Abstract
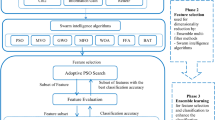
Gene expression data mostly available as cancer data have major challenges such as analyze, pattern matching and classification. Sometime task become more complex with large number of genes and small samples are available with noise and redundant information. Meaningful correlated information from dataset is the first and most important steps to be extracted for better diagnosis through artificial intelligence (AI). Accordingly, recent work for AI based classification and prognosis are focused in two steps process that is: (a) Feature extraction, and, (b) Ensemble Classification. Feature extraction will help in eliminating redundant and irrelevant genes, whereas ensemble classifier will help to optimize the accuracy. In this paper, we use double RBF kernel function for feature selection and novel fusion-procedure for enhance the performance of three base classifiers i.e., K Nearest Neighbor (KNN), Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP) and Decision Tree (DT). Training of classifier is implemented based on k-fold cross validation techniques. The predicted accuracy of the proposed model has been compared with recent fusion methods such as Majority Voting, Distribution Summation and Dempster–Shafer on six benchmark cancer datasets. Experiment evaluation and result analysis gives promising and better performance than other fusion strategies, aiming at our goal-functions. Wisconsin Breast prognosis dataset is used with the proposed model for gene selection and prognosis prediction.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Deng, L., Yu, D., et al.: Deep learning: methods and applications. Found. Trends Sig. Process. 7(3–4), 197–387 (2014)
Dara, S., Tumma, P.: Feature extraction by using deep learning: a survey. In: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Electronics, Communication and Aerospace Technology (ICECA 2018), pp. 1795–1801 (2018)
Cong, J., Wei, B., He, Y., Yin, Y., Zheng, Y.: A selective ensemble classification method combining mammography images with ultrasound images for breast cancer diagnosis. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 7, 1:7 (2017)
Han, J., Kamber, M., Pei, J.: Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques. The Morgan Kaufmann Series in Data Management Systems (Gray, J. (Series Editor)), 2nd edn. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, Burlington (2006)
Lee, Z.-J.: An integrated algorithm for gene selection and classification applied to microarray data of ovarian cancer. Artif. Intell. Mach. 42(1), 81–93 (2008)
Colin, C., Nello, C.: Simple learning algorithms for training support vector machines. Technical report, University of Bristol, pp. 1–29 (1998)
Cooper, G.F., Herskovita, E.: A Bayesian method for the induction of probabilistic networks from data. Mach. Learn. 9(4), 309–347 (1992)
Cortes, C., Vapnik, V.: Support vector networks. Mach. Learn. 20, 273–297 (1995)
Friedman, N., Linial, M., Nachman, I., Pe’er, D.: Using Bayesian networks to analyze expression data. J. Comput. Biol. 7(3–4), 601–620 (2000)
Xu, L., Krzyzak, A., Suen, C.: Methods of combining multiple classifiers and their applications to hand written numerals. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 22(3), 418–435 (1992)
Hansen, L., Salamon, P.: Neural network ensembles. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 12, 993–1001 (1990)
Hazem, J.M., Bakry, E.: An efficient algorithm for pattern detection using combined classifiers and data fusion. Inf. Fusion 11, 133–148 (2010)
Kilic, E., Alpaydin, E.: Learning the areas of expertise of classifiers in an ensemble. Procedia Comput. Sci. 3, 74–82 (2011)
Kittler, J., Hatef, M., Duin, R.P.W., Matas, J.: On combining classifiers. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 20(3), 226–239 (1998)
Mangai, U.G., Samanta, S., Das, S., Chowdhury, P.R.: A survey of fusion and feature fusion strategies for pattern classification. IETE Tech. Rev. 27(4), 293–307 (2010)
Rokach, L.: Ensemble methods for classifiers. In: Maimon, O., Rokach, L. (eds.) Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery Handbook, pp. 957–980. Springer, Boston (2005)
Senapati, R., Shaw, K., Mishra, S., Mishra, D.: A novel approach for missing value imputation and classification of microarray dataset. Procedia Eng. 38, 1067–1071 (2012)
Liu, S., Xu, C., Zhang, Y., Liu, J., Yu, B., Liu, X., Dehmer, M.: Feature selection of gene expression data for cancer classification using double RBF-kernels. BMC Bioinformatics 19, 396 (2018)
Phienthrakul, T., Kijsirikul, B.: Evolutionary strategies for multi-scale radial basis function kernels in support vector machines. In: Conference on Genetic and Evolutionary Computation, vol. 14, no. 7, pp. 905–911 (2005)
Bernhard, S., Alexander, J.S.: Learning with Kernels. MIT Press, Cambridge (2002)
Chen, H., Zhang, Y., Gutman, I.: A kernel-based clustering method for gene selection with gene expression data. J. Biomed. Inform. 62, 12–20 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbi.2016.05.007
Garcia, S., Derrac, J., Cano, J., Herrera, F.: Prototype selection for nearest neighbor classification: taxonomy and empirical study. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 34(3), 417–435 (2012)
Rosenblatt, F.: Principles of neurodynamics. perceptrons and the theory of brain mechanisms (No. VG-1196-G-8). Cornell Aeronautical Lab Inc., Buffalo, NY (1961)
Rumelhart, D.E., Hinton, G.E., Williams, R.J.: Learning internal representations by error propagation. In: Rumelhart, D.E., McClelland, J.L., PDP Research Group (eds.) Parallel Distributed Processing: Explorations in the Microstructure of Cognition, Volume 1: Foundation. MIT Press, Cambridge (1986)
Cybenko, G.: Approximation by superpositions of a sigmoidal function. Math. Control Signals Systems 2(4), 303–314 (1989)
Haykin, S.: Neural Networks: A Comprehensive Foundation, 2nd edn. Prentice Hall (1998). ISBN 0-13-273350-1
Kamiński, B., Jakubczyk, M., Szufel, P.: A framework for sensitivity analysis of decision trees. CEJOR 26(1), 135–159 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10100-017-0479-6
Wolberg, W.H., Mangasarian, O.: UCI Machine Learning Repository. http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml. Irvine
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Maurya, R.K., Yadav, S.K., Rishabh (2020). Ensemble Classification Approach for Cancer Prognosis and Prediction. In: Dehuri, S., Mishra, B., Mallick, P., Cho, SB., Favorskaya, M. (eds) Biologically Inspired Techniques in Many-Criteria Decision Making. BITMDM 2019. Learning and Analytics in Intelligent Systems, vol 10. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-39033-4_12
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-39033-4_12
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-39032-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-39033-4
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)