Abstract
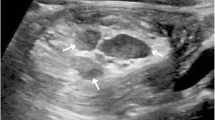
Intussusception is an acquired invagination of the bowel into itself; it may occur anywhere along the length of the bowel from the stomach into the esophagus to the rectum. It is an emergency where a delay in diagnosis increases the risk of bowel perforation, obstruction, and necrosis.Ultrasound is the accepted imaging modality of choice for the initial evaluation and diagnosis of intussusception. It has higher accuracy for diagnosis of intussusception than plain radiographs and higher diagnostic accuracy in identifying pathologic lead points and complications than plain radiographs or fluoroscopy-guided enema. Additionally, ultrasound is now more widely available than other imaging methods. There is no role for CT or MRI in the initial diagnosis of intussusception. However, CT can accurately diagnose intussusception in cases outside the typical age range or with atypical clinical presentation.Image-guided enema is widely accepted for the initial management of intussusception. Most studies suggest equivalency between fluoroscopic and ultrasound guidance regarding successful reduction rates, recurrence, and outcomes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Edwards EA, Pigg N, Courtier J, Zapala MA, MacKenzie JD, Phelps AS. Intussusception: past, present and future. Pediatr Radiol. 2017;47(9):1101–8.
Bisset GS, Kirks DR. Intussusception in infants and children: diagnosis and therapy. Radiology. 1988;168(1):141–5.
Applegate KE, Sadigh G. Intussusception in infants and children: diagnostic evidence-based emergency imaging and treatment. In: Kelly A, Cronin P, Puig S, Applegate KE, editors. Evidence-based emergency imaging: optimizing diagnostic imaging of patients in the emergency care setting. Cham: Springer International Publishing; 2018. p. 567–82.
Lin SL, Kong MS, Houng DS. Decreasing early recurrence rate of acute intussusception by the use of dexamethasone. Eur J Pediatr. 2000;159(7):551–2.
Navarro O, Dugougeat F, Kornecki A, Shuckett B, Alton DJ, Daneman A. The impact of imaging in the management of intussusception owing to pathologic lead points in children. A review of 43 cases. Pediatr Radiol. 2000;30(9):594–603.
Zhang Y, Dong Q, Li S-X, Ren W-D, Shi B, Bai Y-Z, et al. Clinical and ultrasonographic features of secondary intussusception in children. Eur Radiol. 2016;26(12):4329–38.
Parashar UD, Holman RC, Cummings KC, Staggs NW, Curns AT, Zimmerman CM, et al. Trends in intussusception-associated hospitalizations and deaths among US infants. Pediatrics. 2000;106(6):1413–21.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Withdrawal of rotavirus vaccine recommendation. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1999;48(43):1007.
Rotavirus vaccines | CDC [Internet]. [cited 2022 Jan 19]. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/rotavirus/vaccination.html
Tapiainen T, Bär G, Bonhoeffer J, Heininger U. Evaluation of the Brighton Collaboration case definition of acute intussusception during active surveillance. Vaccine. 2006;24(9):1483–7.
Case Definitions Archives – Brighton Collaboration [Internet]. [cited 2022 Aug 1]. Available from: https://brightoncollaboration.us/category/pubs-tools/case-definitions/
Usang UE, Inah GB, Inyang AW, Ekabua AT. Intussusception in children: comparison between ultrasound diagnosis and operation findings in a tropical developing country. Afr J Paediatr Surg. 2013;10(2):87–90.
Harrington L, Connolly B, Hu X, Wesson DE, Babyn P, Schuh S. Ultrasonographic and clinical predictors of intussusception. J Pediatr. 1998;132(5):836–9.
Singh JV, Kamath V, Shetty R, Kumar V, Prasad R, Saluja T, et al. Retrospective surveillance for intussusception in children aged less than five years at two tertiary care centers in India. Vaccine. 2014;32(Suppl 1):A95–8.
Meier DE, Coln CD, Rescorla FJ, OlaOlorun A, Tarpley JL. Intussusception in children: international perspective. World J Surg. 1996;20(8):1035–9; discussion 1040
Otero HJ, White AM, Khwaja AB, Griffis H, Katcoff H, Bresnahan BW. Imaging intussusception in children’s hospitals in the United States: trends, outcomes, and costs. J Am Coll Radiol. 2019;16(12):1636–44.
