprotein-mediated efflux of norbuprenorphine at the blood-brain barrier in mice. Crit Care Med 40:3215–3223
Alhaddad H, Cisternino S, Saubamea B et al (2013) Gender and strain contributions to the variability of buprenorphine-related respiratory toxicity in mice. Toxicology 305:99–108
Alho H, Sinclair D, Vuori E, Holopainen A (2007) Abuse liability of buprenorphine-naloxone tablets in untreated IV drug users. Drug Alcohol Depend 88(1):75–78
Auriacombe M, Fatseas M, Dubernet J et al (2004) French field experience with buprenorphine. Am J Addict 13(Suppl 1):S17–S28
Bardy G, Cathala P, Eiden C et al (2015) An unusual case of death probably triggered by the association of buprenorphine at therapeutic dose with ethanol and benzodiazepines and with very low norbuprenorphine level. J Forensic Sci 60(Suppl 1):S269–S271
Bickel WK, Stitzer ML, Bigelow GE et al (1988) Buprenorphine: dose-related blockade of opioid challenge effects in opioid dependent humans. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 247:47–53
Bishop-Freeman SC, Friederich LW, Feaster MS, Hudson JS (2021) Buprenorphine-related deaths in North Carolina from 2010–2018. J Anal Toxicol. https://doi.org/10.1093/jat/bkab073
Blom Y, Bondesson U, Anggard E (1985) Analysis of buprenorphine and its N-dealkylated metabolite in plasma and urine by selected-ion monitoring. J Chromatogr 338:89–98
Boas RA, Villiger JW (1985) Clinical actions of fentanyl and buprenorphine. The significance of receptor binding. Br J Anaesth 57:192–196
Brewster D, Humphrey MJ, McLeavy MA (1981) Biliary excretion, metabolism and enterohepatic circulation of buprenorphine. Xenobiotica 11:189–196
Brunt TM, Lefrançois E, Gunnar T et al (2021) Substances detected in used syringes of injecting drug users across 7 cities in Europe in 2017 and 2018: the European Syringe Collection and Analysis Project Enterprise (ESCAPE). Int J Drug Policy 95:103130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugpo.2021.103130. Online ahead of print
Chang Y, Moody DE, McCance-Katz EF (2006) Novel metabolites of buprenorphine detected in human liver microsomes and human urine. Drug Metab Dispos 34:440–448
Chilcoat HD, Amick HR, Sherwood MR, Dunn KE (2019) Buprenorphine in the United States: motives for abuse, misuse, and diversion. J Subst Abus Treat 104:148–157
Cicero TJ, Ellis MS, Surratt HL, Kurtz SP (2014) Factors contributing to the rise of buprenorphine misuse: 2008–2013. Drug Alcohol Depend 142:98–104
Coe MA, Lofwall MR, Walsh SL (2019) Buprenorphine pharmacology review: update on transmucosal and long-acting formulations. J Addict Med 13:93–103
Cone EJ, Gorodetzky CW, Yousefnejad D et al (1984) The metabolism and excretion of buprenorphine in humans. Drug Metab Dispos 12:577–581
Cowan A (2007) Buprenorphine: the basic pharmacology revisited. J Addict Med 1:68–72
Cowan A, Lewis JW, Macfarlane IR (1977) Agonist and antagonist properties of buprenorphine, a new antinociceptive agent. Br J Pharmacol 60:537–545
Darke S, Duflou J, Larance B et al (2021) Characteristics and circumstances of death related to buprenorphine toxicity in Australia. Drug Alcohol Depend. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2020.108360
Elkader A, Sproule B (2005) Buprenorphine: clinical pharmacokinetics in the treatment of opioid dependence. Clin Pharmacokinet 44:661–680
Gaulier JM, Marquet P, Lacassie E et al (2000) Fatal intoxication following self-administration of a massive dose of buprenorphine. J Forensic Sci 45:226–228
Greenwald M, Johanson CE, Bueller J et al (2007) Buprenorphine duration of action: mu-opioid receptor availability and pharmacokinetic and behavioral indices. Biol Psychiatry 61:101–110
Häkkinen M, Launiainen T, Vuori E, Ojanperä I (2012) Benzodiazepines and alcohol are associated with cases of fatal buprenorphine poisoning. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 68:301–309
Harris DS, Jones RT, Welm S et al (2000) Buprenorphine and naloxone co-administration in opiate-dependent patients stabilized on sublingual buprenorphine. Drug Alcohol Depend 61:85–94
