Abstract
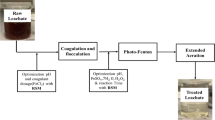
Oil refinery wastewater is one of the most polluted types of wastewater with a large variety of organic and mineral pollutants, which need treatment before discharge to the receiving environment. The coagulation–flocculation process was used to treat oil refinery wastewater with ferric chloride (FeCl3-40%) as a coagulant and cactus juice was used as a flocculant to reduce turbidity and chemical oxygen demand (COD).
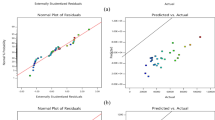
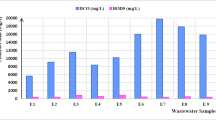
A response surface methodology (RSM) design was applied to optimize the process the three factors coagulant, bio-flocculant doses, and pH. Obtained optimal dosages were: 1.12 g/l of coagulant and 11.6 ml/l of bio-flocculant and 9.38 of pH. Removal efficiencies under optimal conditions reached: 97.92 ± 0.66% and 62.41 ± 8.12% for turbidity and COD, respectively. The experiment results showed the capability of ferric chloride as coagulant and cactus as bio-flocculant for reducing the pollutants from oil refinery wastewater.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
National Environmental Standard and Regulatory Enforcement Agency Federtal Republic of Nigeria Official Gazette, Lagos (2011)
Chatoui, M., Lahsaini, S., Souabi, S., Bahlaoui, M.A., Hobaizi, S., Pala, A.: Study of refining wastewater pollution: case of vegetable oil refining industry Morocco. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 7(10), 3906–3915 (2016)
Patale, V., Pandya, J.: Mucilage extract of Coccinia indica fruit as coagulant-flocculent for turbid water treatment. Asian J. Plant Sci. Res. 2, 442–445 (2012)
Sciban, M., Klaˇsnja, M., Antov, M., Skrbic, B.: Removal of water turbidity by natural coagulants obtained from chestnut and acorn. Bioresour. Technol. 100, 6639–6643 (2009)
Oladoja, N.A.: Headway on natural polymeric coagulants in water and waste-water treatment operations. J. Water Process. Eng. 6, 174–192 (2015)
Vijayaraghavan, G., Sivakumar, T., Vimal Kumar, A.: Application of plant based coagulants for waste water treatment. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Res. Stud. 1, 88–92 (2011). E-ISSN2249-8974
Wang, Y., Chen, K., Moa, L., Li, J., Xu, J.: Optimization of coagulation–flocculation process for papermaking-reconstituted tobacco slice wastewater treatment using response surface methodology. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 20, 391–396 (2014)
APHA, WPCE, AWWA. Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 19th edn. American Public Health Association (APHA), Washington, DC (1992)
Goupy, J., Creighton, L.: Introduction aux plans d’expériences. Edition Dunod, Paris (2006)
Ravikumar, K., Pakshirajan, K., Swaminathan, T., Balu, K.: Optimization of batch process parameters using response surface methodology for dye removal by a novel adsorbent. J. Chem. Eng. 105, 131–138 (2005)
Martin, M.A., Gonzalez, I., Berrios, M., Siles, J.A., Martin, A.: J Chem Eng. 172, 771 (2011)
Oubrayme, H., Souabi, S., Bouhria, M., Tahiri, M., Alami younssi, S., Albizane, A.: Optimization of the coagulation/flocculation of wastewater from oil refineries use of Response Surface Methodology. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 7(11), 4299–4310 (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Dkhissi, O. et al. (2020). Optimization of Opuntia Dose as Bio-flocculant for Oil Refinery Wastewater Using Response Surface Methodology. In: Ezziyyani, M. (eds) Advanced Intelligent Systems for Sustainable Development (AI2SD’2019). AI2SD 2019. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 1104. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-36671-1_44
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-36671-1_44
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-36670-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-36671-1
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)