Territo HM, Wrotniak BH, Qiao H, Lillis K. Clinical signs and symptoms associated with intussusception in young children undergoing ultrasound in the emergency room. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2014;30(10):718–22.
Klein EJ, Kapoor D, Shugerman RP. The diagnosis of intussusception. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 2004;43(4):343–7.
Lai W-P, Yang Y-J, Cheng C-N, Chen J-S. Clinico-pathological features of intussusception in children beyond five years old. Acta Paediatr Taiwan. 2007;48(5):267–71.
Sadigh G, Zou KH, Razavi SA, Khan R, Applegate KE. Meta-analysis of air versus liquid enema for intussusception reduction in children. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2015;205(5):W542–9.
West KW, Stephens B, Vane DW, Grosfeld JL. Intussusception: current management in infants and children. Surgery. 1987;102(4):704–10.
Roskind CG, Ruzal-Shapiro CB, Dowd EK, Dayan PS. Test characteristics of the 3-view abdominal radiograph series in the diagnosis of intussusception. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2007;23(11):785–9.
Daneman A, Navarro O. Intussusception. Part 1: a review of diagnostic approaches. Pediatr Radiol. 2003;33(2):79–85.
Hernandez JA, Swischuk LE, Angel CA. Validity of plain films in intussusception. Emerg Radiol. 2004;10(6):323–6.
Hooker RL, Hernanz-Schulman M, Yu C, Kan JH. Radiographic evaluation of intussusception: utility of left-side-down decubitus view. Radiology. 2008;248(3):987–94.
Saverino BP, Lava C, Lowe LH, Rivard DC. Radiographic findings in the diagnosis of pediatric ileocolic intussusception: comparison to a control population. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2010;26(4):281–4.
Henderson AA, Anupindi SA, Servaes S, Markowitz RI, Aronson PL, McLoughlin RJ, et al. Comparison of 2-view abdominal radiographs with ultrasound in children with suspected intussusception. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2013;29(2):145–50.
Roskind CG, Kamdar G, Ruzal-Shapiro CB, Bennett JE, Dayan PS. Accuracy of plain radiographs to exclude the diagnosis of intussusception. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2012;28(9):855–8.
Tareen F, Mc Laughlin D, Cianci F, Hoare SM, Sweeney B, Mortell A, et al. Abdominal radiography is not necessary in children with intussusception. Pediatr Surg Int. 2016;32(1):89–92.
Weihmiller SN, Buonomo C, Bachur R. Risk stratification of children being evaluated for intussusception. Pediatrics. 2011;127(2):e296–303.
Mendez D, Caviness AC, Ma L, Macias CC. The diagnostic accuracy of an abdominal radiograph with signs and symptoms of intussusception. Am J Emerg Med. 2012;30(3):426–31.
del-Pozo G, Albillos JC, Tejedor D, Calero R, Rasero M, de la Calle U, et al. Intussusception in children: current concepts in diagnosis and enema reduction. Radiographics. 1999;19(2):299–319.
Tiao MM, Wan YL, Ng SH, Ko SF, Lee TY, Chen MC, et al. Sonographic features of small-bowel intussusception in pediatric patients. Acad Emerg Med. 2001;8(4):368–73.
Justice FA, de Campo M, Liem NT, Son TN, Ninh TP, Bines JE. Accuracy of ultrasonography for the diagnosis of intussusception in infants in Vietnam. Pediatr Radiol. 2007;37(2):195–9.
Shekherdimian S, Lee SL, Sydorak RM, Applebaum H. Contrast enema for pediatric intussusception: is reflux into the terminal ileum necessary for complete reduction? J Pediatr Surg. 2009;44(1):247–9; discussion 249
Verschelden P, Filiatrault D, Garel L, Grignon A, Perreault G, Boisvert J, et al. Intussusception in children: reliability of US in diagnosis – a prospective study. Radiology. 1992;184(3):741–4.
Weinberger E, Winters WD. Intussusception in children: the role of sonography. Radiology. 1992;184(3):601–2.