Haukka J, Kriikku P, Mariottini C et al (2018) Non-medical use of psychoactive prescription drugs is associated with fatal poisoning. Addiction 113(3):464–472
Heikman PK, Muhonen LH, Ojanperä IA (2017) Polydrug abuse among opioid maintenance treatment patients is related to inadequate dose of maintenance treatment medicine. BMC Psychiatry 17(1):245
Høiseth G, Middelkoop G, Mørland J, Gjerde H (2015) Has previous abuse of flunitrazepam been replaced by clonazepam? Eur Addict Res 21(4):217–221
Huang P, Kehner GB, Cowan A, Liu-Chen LY (2001) Comparison of pharmacological activities of buprenorphine and norbuprenorphine: norbuprenorphine is a potent opioid agonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 297:688–695
Jasinski DR, Pevnick JS, Griffith JD (1978) Human pharmacology and abuse potential of the analgesic buprenorphine: a potential agent for treating narcotic addiction. Arch Gen Psychiatry 35:501–516
Jin H, Marshall BDL, Degenhardt L et al (2020) Global opioid agonist treatment: a review of clinical practices by country. Addiction 115(12):2243–2254
Johnson RE, Fudala PJ, Payne R (2005) Buprenorphine: considerations for pain management. J Pain Symptom Manag 29:297–326
Jones JD, Mogali S, Comer SD (2012) Polydrug abuse: a review of opioid and benzodiazepine combination use. Drug Alcohol Depend 125(1–2):8–18
Kintz P (2001) Deaths involving buprenorphine: a compendium of French cases. Forensic Sci Int 121:65–69
Kintz P (2002) A new series of 13 buprenorphine-related deaths. Clin Biochem 35(7):513–516
Kosten TR, George TP (2002) The neurobiology of opioid dependence: implications for treatment. Sci Pract Perspect 1:13–20
Kress HG (2009) Clinical update on the pharmacology, efficacy and safety of transdermal buprenorphine. Eur J Pain 13:219–230
Kriikku P, Häkkinen M, Ojanperä I (2018) High buprenorphine-related mortality is persistent in Finland. Forensic Sci Int 291:76–82
Kuhlman JJ, Lalani S, Magluilo J et al (1996) Human pharmacokinetics of intravenous, sublingual, and buccal buprenorphine. J Anal Toxicol 20:369–378
Larance B, Lintzeris N, Ali R et al (2014) The diversion and injection of a buprenorphine-naloxone soluble film formulation. Drug Alcohol Depend 136:21–27
Lofwall MR, Walsh SL (2014) A review of buprenorphine diversion and misuse: the current evidence base and experiences from around the world. J Addict Med 8(5):315–326
MacDonald K, Lamb K, Thomas ML, Khentigan W (2016) Buprenorphine maintenance treatment of opiate dependence: correlations between prescriber beliefs and practices. Subst Use Misuse 51:85–90
Macleod J, Steer C, Tilling K et al (2019) Prescription of benzodiazepines, z-drugs, and gabapentinoids and mortality risk in people receiving opioid agonist treatment: observational study based on the UK Clinical Practice Research Datalink and Office for National Statistics death records. PLoS Med. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1002965
Mahoney JJ, Winstanley EL, Lander LR et al (2021) High prevalence of co-occurring substance use in individuals with opioid use disorder. Addict Behav. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addbeh.2020.106752
Mariottini C, Kriikku P, Ojanperä I (2021) Concomitant drugs with buprenorphine user deaths. Drug Alcohol Depend. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2020.108345
Mattick RP, Breen C, Kimber J, Davoli M (2014) Buprenorphine maintenance versus placebo or methadone maintenance for opioid dependence. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD002207.pub4
Mégarbane B, Marie N, Pirnay S et al (2006) Buprenorphine is protective against the depressive effects of norbuprenorphine on ventilation. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 212:256–267
Mégarbane B, Chevillard L, Vodovar D (2020) Naloxone should remain the appropriate antidote to treat opioid overdose. Crit Care 24(1):173
Mendelson J, Upton RA, Everhart ET et al (1997) Bioavailability of sublingual buprenorphine. J Clin Pharmacol 37:31–37
Nath RP, Upton RA, Everhart ET et al (1999) Buprenorphine pharmacokinetics: relative bioavailability of sublingual tablet and liquid formulations. J Clin Pharmacol 39:619–623
