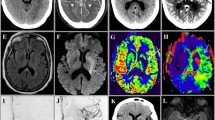
Abstract
Imaging is essential for accurate diagnosis and timely treatment of acute ischemic stroke (AIS), which is caused by an occlusion of an intracranial artery. There are typical findings on imaging that lead toward correct and timely diagnosis. The two major treatment options for AIS patients are endovascular treatment and intravenous thrombolysis, both of which are highly time-dependent. Thus, the overarching goal of acute stroke imaging is to allow for accurate and fast diagnosis, which, in turn, results in faster treatment and ultimately in better patient outcomes. This chapter will outline the typical imaging findings of AIS and point out some of the pitfalls in acute stroke imaging, with special emphasis on the imaging findings that are of relevance for treatment decision-making and patient management.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Writing Group M, Mozaffarian D, Benjamin EJ, Go AS, Arnett DK, Blaha MJ, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2016 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2016;133(4):e38–360.
Adams HP Jr, Bendixen BH, Kappelle LJ, Biller J, Love BB, Gordon DL, et al. Classification of subtype of acute ischemic stroke. Definitions for use in a multicenter clinical trial. TOAST. Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment. Stroke. 1993;24(1):35–41.
Kamel H, Navi BB, Merkler AE, Baradaran H, Diaz I, Parikh NS, et al. Reclassification of ischemic stroke etiological subtypes on the basis of high-risk nonstenosing carotid plaque. Stroke. 2019:STROKEAHA119027970.
Ospel JM, Singh N, Marko M, Almekhlafi M, Dowlatshahi D, Puig J, et al. Prevalence of ipsilateral nonstenotic carotid plaques on computed tomography angiography in embolic stroke of undetermined source. Stroke. 2020:STROKEAHA120029404.
Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T, Adeoye OM, Bambakidis NC, Becker K, et al. 2018 guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2018;49(3):e46–e110.
Goyal M, Menon BK, van Zwam WH, Dippel DW, Mitchell PJ, Demchuk AM, et al. Endovascular thrombectomy after large-vessel ischaemic stroke: a meta-analysis of individual patient data from five randomised trials. Lancet. 2016;387(10029):1723–31.
Saver JL. Time is brain--quantified. Stroke. 2006;37(1):263–6.
Olive-Gadea M, Martins N, Boned S, Carvajal J, Moreno MJ, Muchada M, et al. Baseline ASPECTS and e-ASPECTS correlation with infarct volume and functional outcome in patients undergoing mechanical thrombectomy. J Neuroimaging. 2019;29(2):198–202.
Bal S, Bhatia R, Menon BK, Shobha N, Puetz V, Dzialowski I, et al. Time dependence of reliability of noncontrast computed tomography in comparison to computed tomography angiography source image in acute ischemic stroke. Int J Stroke. 2015;10(1):55–60.
Hagmann P, Jonasson L, Maeder P, Thiran JP, Wedeen VJ, Meuli R. Understanding diffusion MR imaging techniques: from scalar diffusion-weighted imaging to diffusion tensor imaging and beyond. Radiographics. 2006;26 Suppl 1:S205–23.
Tortora F, Cirillo M, Ferrara M, Manto A, Briganti F, Cirillo S. DWI reversibility after intra-arterial thrombolysis. A case report and literature review. Neuroradiol J. 2010;23(6):752–62.
Edlow BL, Hurwitz S, Edlow JA. Diagnosis of DWI-negative acute ischemic stroke: a meta-analysis. Neurology. 2017;89(3):256–62.
Albers GW, Marks MP, Kemp S, Christensen S, Tsai JP, Ortega-Gutierrez S, et al. Thrombectomy for stroke at 6 to 16 hours with selection by perfusion imaging. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(8):708–18.
Campbell BC, Mitchell PJ, Kleinig TJ, Dewey HM, Churilov L, Yassi N, et al. Endovascular therapy for ischemic stroke with perfusion-imaging selection. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(11):1009–18.
Goyal M, Demchuk AM, Menon BK, Eesa M, Rempel JL, Thornton J, et al. Randomized assessment of rapid endovascular treatment of ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(11):1019–30.
Saver JL, Goyal M, Bonafe A, Diener HC, Levy EI, Pereira VM, et al. Solitaire with the intention for thrombectomy as primary endovascular treatment for acute ischemic stroke (SWIFT PRIME) trial: protocol for a randomized, controlled, multicenter study comparing the Solitaire revascularization device with IV tPA with IV tPA alone in acute ischemic stroke. Int J Stroke. 2015;10(3):439–48.
