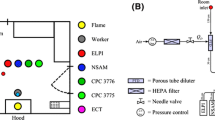
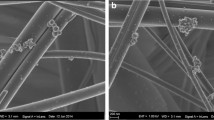
Abstract
Chapter evaluates the current state of health and safety related problems of people exposed to environmental burden due to occupational requirements. In such conditions, particulate nanoscale aerosols play an important role, therefore the survey is focused on personal protective equipment used against inhalation of pollutants from the air. Respiratory protective filters work against inhalation of pollutants by exposed persons. Filter efficiency is determined according to standardized methods given by the standardized Czech technical norms. However, such rehearsals are not specifically focused on an ultrafine aerosol with the content of nanoparticles in the range of 7.6–299.6 nm. The chapter evaluates permeability of one of the most often used protective filter OF-90 against ultrafine aerosol lead oxide with predetermined characteristics.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amster, E.D., et al.: Occupational exposures and symptoms among firefighters and police during the carmel cohort study. Isr. Med. Assoc. J. 15, 288–292 (2013)
Anderson, M.K., et al.: Occupation and other risk factors for injury among enlisted U.S. Army Soldiers. Public Health 129, 531–538 (2015)
CR–Technology Agency of the Czech Republic: Certified methodology for providing personal protective equipment in a nanoparticle environment. 15 (2016)
CR: Government Decree No. 361/2007 Coll., Laying down the conditions for the protection of the health of workers at work (2007)
Czech Defence Standard: Respiratory devices for individual protection - Military protective masks. Office for Defence Standardization Cataloging and State Quality Assurance 20 (2007)
EC: Official Journal of the European Recommendations on the definition of nanomaterial. http://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2011:275:0038:0040:EN:PDF (2011) Accessed 30 Jan 2018
Hrůza, J.: Improvement of Filtration Features of Materials, 1st edn. Technical university of Liberec, Liberec (2005)
Hylák, Č., Pivovarník, J.: Individual and Collective Civil Protection of the Czech Republic, 1st edn. Ministry of the Interior of the Czech Republic, Prague (2016). ISBN 978-80-87544-18-1
Hošková-Mayerová, S.: An overview of topological and fuzzy topological hypergroupoids. Ratio Math. 33, 21–38 (2017)
Kendall, M., Holgate, S.: Health impact and toxicological effects of nanomaterials in the lung. Respirology 17, 743–758 (2012)
Korzeniewski, K., Nitsch-Osuch, A., Konior, M., Lass, A.: Respiratory tract infections in the military environment. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 209, 76–80 (2015)
Martínek, B., Linhart, P.: Civil Protection, 1st edn. Ministry of Interior – The General Directorate of the Fire Rescue Brigade of the Czech Republic, Prague (2006)
Martinello, K., et al.: Direct identification of hazardous elements in ultra-fine and nanominerals from coal fly ash produced during diesel co-firing. Sci. Total Environ. 470–471, 444–452 (2014)
Maturo, F.: Dealing with randomness and vagueness in business and management sciences: the fuzzy-probabilistic approach as a tool for the study of statistical relationships between imprecise variables. Ratio Math. 30(1), 45–58 (2016)
Maturo, F., Hošková-Mayerová, Š.: Fuzzy Regression Models and Alternative Operations for Economic and Social Sciences. Studies in Systems, Decision and Control, pp. 235–247 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-40585-8_21
Maturo, F., Fortuna, F.: Bell-shaped fuzzy numbers associated with the normal curve. Topics on Methodological and Applied Statistical Inference, pp. 131–144 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-44093-4_13
Maturo, A., Maturo, F.: Research in Social Sciences: Fuzzy Regression and Causal Complexity. Studies in Fuzziness and Soft Computing, pp. 237–249 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-35635-3_18
Minigalieva, I.A., et al.: In vivo toxicity of copper oxide, lead oxide and zinc oxide nanoparticles acting in different combinations and its attenuation with a complex of innocuous bio-protectors. Toxicology 380, 72–93 (2017)
Mosteanu, D., Barsan, G., Otřísal, P., Giurgiu, L., Oancea, R.: Obtaining the Volatile oils from wormwood and tarragon plants by a new microwave hydrodistillation method. Revista de Chimie 68(11), 2499–2502 (2017). ISSN 0034-7752
Nindl, B.C., et al.: Physiological Employment Standards III: physiological challenges and consequences encountered during international military deployments. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 113, 2655–2672 (2013)
Niu, J., Rasmussen, P.E., Hassan, N.M., Vincent, R.: Concentration distribution and bioaccessibility of trace elements in nano and fine urban airborne particulate matter: influence of particle size. Water Air Soil Pollut. 213, 211–225 (2010)
Otřísal, P., Florus, S.: Resistance of the isolative protective garment designated for specialists´ protection against selected chlorinated hydrocarbons. Vojenské zdravotnické listy 83(1), 11–17 (2014). ISSN 0372-7025
Otřísal, P., Florus, S., Barsan, G., Mosteanu, D.: Employment of simulants for testing constructive materials designed for body surface isolative protection in relation to chemical warfare agents. Revista de Chimie 69(2), 300–304 (2018). ISSN 0034-7752
Otřísal, P., Florus, S., Švorc, Ľ., Barsan, G., Mosteanu, D.A.: New colorimetric assay for determination of selected toxic vapors and liquids permeation through barrier materials using the minitest device. Revistad De Materiale Plastice 54(4), 748–751 (2017). ISSN 0025-5289
Pedata, P., et al.: Apoptotic and proinflammatory effect of combustion generated organic nanoparticles in endothelial cells. Toxicol. Lett. 219, 307–314 (2013)
Savabieasfahani, M., et al.: Elevated titanium levels in Iraqi children with neurodevelopmental disorders echo findings in occupation soldiers. Environ. Monit. Assess. 187(4127), 1–11 (2015)
Schulte, P.A., et al.: Occupational exposure limits for nanomaterials: state of the art. J. Nanopart. Res. 12, 1971–1987 (2010)
TACZ 2010: Technological Agency of the Czech Republic, https://www.tacr.cz/index.php/en/
TSI: Aerosol Instrument Manager® Software, USA, TSI (2010)
Vávra, S., Braun, P.: Methodology of testing the content of pollutants during operation and shooting of military vehicles of the CAF, 1st edn. Military Technical Institute Division, Vyškov (2007)
Wobst, M., Wichmann, H., Bahadir, M.: Influence of heavy metals on the formation and the distribution behavior of PAH and PCDD/F during simulated fires. Chemosphere 51, 109–115 (2003)
Xiang, J., BI, P., Pisaniello, D., Hansen, A.: Health impacts of workplace heat exposure. Ind. Health 52, 91–101 (2014)
Zhao, S., Yu, Y., Yin, D., He, J.: Effective density of submicron aerosol particles in a typical valley city, Western China. Aerosol. Air Qual. Res. 17, 1–13 (2016)
Acknowledgements
The work presented in this paper was supported by a grant project run at the IACH CAS (GAP503/11/2315). The financial support of the University of Defence thanks to the specific research project (SV16-FVL-K106-KELL) is also valued.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Kellnerová, E., Binková, K., Hošková-Mayerová, Š. (2019). Assessment of the Efficiency of Respiratory Protection Devices Against Lead Oxide Nanoparticles. In: Flaut, C., Hošková-Mayerová, Š., Flaut, D. (eds) Models and Theories in Social Systems. Studies in Systems, Decision and Control, vol 179. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-00084-4_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-00084-4_14
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-00083-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-00084-4
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)