Abstract
With the increase of building density in contemporary urban building space, the layout design of guiding signs has become a typical problem. There are few studies on the special characteristics of the building environment such as narrow passageways. Therefore, this paper studies the angle of clearly can be seen and the angle of comfortably can be seen based on visual sensitivity by experimental method, considering different eye heights and viewing distances so as to provide some references for the guided sign setting in narrow passageways and similar environment.
Access provided by Autonomous University of Puebla. Download conference paper PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Keywords
1 Introduction
With the increase of building density in contemporary urban building space, the layout design of guiding signs has become a typical problem. The Beijing subway signage system was studied with the relating factors in design such as feathers of passenger behavior, transit mode, information hierarchy and environmental factors so on [1]. The guiding sign system in High-speed railway station was studied based on the layout optimization design [2]. There are also many researches on the guiding sign with human characteristic too, such as visual field, range of visibility visual angle and visual colors [3,4,5]. But most of this literatures have studied the setting of guiding signs from a global perspective or base on the national standards, but there are few studies on the special characteristics of the building environment such as narrow passageways.
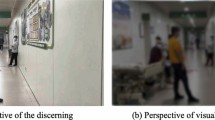
Most guiding signs are set erectly due to standard. In some environments, the erectly setting may cause a person raise his head hardly to see clearly especially in short distance (see Fig. 1). Fortunately, some designers have also concerned about the setting angle of guiding signs to make the watching more comfortable and easily (see Fig. 2).
So, this paper studies the angle of clearly can be seen and the angle of comfortably can be seen based on visual sensitivity by experimental method, considering different eye heights and viewing distances so as to provide some references for the guided sign setting in narrow passageways and similar environment.
2 Experiment
The 3 × 2 factors within-subjects were designed, and the independent variables were the eye height and view distance. Two dependent visual sensitivity variables were studied in this paper: Clearly visible angle (the Chinese font strokes are clearly visible, no overlaps) and Comfortable angle (the Chinese font can be seen clearly, and people’s head, neck and eyes are comfortable).
2.1 Experimental Material
To explore the suitable angle of guiding sign, a similar sign size (width 200 mm * height 1500 mm) was made and set on a rotating device. The guide sign is shown in the following Pic1 (see Fig. 3).
2.2 Experimental Environment
In the experiment, a two-factor 3 × 2 level of intra-subject design was adopted, and the independent variables were height (level 3) and distance (level 2).
A narrow and long channel was selected as the experimental site, with a width of 1.9 m and a height of 2.5 m. The basic illumination was 300lx–500lx. The test material drawing is printed with hard foam board and hung by tripod. The lowest edge of the sign is 2.2 m–2.3 m from the ground. Set a ruler on the floor of the straight corridor, measure the distance 2 m and 5 m from the sign, and mark it (see Fig. 4).
The view distance was two levels: 2 m and 5 m. Two dependent visual sensitivity variables were studied in this paper: Clearly visible angle (the Chinese font strokes are clearly visible, no overlaps) and Comfortable angle (the Chinese font can be seen clearly, and people’s head, neck and eyes are comfortable).
2.3 Participants
The eye height (3 levels, see Fig. 5) were selected from the GB 10000-88 standard “Human dimensions of Chinese adults”, including the eye height of 5 percentiles for adult women, 50 percentiles for adult men and 95 percentiles for adult men, see Table 1.
Thirty adults (13 males and 15 females), aged from 18 to 50 (32.3 ± 10.9 yrs.), with normal vision or corrected-to-normal vision, participated in this study. The specific conditions of the subjects are shown in Table 1, in which the height of the subjects is divided into three levels: G1(1550 mm and below); G2(1650 mm–1678 mm); G3(1760 mm–1780 mm).
2.4 Procedures
The test was conducted separately. After entering the laboratory, the participants were tested for visual acuity first. Those with normal visual acuity or corrected visual acuity could participate in the experiment and their height was measured at the same time. After the measurement, the participant was asked to stand at the mark line 5 m away from the guiding sign to start the test.
When the steering signs rotated slowly forward (see Fig. 6) and backward (see Fig. 7) respectively, the subjects were asked to report the angles of starting to see clearly, beginning to feel comfortable, beginning to feel uncomfortable and beginning to not see clearly. The whole process was measured three times. The results were statistically analyzed and the visual sensitivity variables were divided into four: Clearly visible anglelower and Clearly visible angleupper, Comfortable anglelower and Comfortable angleupper. The device was repeating the rotating three times totally.
When the line 5 m operation was finished, then the participant was asked to stand in front of the guiding sign 2 m away. And then the process of three time rotating backward and afterward was repeated, the four angles were recorded each time separately.