Berkhemer OA, Fransen PS, Beumer D, van den Berg LA, Lingsma HF, Yoo AJ, et al. A randomized trial of intraarterial treatment for acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(1):11–20.
Jovin TG, Chamorro A, Cobo E, de Miquel MA, Molina CA, Rovira A, et al. Thrombectomy within 8 hours after symptom onset in ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(24):2296–306.
Amukotuwa SA, Straka M, Dehkharghani S, Bammer R. Fast automatic detection of large vessel occlusions on CT angiography. Stroke. 2019;50(12):3431–8.
Bash S, Villablanca JP, Jahan R, Duckwiler G, Tillis M, Kidwell C, et al. Intracranial vascular stenosis and occlusive disease: evaluation with CT angiography, MR angiography, and digital subtraction angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005;26(5):1012–21.
Hirai T, Korogi Y, Ono K, Nagano M, Maruoka K, Uemura S, et al. Prospective evaluation of suspected stenoocclusive disease of the intracranial artery: combined MR angiography and CT angiography compared with digital subtraction angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2002;23(1):93–101.
Demchuk AM, Menon BK, Goyal M. Comparing vessel imaging: noncontrast computed tomography/computed tomographic angiography should be the new minimum standard in acute disabling stroke. Stroke. 2016;47(1):273–81.
Jain AR, Jain M, Kanthala AR, Damania D, Stead LG, Wang HZ, et al. Association of CT perfusion parameters with hemorrhagic transformation in acute ischemic stroke. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2013;34(10):1895–900.
Roman LS, Menon BK, Blasco J, Hernandez-Perez M, Davalos A, Majoie C, et al. Imaging features and safety and efficacy of endovascular stroke treatment: a meta-analysis of individual patient-level data. Lancet Neurol. 2018;17(10):895–904.
Menon BK, d'Esterre CD, Qazi EM, Almekhlafi M, Hahn L, Demchuk AM, et al. Multiphase CT angiography: a new tool for the imaging triage of patients with acute ischemic stroke. Radiology. 2015;275(2):510–20.
Allmendinger AM, Tang ER, Lui YW, Spektor V. Imaging of stroke: part 1, perfusion CT--overview of imaging technique, interpretation pearls, and common pitfalls. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2012;198(1):52–62.
Lui YW, Tang ER, Allmendinger AM, Spektor V. Evaluation of CT perfusion in the setting of cerebral ischemia: patterns and pitfalls. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2010;31(9):1552–63.
Yu Y, Han Q, Ding X, Chen Q, Ye K, Zhang S, et al. Defining core and penumbra in ischemic stroke: a voxel- and volume-based analysis of whole brain CT perfusion. Sci Rep. 2016;6:20932.
McTaggart RA, Ansari SA, Goyal M, Abruzzo TA, Albani B, Arthur AJ, et al. Initial hospital management of patients with emergent large vessel occlusion (ELVO): report of the standards and guidelines committee of the Society of NeuroInterventional Surgery. J Neurointerv Surg. 2017;9(3):316–23.
Sheth KN, Terry JB, Nogueira RG, Horev A, Nguyen TN, Fong AK, et al. Advanced modality imaging evaluation in acute ischemic stroke may lead to delayed endovascular reperfusion therapy without improvement in clinical outcomes. J Neurointerv Surg. 2013;5 Suppl 1:i62–5.
Schaefer PW, Souza L, Kamalian S, Hirsch JA, Yoo AJ, Kamalian S, et al. Limited reliability of computed tomographic perfusion acute infarct volume measurements compared with diffusion-weighted imaging in anterior circulation stroke. Stroke. 2015;46(2):419–24.
Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T, Adeoye OM, Bambakidis NC, Becker K, et al. Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: 2019 update to the 2018 guidelines for the early management of acute ischemic stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2019;50(12):e344–418.
Thomalla G, Simonsen CZ, Boutitie F, Andersen G, Berthezene Y, Cheng B, et al. MRI-guided thrombolysis for stroke with unknown time of onset. N Engl J Med. 2018;379(7):611–22.
Nogueira RG, Jadhav AP, Haussen DC, Bonafe A, Budzik RF, Bhuva P, et al. Thrombectomy 6 to 24 hours after stroke with a mismatch between deficit and infarct. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(1):11–21.