Hryhorczuk AL, Strouse PJ. Validation of US as a first-line diagnostic test for assessment of pediatric ileocolic intussusception. Pediatr Radiol. 2009;39(10):1075–9.
Eshed I, Gorenstein A, Serour F, Witzling M. Intussusception in children: can we rely on screening sonography performed by junior residents? Pediatr Radiol. 2004;34(2):134–7.
Henrikson S, Blane CE, Koujok K, Strouse PJ, DiPietro MA, Goodsitt MM. The effect of screening sonography on the positive rate of enemas for intussusception. Pediatr Radiol. 2003;33(3):190–3.
Chang Y-J, Chao H-C, Wang C-J, Lo W-C, Yan D-C. Evaluating pediatric intussusception using 24-hour ultrasound. Pediatr Neonatol. 2013;54(4):235–8.
Bowerman RA, Silver TM, Jaffe MH. Real-time ultrasound diagnosis of intussusception in children. Radiology. 1982;143(2):527–9.
Ja Lim K, Lee K, Yoon DY, Moon JH, Lee H, Kim M-J, et al. The role of US in finding intussusception and alternative diagnosis: a report of 100 pediatric cases. Acta Radiol. 2015;56(2):228–33.
Ayaz UY, Dilli A, Ayaz S, Api A. Ultrasonographic findings of intussusception in pediatric cases. Med Ultrason. 2011;13(4):272–6.
Wiersma F, Allema JH, Holscher HC. Ileoileal intussusception in children: ultrasonographic differentiation from ileocolic intussusception. Pediatr Radiol. 2006;36(11):1177–81.
Lioubashevsky N, Hiller N, Rozovsky K, Segev L, Simanovsky N. Ileocolic versus small-bowel intussusception in children: can US enable reliable differentiation? Radiology. 2013;269(1):266–71.
Park BL, Rabiner JE, Tsung JW. Point-of-care ultrasound diagnosis of small bowel-small bowel vs ileocolic intussusception. Am J Emerg Med. 2019;37(9):1746–50.
Park NH, Park SI, Park CS, Lee EJ, Kim MS, Ryu JA, et al. Ultrasonographic findings of small bowel intussusception, focusing on differentiation from ileocolic intussusception. Br J Radiol. 2007;80(958):798–802.
Koh EPK, Chua JHY, Chui CH, Jacobsen AS. A report of 6 children with small bowel intussusception that required surgical intervention. J Pediatr Surg. 2006;41(4):817–20.
Munden MM, Bruzzi JF, Coley BD, Munden RF. Sonography of pediatric small-bowel intussusception: differentiating surgical from nonsurgical cases. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2007;188(1):275–9.
Navarro O, Daneman A. Intussusception. Part 3: diagnosis and management of those with an identifiable or predisposing cause and those that reduce spontaneously. Pediatr Radiol. 2004;34(4):305–12; quiz 369
Sargent MA, Babyn P, Alton DJ. Plain abdominal radiography in suspected intussusception: a reassessment. Pediatr Radiol. 1994;24(1):17–20.
Hughes UM, Connolly BL, Chait PG, Muraca S. Further report of small-bowel intussusceptions related to gastrojejunostomy tubes. Pediatr Radiol. 2000;30(9):614–7.
Rajagopal R, Mishra N, Yadav N, Jhanwar V, Thakur A, Mannan N. Transient versus surgically managed small bowel intussusception in children: role of ultrasound. Afr J Paediatr Surg. 2015;12(2):140–2.
Kim JH. US features of transient small bowel intussusception in pediatric patients. Korean J Radiol. 2004;5(3):178–84.
Vandewalle RJ, Bagwell AK, Shields JR, Burns RC, Brown BP, Landman MP. Radiographic and clinical factors in pediatric patients with surgical small-bowel intussusception. J Surg Res. 2019;233:167–72.
Zhang Y, Bai Y-Z, Li S-X, Liu S-J, Ren W-D, Zheng L-Q. Sonographic findings predictive of the need for surgical management in pediatric patients with small bowel intussusceptions. Langenbeck’s Arch Surg. 2011;396(7):1035–40.