2.5 Data Analysis
In this research, each participant’s three times of clearly see and comfortable angles in each viewing distance will be averaged after outliers’ elimination. The two main factors human’s height and the viewing distance will be discussed separately following.
A repeated ANOVA were used for statistical analysis. SPSS (16.0 J, SPSS Inc.) was used for calculation.
3 Results
The following is the result of subjective and objective measurement we obtained in the experiment.
3.1 The Result of the Impact of Height on Angle Value
The height of subjects was divided into three groups: G1(1550 mm and below); G2(1650 mm–1670 mm); G3(1760 mm–1780 mm). It can be inferred from the table that the average angle was various of different height groups.
Some obvious trends can be draw from the numbers that the Clearly visible angle no matter the lower or the upper will increases while the height becomes lower. The comfortable anglelower is the same trend, but the comfortable angleupper is the opposite trend decline with the height becomes lower. And the trends are the same in 2 m between 5 m, see Table 2.
The repeated measure ANOVA shows no significant main effects of different height groups on the Clearly visible angle and the Comfort angle(P > 0.05), see Table 3.
3.2 The Result of the Impact of Distance on Angle Value
The paired T-test was carried out for the Angle values at different distance levels. The results showed significant main effects of different distances on Clearly visible anglelower, Clearly visible angleupper and Comfortable anglelower. However, there is no significant difference in the Comfortable angleupper at the distance level.
The paired T-test was performed separately, and the following results were obtained:
-
(a)
PClearly visible angle lower = 0.015 < 0.05, it shows significant difference, and the angle is bigger in 2 m.
-
(b)
PClearly visible angle upper = 0.000 < 0.05, it shows significant difference, and the angle is bigger in 2 m.
-
(c)
PComfortable angle lower = 0.003 < 0.05, it shows significant difference, and the angle is bigger in 2 m.
-
(d)
PComfortable angle upper = 0.323 > 0.05, it shows no significant difference.
From the above analysis, it can be seen that the viewing distance is the main factor affected the subject visual sensitivity, and it has obvious influence on comfortable Angle range, but not the uncomfortable Angle range.
3.3 The Suitable View Angle of the Guiding Sign
Based on the results of this study, the following conclusions can be drawn: the angle can be clearly seen of guiding sign can be set between 32.24°–174.16°,but the comfortable angle can be set between 72.68°–127.44° when the guiding sign is to be seen in 2 m. the angle can be clearly seen of guiding sign can be set between 27.46°–165.69°,but the comfortable angle can be set between 67.04°–123.83° when the guiding sign is to be seen in 5 m (Fig. 8 and 9).
4 Discussion and Conclusion
The present study was concerned with clearly visible and comfortable angle of the setting of guiding sign based on Ergonomics. The height of viewer and the viewing distance was considered to be the main factor to infect the setting angle. According to the standard GB-10000 of Human Dimension of Chinese Adults, 30 volunteers were recruited, and they could represent the wildly population of the physical characters in domestic. A guiding sign was set on a rotation device to rotate forward and backward to obtain the clearly visible and comfortable angle under 2 and 5 m.
The results from the experiment showed that there were no significant main effects of different heights of human but significant main effects of viewing distances on the angle. We guess it may due to the size of the guiding sign from the participants’ interview after the test.
In conclusion, the guiding sign setting angle can be draw as 72.68°–123.83° reference to the comfortable angle.
Some factors haven’t been concerned unfortunately due to various reasons, such as the sign’s size. Different size of the sign will impact the setting angle of comfortable. In addition, the speed of people whose looking for the sign will do an important role to the setting angles too. Further study may focus on the more influence factors and conditions to acquire the reasonable angle of sign setting.
References
Peng, J.: The study of Beijing subway Signage System. Tongji University (2007)
He, H.: The Research on Evaluation of Guiding Sign in High-speed Railway Station. Southwest Jiaotong University, Xian (2014)
Chen, S.: A Sign Design Research on Based of Human Visual Characteristics. DongHua University (2014)
Ma, X.: The Design of Guide-Sign System in Underground Spaces. Tianjin University (2009)
Xu, L., Zhang, W., Tang, Z.: A virtue reality study of wayfinding and the sign layout in subway station. Architectural J. 1–4 (2010)
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by National Key R&D Program of China (2016YFF0201700).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Luo, L., Wang, Z., Ran, L., Zou, C., Wu, H. (2020). Research on Guiding Sign Ergonomic Setting Based on Visual Sensitivity in Long and Narrow Passageway. In: Rebelo, F., Soares, M. (eds) Advances in Ergonomics in Design. AHFE 2019. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 955. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-20227-9_61
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-20227-9_61
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-20226-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-20227-9
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)