Obadia Y, Perrin V, Feroni I et al (2001) Injecting misuse of buprenorphine among French drug users. Addiction 96:267–272
Ohtani M, Kotaki H, Uchino K et al (1994) Pharmacokinetic analysis of enterohepatic circulation of buprenorphine and its active metabolite, norbuprenorphine, in rats. Drug Metab Dispos 22:2–7
Ohtani M, Kotaki H, Sawada Y, Iga T (1995) Comparative analysis of buprenorphine- and norbuprenorphine-induced analgesic effects based on pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic modeling. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 272:505–510
Park TW, Larochelle MR, Saitz R et al (2020) Associations between prescribed benzodiazepines, overdose death and buprenorphine discontinuation among people receiving buprenorphine. Addiction 115(5):924–932
Reynaud M, Petit G, Potard D, Courty P (1998) Six deaths linked to concomitant use of buprenorphine and benzodiazepines. Addiction 93:1385–1392
Santo T Jr, Clark B, Hickman M et al (2021) Association of opioid agonist treatment with all-cause mortality and specific causes of death among people with opioid dependence: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Psychiat 78(9):979–993
Seldén T, Ahlner J, Druid H, Krostrand R (2012) Toxicological and pathological findings in a series of buprenorphine related deaths. Possible risk factors for fatal outcome. Forensic Sci Int 220(1–3):284–290
Shulman M, Wai JM, Nunes EV (2019) Buprenorphine treatment for opioid use disorder: an overview. CNS Drugs 33:567–580
Simonsen KW, Kriikku P, Thelander G et al (2020) Fatal poisoning in drug addicts in the Nordic countries in 2017. Forensic Sci Int 313:110343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.forsciint.2020.110343. Epub 2020 May 20
Stein MD, Kanabar M, Anderson BJ et al (2016) Reasons for benzodiazepine use among persons seeking opioid detoxification. J Subst Abus Treat 68:57–61
Stinchcomb AL, Paliwal A, Dua R et al (1996) Permeation of buprenorphine and its 3-alkyl-ester prodrugs through human skin. Pharm Res 13:1519–1523
Strain EC, Walsh SL, Bigelow GE (2002) Blockade of hydromorphone effects by buprenorphine/naloxone and buprenorphine. Psychopharmacology 159:161–166
Sun EC, Dixit A, Humphreys K et al (2017) Association between concurrent use of prescription opioids and benzodiazepines and overdose: retrospective analysis. BMJ 356:j760
Tournier N, Chevillard L, Mégarbane B et al (2010) Interaction of drugs of abuse and maintenance treatments with human P-glycoprotein (ABCB1) and breast cancer resistance protein (ABCG2). Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 13:905–915
Tracqui A, Kintz P, Ludes B (1998) Buprenorphine-related deaths among drug addicts in France: a report on 20 fatalities. J Anal Toxicol 22:430–434
Vodovar D, Tournier N, Mégarbane B (2021) Ventilatory depression following oral buprenorphine exposure: insight into the involved mechanisms. Clin Toxicol (Phila) 59(7):677–679
Walsh SL, Preston KL, Stitzer ML et al (1994) Clinical pharmacology of buprenorphine: ceiling effects at high doses. Clin Pharmacol Ther 55(5):569–580
Walsh SL, Nuzzo PA, Babalonis S et al (2016) Intranasal buprenorphine alone and in combination with naloxone: abuse liability and reinforcing efficacy in physically dependent opioid abusers. Drug Alcohol Depend 162:190–198
Welsh C, Valadez-Meltzer A (2005) Buprenorphine: a (relatively) new treatment for opioid dependence. Psychiatry (Edgmont) 2:29–39
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this entry
Cite this entry
Ojanperä, I., Mariottini, C., Kriikku, P. (2022). Buprenorphine, Polydrug Use and Deaths. In: Patel, V.B., Preedy, V.R. (eds) Handbook of Substance Misuse and Addictions. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-67928-6_156-1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-67928-6_156-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-67928-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-67928-6
eBook Packages: Springer Reference MedicineReference Module Medicine