Abstract
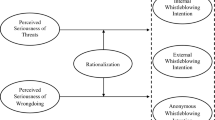
Apaza and Chang develop an analysis framework for effective whistleblowing that contains five crucial factors: (1) the type of whistleblowing (Internal and External Whistleblowing), (2) the role of the mass media (use of mass media to disclose corruption), (3) the documentation of evidence (collection of supporting documentation before blowing the whistle), (4) the form of retaliation (inappropriate work assignments or transfer, threats of physical harm, harassment, humiliation, or isolation, etc.), and (5) legal protections (whistleblowing protection laws issued and implemented).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amoedo, D. (2017). Elementos Esenciales para un Sistema de Protección de Denunciantes. R.I.T.I. 4 (Mayo-Agosto 2017).
Apaza, C. (2008, June). Whistleblowing and the federal employee: Effective legal protection, open communication and organizational attitude. PA Times, ASPA. Special Section, p. 6.
Apaza, C. (2017). Whistleblowing in Peru. In Chapter in whistleblowing in the world. Cham: Palgrave Macmillan.
Apaza, C., & Chang, Y. (2011). What makes whistleblowing effective: Whistleblowing in Peru and South Korea. Public Integrity, 13(2), 113–130.
Apaza, C., & Chang, Y. (2017). Whistleblowing in the world. Cham: Palgrave Macmillan.
Banisar, D. (2006, March 23–25). Whistleblowing international standards and developments. Paper presented at the Primera Conferencia International Sobre Corruption y Transparencia, Ciudad de Mexico.
Benson, J. A., & Ross, D. L. (1998). Sundstrand: A case study in transformation of cultural ethics. Journal of Business Ethics, 17(14), 1517–1527.
Callahan, E. S., & Dworkin, T. M. (1994). Who blows the whistle to the media, and why organizational characteristics of media whistleblowers. American Business Law Journal, 32(2), 151–184.
Cassematis, P., & Wortley, R. (2013). Prediction of whistleblowing or non-reporting observation: The role of personal and situational factors. Econpapers, 117(3), 615–634.
Chang, Y., Wilding, M., & Shin, M. C. (2017). Determinants of whistleblowing intention: Evidence from the South Korean government. Public Performance & Management Review, 40(4), 676–700.
Cho, Y. J., & Song, H. J. (2015). Determinants of whistleblowing within government agencies. Public Personnel Management, 44(4), 450–472.
Culiberg, B., & Mihelic, K. (2017). The evolution of whistleblowing studies: A critical review and research agenda. Journal of Business Ethics, 146(4), 787–803.
Davis, A. J., & Konishi, E. (2007). Whistleblowing in Japan. Nursing Ethics, 14(2), 194–202.
Devine, T. (2017). Whistleblowing in the United States of America:“irrefragable proof” and the next generation of US government whistleblower rights. In Whistleblowing in the world (pp. 59–76). Cham: Palgrave Macmillan.
Devraj, R. (2003). Murder revives Indian whistleblowers’ bill. Asia Times Online, from http://www.atimes.com/atimes/South_Asia/EL12Df02.html.
Dworkin, T. M., & Baucus, M. S. (1998). Internal vs. external whistleblowers: A comparison of whistleblowing processes. Journal of Business Ethics, 17(12), 1281–1298.
Dworkin, T. M., & Brown, A. J. (2013). The money or the media? Lessons from contrasting developments in US and Australian whistleblowing Laws. Seattle Journal for Social Justice, 11(2), 653–713.
Ellison, F., Keenan, J., Lockhart, P., & Schaick, J. V. (1985). Whistleblowing research: Methodological and moral issues. New York: Praeger Publishers.
Figg, J. (2000). Whistleblowing. Internal Auditor, 57(2), 30–37.
George, A. L., Bennett, A., Lynn-Jones, S. M., & Miller, S. E. (2005). Case studies and theory development in the social sciences. Cambridge: MIT Press.
Guerrero, C. (2018). Retos en México en Materia de Protección de Denunciantes con relación a Estándares Internacionales. R.I.T.I. 8 (Septiembre-Diciembre 2018).
Hwang, D. B., Chen, Y., Staley, A. B., Tsai, Y., & Chu, C. L. (2013). A comparative study of the propensity of whistle-blowing: Empirical evidence from China, Taiwan, and the United States. International Journal of Accounting and Financial Reporting, 3(2), 202.
Jakes, S. (2003). Jiang Yanyong. Time. Available at http://www.time.com/time/asia/2003/poypm2003/jiang_yanyong.html. Last visited on 27 Sep 2009.
Jensen, J. L., & Rodgers, R. (2001). Cumulating the intellectual gold of case study research. Public Administration Review, 61(2), 235–246.
Johnson, R. A. (Ed.). (2004). The struggle against corruption. New York: Palgrave Macmillan.
Jos, P. H. (1991). The nature and limits of the Whistleblower's contribution to administrative responsibility. American Review of Public Administration, 21(2), 105–118.