Mateen MA, Saleem S, Rao PC, Gangadhar V, Reddy DN. Transient small bowel intussusceptions: ultrasound findings and clinical significance. Abdom Imaging. 2006;31(4):410–6.
Stranzinger E, Dipietro MA, Yarram S, Khalatbari S, Strouse PJ. Intramural and subserosal echogenic foci on US in large-bowel intussusceptions: prognostic indicator for reducibility? Pediatr Radiol. 2009;39(1):42–6.
Gartner RD, Levin TL, Borenstein SH, Han BK, Blumfield E, Murphy R, et al. Interloop fluid in intussusception: what is its significance? Pediatr Radiol. 2011;41(6):727–31.
Koumanidou C, Vakaki M, Pitsoulakis G, Kakavakis K, Mirilas P. Sonographic detection of lymph nodes in the intussusception of infants and young children: clinical evaluation and hydrostatic reduction. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2002;178(2):445–50.
Carroll AG, Kavanagh RG, Ni Leidhin C, Cullinan NM, Lavelle LP, Malone DE. Comparative effectiveness of imaging modalities for the diagnosis and treatment of intussusception: a critically appraised topic. Acad Radiol. 2017;24(5):521–9.
Plut D, Phillips GS, Johnston PR, Lee EY. Practical imaging strategies for intussusception in children. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2020;215(6):1449–63.
Puapong D, Lee SL, Radner G, Tsai PI, Katz DS, Abbas MA, et al. Computed tomography findings of unanticipated prolonged ileocolic intussusception in children. Perm J. 2008;12(3):22–4.
Strouse PJ, DiPietro MA, Saez F. Transient small-bowel intussusception in children on CT. Pediatr Radiol. 2003;33(5):316–20.
Ko S-F, Lee T-Y, Ng S-H, Wan Y-L, Chen M-C, Tiao M-M, et al. Small bowel intussusception in symptomatic pediatric patients: experiences with 19 surgically proven cases. World J Surg. 2002;26(4):438–43.
Ko S-F, Tiao M-M, Hsieh C-S, Huang F-C, Huang C-C, Ng S-H, et al. Pediatric small bowel intussusception disease: feasibility of screening for surgery with early computed tomographic evaluation. Surgery. 2010;147(4):521–8.
Bucher BT, Hall BL, Warner BW, Keller MS. Intussusception in children: cost-effectiveness of ultrasound vs diagnostic contrast enema. J Pediatr Surg. 2011;46(6):1099–105.
Lampl BS, Glaab J, Ayyala RS, Kanchi R, Ruzal-Shapiro CB. Is intussusception a middle-of-the-night emergency? Pediatr Emerg Care. 2019;35(10):684–6.
Stein-Wexler R, O’Connor R, Daldrup-Link H, Wootton-Gorges SL. Current methods for reducing intussusception: survey results. Pediatr Radiol. 2015;45(5):667–74.
Gluckman S, Karpelowsky J, Webster AC, McGee RG. Management for intussusception in children. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;(6):CD006476.
Takahashi T, Okazaki T, Watayo H, Ogasawara Y, Nakazawa N, Kato Y, et al. Radiographic signs predictive of success of hydrostatic reduction of intussusception. Pediatr Surg Int. 2009;25(11):977–80.
Kaiser AD, Applegate KE, Ladd AP. Current success in the treatment of intussusception in children. Surgery. 2007;142(4):469–75; discussion 475
Curtis JL, Gutierrez IM, Kirk SR, Gollin G. Failure of enema reduction for ileocolic intussusception at a referring hospital does not preclude repeat attempts at a children’s hospital. J Pediatr Surg. 2010;45(6):1178–81.
Herwig K, Brenkert T, Losek JD. Enema-reduced intussusception management: is hospitalization necessary? Pediatr Emerg Care. 2009;25(2):74–7.
Sujka JA, Dalton B, Gonzalez K, Tarantino C, Schroeder L, Giovanni J, et al. Emergency department discharge following successful radiologic reduction of ileocolic intussusception in children: a protocol based prospective observational study. J Pediatr Surg. 2019;54(8):1609–12.
Simanovsky N, Issachar O, Koplewitz B, Lev-Cohain N, Rekhtman D, Hiller N. Early recurrence of ileocolic intussusception after successful air enema reduction: incidence and predisposing factors. Emerg Radiol. 2019;26(1):1–4.