National Institute of Neurological D, Stroke rt PASSG. Tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. 1995;333(24):1581–7.
Hacke W, Kaste M, Fieschi C, von Kummer R, Davalos A, Meier D, et al. Randomised double-blind placebo-controlled trial of thrombolytic therapy with intravenous alteplase in acute ischaemic stroke (ECASS II). Second European-Australasian Acute Stroke Study Investigators. Lancet. 1998;352(9136):1245–51.
Hacke W, Kaste M, Bluhmki E, Brozman M, Davalos A, Guidetti D, et al. Thrombolysis with alteplase 3 to 4.5 hours after acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. 2008;359(13):1317–29.
group ISTc, Sandercock P, Wardlaw JM, Lindley RI, Dennis M, Cohen G, et al. The benefits and harms of intravenous thrombolysis with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator within 6 h of acute ischaemic stroke (the third international stroke trial [IST-3]): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2012;379(9834):2352–63.
Lees KR, Emberson J, Blackwell L, Bluhmki E, Davis SM, Donnan GA, et al. Effects of alteplase for acute stroke on the distribution of functional outcomes: a pooled analysis of 9 trials. Stroke. 2016;47(9):2373–9.
Campbell BCV, Mitchell PJ, Churilov L, Yassi N, Kleinig TJ, Dowling RJ, et al. Tenecteplase versus alteplase before thrombectomy for ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(17):1573–82.
Hill MD, Goyal M, Menon BK, Nogueira RG, McTaggart RA, Demchuk AM, et al. Efficacy and safety of nerinetide for the treatment of acute ischaemic stroke (ESCAPE-NA1): a multicentre, double-blind, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2020;395(10227):878–87.
Saver JL, Goyal M, Bonafe A, Diener HC, Levy EI, Pereira VM, et al. Stent-retriever thrombectomy after intravenous t-PA vs. t-PA alone in stroke. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(24):2285–95.
Yang P, Zhang Y, Zhang L, Zhang Y, Treurniet KM, Chen W, et al. Endovascular thrombectomy with or without intravenous alteplase in acute stroke. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(21):1981–93.
Zhang J, Yang Y, Sun H, Xing Y. Hemorrhagic transformation after cerebral infarction: current concepts and challenges. Ann Transl Med. 2014;2(8):81.
Larrue V, von Kummer RR, Muller A, Bluhmki E. Risk factors for severe hemorrhagic transformation in ischemic stroke patients treated with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator: a secondary analysis of the European-Australasian Acute Stroke Study (ECASS II). Stroke. 2001;32(2):438–41.
Saposnik G, Barinagarrementeria F, Brown RD Jr, Bushnell CD, Cucchiara B, Cushman M, et al. Diagnosis and management of cerebral venous thrombosis: a statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2011;42(4):1158–92.
Rodallec MH, Krainik A, Feydy A, Helias A, Colombani JM, Julles MC, et al. Cerebral venous thrombosis and multidetector CT angiography: tips and tricks. Radiographics. 2006;26 Suppl 1:S5–18; discussion S42-3.
Kuang H, Najm M, Chakraborty D, Maraj N, Sohn SI, Goyal M, et al. Automated ASPECTS on noncontrast CT scans in patients with acute ischemic stroke using machine learning. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2019;40(1):33–8.
Byrne D, Walsh JP, Sugrue G, Stanley E, Marnane M, Walsh CD, et al. Subtraction multiphase CT angiography: a new technique for faster detection of intracranial arterial occlusions. Eur Radiol. 2018;28(4):1731–8.
Moussady A SA, Al-Sultan A, Maraj N, Najm M, Demchuk A, Goyal M, Menon B. Predicting regional tissue fate in ischemic stroke using color coded mCTA-based collaterals assessment international stroke conference; Hawaii 2019.
Forest-Devices. Forest Devices: Alpha Stroke 2020. Available from: https://www.forestdevices.com.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Section Editor information
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this entry
Cite this entry
Ospel, J.M., Cimflova, P., Goyal, M. (2021). Stroke Imaging. In: Patlas, M.N., Katz, D.S., Scaglione, M. (eds) Atlas of Emergency Imaging from Head-to-Toe. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-44092-3_8-1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-44092-3_8-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-44092-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-44092-3
eBook Packages: Springer Reference MedicineReference Module Medicine