Jos, P. H., Tompkins, M. E., & Hays, S. W. (1989). In praise of difficult people: A portrait of the committed whistleblower. Public Administration Review, 49(6), 552–561.
Kaplan, E. (2001). The international emergence of legal protections for whistleblowers (pp. 37–42). Fall/Winter: The Journal of Public Inquiry.
Kenny, K., Fotaki, M. & Scriver, S. (2019). Mental Heath as a Weapon: Whistleblower Retaliation and Normative. Journal of Business Ethics, 160(12). Published online: 17 April 2018.
Latan, H., Ringle, C. M., & Jabbour, C. J. C. (2018). Whistleblowing intentions among public accountants in Indonesia: Testing for the moderation effects. Journal of Business Ethics, 152(2), 573–588.
Liyanarachchi, G., & Newdick, C. (2009). The impact of moral reasoning and retaliation on whistle-blowing: New Zealand evidence. Journal of Business Ethics, 89(1), 37–57.
Mesmer-Magnus, J. R., & Viswesvaran, C. (2005). Whistleblowing in organizations: An examination of correlates of whistleblowing intentions, actions, and retaliation. Journal of Business Ethics, 62(3), 277–297.
National Whistleblower Center. (2019). Proposed national whistleblower protection act. Retrieved from https://www.whistleblowers.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/10/model.law_.pdf
Near, J. P., & Miceli, M. P. (1985). Organizational dissidence: The case of whistleblowing. Journal of Business Ethics, 4, 1–16.
Near, J. P., & Miceli, M. P. (1995). Effective whistle-blowing. The Academy of Management Review, 20(3), 679–708.
Nielsen, R. P. (2018). Reformed national security internal whistleblowing systems and external whistleblowing as countervailing ethics methods. Administration and Society. https://doi.org/10.1177/0095399718760583.
OCDE. (2011). G20 anti-corruption action plan. Protection of whistleblowers. Study on whistleblower protection frameworks, compendium of best practices and guiding principles for legislation. Retrieved from https://www.oecd.org/g20/topics/anti-corruption/48972967.pdf
Park, H., Bjørkelo, B., & Blenkinsopp, J. (2018). External whistleblowers’ experiences of workplace bullying by superiors and colleagues. Journal of Business Ethics, 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-018-3936-9.
Perez, J. (2018). Whistleblowing, Eunomia. 14(Abril 2018 – Septiembre 2018).
Pillay, S., Ramphul, N., Dorasamy, N., & Meyer, D. (2018). Predictors of whistle-blowing intentions: An analysis of multi-level variables. Administration and Society, 50(2), 186–216.
Rehg, M. T., Miceli, M. P., Near, J. P., & Van Scotter, J. R. (2008). Antecedents and outcomes of retaliation against whistleblowers: Gender differences and power relationships. Organization Science, 19(2), 221–240.
Rosen, B. (1998). Holding government bureaucracies accountable (3rd ed.). Westport: Praeger Publishers.
Rosenbloom, D. H. (1994). The use of case studies in public administrative education in the USA. Journal of Management History, 1(1), 33–46.
Rosenbloom, D. H. (2003). Administrative law for public managers. Boulder: Westview Press.
Rosenbloom, D. H. (2015). Administrative law for public managers (2nd ed.). Boulder: Westview Press.
Rothschild, J. (2008). Freedom of speech denied, dignity assaulted: What the whistleblowers experience in the US. Current Sociology, 56(6), 884–903.
Rothschild, J., & Miethe, T. D. (1999). Whistle-blower disclosures and management retaliation. Work and Occupations, 26(1), 107–128.
Salas A. (2017, May 8). Are Latin America’s new whistleblowing Laws working? Latin America Advisor.
Skivenes, M., & Trygstad, S. (2017). Explaining whistle blowing processes in the Norwegian labour market: Between individual power resources and institutional arrangements. Economic and Industrial Democracy, 38(1), 119–143.
Vandekerckhove, W. (2010). European whistleblowing policies: Tiers or tears? In D. Lewis (Ed.), A global approach to public interest disclosure: What can we learn from existing whistleblowing legislation and research? (pp. 15–35). Cheltenham: Edward Elgar.
Yin, R. K. (2003). Case study research: Design and methods (3rd ed.). Thousand Oaks: Sage Publications.
Yin, R. K. (2009). Case study research: Design and methods (4th ed.). Thousand Oaks: Sage Publications.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 The Author(s)
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Apaza, C.R., Chang, Y. (2020). Effective Whistleblowing Conceptual Framework. In: Apaza, C., Chang, Y. (eds) What Makes Effective Whistleblowing. Palgrave Macmillan, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-40200-6_1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-40200-6_1
Published:
Publisher Name: Palgrave Macmillan, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-40199-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-40200-6
eBook Packages: Political Science and International StudiesPolitical Science and International Studies (R0)