Mallicote MU, Isani MA, Roberts AS, Jones NE, Bowen-Jallow KA, Burke RV, et al. Hospital admission unnecessary for successful uncomplicated radiographic reduction of pediatric intussusception. Am J Surg. 2017;214(6):1203–7.
Golriz F, Cassady CI, Bales B, Herrejon C, Hicks MJ, Zhang W, et al. Comparative safety and efficacy of balloon use in air enema reduction for pediatric intussusception. Pediatr Radiol. 2018;48(10):1423–31.
Lui KW, Wong HF, Cheung YC, See LC, Ng KK, Kong MS, et al. Air enema for diagnosis and reduction of intussusception in children: clinical experience and fluoroscopy time correlation. J Pediatr Surg. 2001;36(3):479–81.
Heenan SD, Kyriou J, Fitzgerald M, Adam EJ. Effective dose at pneumatic reduction of paediatric intussusception. Clin Radiol. 2000;55(11):811–6.
Ilivitzki A, Shtark LG, Arish K, Engel A. Deep sedation during pneumatic reduction of intussusception. Pediatr Radiol. 2012;42(5):562–5.
Xie X, Wu Y, Wang Q, Zhao Y, Chen G, Xiang B. A randomized trial of pneumatic reduction versus hydrostatic reduction for intussusception in pediatric patients. J Pediatr Surg. 2018;53(8):1464–8.
Prana L, Baijoob S, Rampersad B. Are we doing better? Barium enema reduction of intussusception. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2018;100(5):388–91.
Rubí I, Vera R, Rubí SC, Torres EE, Luna A, Arcos J, et al. Air reduction of intussusception. Eur J Pediatr Surg. 2002;12(6):387–90.
Medina LS, Applegate KE, Blackmore CC, editors. Evidence-Based Imaging in Pediatrics. New York, NY: Springer New York; 2010. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-0922-0.
Pomerantz B, Anupindi S, Wales PW, Doody DP, Masiakos PT. Radiographic reduction of intussusception in patients with cystic fibrosis. Pediatr Surg Int. 2007;23(8):763–5.
Schwab J, Benya E, Lin R, Majd K. Contrast enema in children with Henoch-Schönlein purpura. J Pediatr Surg. 2005;40(8):1221–3.
Saxena AK, Seebacher U, Bernhardt C, Höllwarth ME. Small bowel intussusceptions: issues and controversies related to pneumatic reduction and surgical approach. Acta Paediatr. 2007;96(11):1651–4.
Navarro OM, Daneman A, Chae A. Intussusception: the use of delayed, repeated reduction attempts and the management of intussusceptions due to pathologic lead points in pediatric patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004;182(5):1169–76.
Hadidi AT, El Shal N. Childhood intussusception: a comparative study of nonsurgical management. J Pediatr Surg. 1999;34(2):304–7.
Vujović D, Lukac M, Sretenović A, Krstajić T, Ljubić V, Antunović SS. Indications for repeated enema reduction of intussusception in children. Srp Arh Celok Lek. 2014;142(5–6):320–4.
Pazo A, Hill J, Losek JD. Delayed repeat enema in the management of intussusception. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2010;26(9):640–5.
Okazaki T, Ogasawara Y, Nakazawa N, Kobayashi H, Kato Y, Lane GJ, et al. Reduction of intussusception in infants by a pediatric surgical team: improvement in safety and outcome. Pediatr Surg Int. 2006;22(11):897–900.
Eisapour A, Mehrayin R, Esmaeili-Dooki M. The effect of midazolam on decreasing the duration of intussusception hydrostatic reduction in children. Med Arch. 2015;69(5):289–92.
Esposito F, Ambrosio C, De Fronzo S, Panico MR, D’Aprano M, Giugliano AM, et al. Fluoroscopy-guided hydrostatic reduction of intussusception in infancy: role of pharmacological premedication. Radiol Med. 2015;120(6):549–56.
Cullmann JL, Heverhagen JT, Puig S. Radiation dose in pneumatic reduction of ileo-colic intussusceptions – results from a single-institution study. Pediatr Radiol. 2015;45(5):675–7.
Burns R, Adler M, Benya E, Guthrie B. Fluoroscopy screen time during contrast enema for the evaluation and treatment of intussusception. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2014;30(5):327–30.
Kaplan SL, Magill D, Felice MA, Edgar JC, Anupindi SA, Zhu X. Intussusception reduction: effect of air vs. liquid enema on radiation dose. Pediatr Radiol. 2017;47(11):1471–6.
Kim YG, Choi BI, Yeon KM, Kim JW. Diagnosis and treatment of childhood intussusception using rea-time ultrasonography and saline enema: preliminary report. J Korean Soc Med Ultrasound. 1982.
Sanchez TRS, Potnick A, Graf JL, Abramson LP, Patel CV. Sonographically guided enema for intussusception reduction: a safer alternative to fluoroscopy. J Ultrasound Med. 2012;31(10):1505–8.
Sanchez TR, Doskocil B, Stein-Wexler R. Nonsurgical management of childhood intussusception: retrospective comparison between sonographic and fluoroscopic guidance. J Ultrasound Med. 2015;34(1):59–63.
Gu L, Zhu H, Wang S, Han Y, Wu X, Miao H. Sonographic guidance of air enema for intussusception reduction in children. Pediatr Radiol. 2000;30(5):339–42.
Xiaolong X, Yang W, Qi W, Yiyang Z, Bo X. Risk factors for failure of hydrostatic reduction of intussusception in pediatric patients: a retrospective study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019;98(1):e13826.
Krishnakumar HS, Umamaheshwari. Ultrasound guided hydrostatic reduction in the management of intussusception. Indian J Pediatr. 2006;73(3):217–20.
Di Renzo D, Colangelo M, Lauriti G, De Girolamo F, Persico A, Lelli CP. Ultrasound-guided Hartmann’s solution enema: first-choice procedure for reducing idiopathic intussusception. Radiol Med. 2012;117(4):679–89.
Kelley-Quon LI, Arthur LG, Williams RF, Goldin AB, St Peter SD, Beres AL, et al. Management of intussusception in children: a systematic review. J Pediatr Surg. 2021;56(3):587–96.
Arshad SA, Hebballi NB, Hegde BN, Avritscher EBC, John SD, Lapus RM, et al. Early discharge after nonoperative management of intussusception is both safe and cost-effective. J Pediatr Surg. 2022;57(1):147–52.
Lautz TB, Thurm CW, Rothstein DH. Delayed repeat enemas are safe and cost-effective in the management of pediatric intussusception. J Pediatr Surg. 2015;50(3):423–7.
Kim JH, Lee JS, Ryu JM, Lim KS, Kim WY. Risk factors for recurrent intussusception after fluoroscopy-guided air enema. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2018;34(7):484–7.
Xie X, Wu Y, Wang Q, Zhao Y, Xiang B. Risk factors for recurrence of intussusception in pediatric patients: a retrospective study. J Pediatr Surg. 2018;53(11):2307–11.
Ksia A, Mosbahi S, Brahim MB, Sahnoun L, Haggui B, Youssef SB, et al. Recurrent intussusception in children and infants. Afr J Paediatr Surg. 2013;10(4):299–301.
Yalcin S, Ciftci AO, Karaagaoglu E, Tanyel FC, Senocak ME. Presenting clinical features and outcome in intussusception. Indian J Pediatr. 2009;76(4):401–5.
Daneman A, Alton DJ, Ein S, Wesson D, Superina R, Thorner P. Perforation during attempted intussusception reduction in children – a comparison of perforation with barium and air. Pediatr Radiol. 1995;25(2):81–8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this entry
Cite this entry
Otero, H.J., De Leon Benedetti, L.S., Applegate, K.E. (2023). Intussusception in Children: Diagnostic Imaging and Treatment. In: Otero, H.J., Kaplan, S.L., Medina, L.S., Blackmore, C.C., Applegate, K.E. (eds) Evidence-Based Imaging in Pediatrics. Evidence-Based Imaging. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-38095-3_31-1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-38095-3_31-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-38095-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-38095-3
eBook Packages: Springer Reference MedicineReference Module Medicine