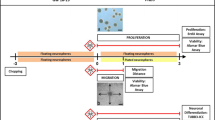
Abstract
The human developing central nervous system is more vulnerable to the adverse effects of chemical agents than the adult brain. At present, due to the lack of available data on human neurodevelopmental toxicants, there is an urgent need for testing and subsequently regulating chemicals for their potential to interfere with nervous system development. Alternative testing strategies might fill that gap as they allow fast and resource-efficient compound screenings for a variety of neurodevelopmental endpoints. Nervous system development is complex calling for a battery of tests that cover early and late developmental stages and a variety of neurodevelopmental processes. One of such assays is the “neurosphere assay,” an in vitro 3D model for developmental neurotoxicity (DNT) evaluation based on human neural progenitor cells. With this assay, one can identify compounds that disturb basic neurodevelopmental processes, such as NPC proliferation, migration, neuronal- and oligodendrocyte differentiation, as well as thyroid hormone (TH)-dependent oligodendrocyte maturation. By including viability and cytotoxicity assays into the workflow, the assays allow the distinction of specific DNT from general cytotoxicity. This chapter explains how the different test methods of the “neurosphere assay,” i.e., NPC1–6, are performed and how some of them can be multiplexed in a time- and cost-efficient manner.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennett D, Bellinger D, Health LB-E et al (2016) Project TENDR: targeting environmental neuro-developmental risks. the TENDR consensus statement. Environ Health Perspect 124:A118–A122
Grandjean P, Landrigan P (2006) Developmental neurotoxicity of industrial chemicals. Lancet 368:2167–2178
Grandjean P, Landrigan PJ (2014) Neurobehavioural effects of developmental toxicity. Lancet Neurol 13:330–338
Schettler T (2001) Toxic threats to neurologic development of children. Environ Health Perspect 109:813–816
Crofton KM, Mundy WR, Shafer TJ (2012) Developmental neurotoxicity testing: a path forward. Congenit Anom (Kyoto) 52:140–146
Goldman LR, Koduru S (2000) Chemicals in the environment and developmental toxicity to children: a public health and policy perspective. Environ Health Perspect 108(Suppl 3):443–448
US-EPA (1998) Health effects test guidelines OPPTS 870.6300. Dev Neurotox Study EPA 712-C-98-239
OECD (2007) OECD guidelines for the testing of chemicals/section 4: Health effects. Test no. 426: developmental neurotoxicity study. Dev Neurotox study P.26
Lein P, Silbergeld E, Locke P et al (2005) In vitro and other alternative approaches to developmental neurotoxicity testing (DNT). Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 19:735–744
Bal-Price A, Crofton KM, Leist M et al (2015) International STakeholder NETwork (ISTNET): creating a developmental neurotoxicity (DNT) testing road map for regulatory purposes. Arch Toxicol 89:269–287
Bal-Price A, Hogberg HT, Crofton KM et al (2018) Recommendation on test readiness criteria for new approach methods in toxicology: exemplified for developmental neurotoxicity. Altex 35:306–352
Bal-Price AK, Coecke S, Costa L et al (2012) Conference report: advancing the science of developmental neurotoxicity (DNT): testing for better safety evaluation. ALTEX 29:202–215
Crofton KM, Mundy WR, Lein PJ et al (2011) Developmental neurotoxicity testing: recommendations for developing alternative methods for the screening and prioritization of chemicals. ALTEX 28:9–15
Fritsche E, Crofton KM, Hernandez AF et al (2017) OECD/EFSA workshop on developmental neurotoxicity (DNT): the use of non-animal test methods for regulatory purposes. ALTEX 34:311–315
Fritsche E, Grandjean P, Crofton KM et al (2018) Consensus statement on the need for innovation, transition and implementation of developmental neurotoxicity (DNT) testing for regulatory purposes. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 354:3–6
Lein P, Locke P, Goldberg A (2007) Meeting report: alternatives for developmental neurotoxicity testing. Environ Health Perspect 115:764–768
Fritsche E (2016) Report on integrated testing strategies for the identification and evaluation of chemical hazards associated with the developmental neurotoxicity (DNT). In: Report of the OECD/EFSA workshop on developmental neurotoxicity (DNT): the use of non-animal test. OECD Environ Heal Saf Publications Ser Test Assess 242
Dach K, Bendt F, Huebenthal U et al (2017) BDE-99 impairs differentiation of human and mouse NPCs into the oligodendroglial lineage by species-specific modes of action. Sci Rep 7:1–11
Gassmann K, Abel J, Bothe H et al (2010) Species-specific differential AhR expression protects human neural progenitor cells against developmental neurotoxicity of PAHs. Environ Health Perspect 118:1571–1577
Gold LS, Manley NB, Slone TH et al (2005) Supplement to the carcinogenic potency database (CPDB): results of animal bioassays published in the general literature through 1997 and by the national toxicology program in 1997–1998. Toxicol Sci 85:747–808
Knight A (2008) Systematic reviews of animal experiments demonstrate poor contributions toward human healthcare. Rev Recent Clin Trials 3:89–96
Leist M, Hartung T (2013) Reprint: inflammatory findings on species extrapolations: humans are definitely no 70-kg mice1. ALTEX 30:227–230
Masjosthusmann S, Becker D, Petzuch B et al (2018) A transcriptome comparison of time-matched developing human, mouse and rat neural progenitor cells reveals human uniqueness. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 354:40–55
Seok J, Warren HS, Cuenca AG et al (2013) Genomic responses in mouse models poorly mimic human inflammatory diseases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:3507–3512
Baumann J, Barenys M, Gassmann K, Fritsche E (2014) Comparative human and rat “neurosphere assay” for developmental neurotoxicity testing. In: Costa LG, Davila JC, Lawrence DA, Reed DJ (eds) Current protocols in toxicology, vol 59. Wiley, pp 12.21.1–12.21.24. https://doi.org/10.1002/0471140856.tx1221s59
Baumann J, Gassmann K, Masjosthusmann S, DeBoer D, Bendt F, Giersiefer S, Fritsche E (2016) Comparative human and rat neurospheres reveal species differences in chemical effects on neurodevelopmental key events. Arch Toxicol 90:1415–1427
Tang H, Hammack C, Ogden SC et al (2016) Zika virus infects human cortical neural progenitors and attenuates their growth. Cell Stem Cell 18:587–590
Baumann J, Dach K, Barenys M, Giersiefer S, Goniwiecha J, Lein PJ, Fritsche E (2015) Application of the Neurosphere assay for DNT Hazard assessment: challenges and limitations. Humana Press, Totowa, pp 1–29
Gassmann K, Baumann J, Giersiefer S, Schuwald J, Schreiber T, Merk HF, Fritsche E (2012) Automated neurosphere sorting and plating by the COPAS large particle sorter is a suitable method for high-throughput 3D in vitro applications. Toxicol In Vitro 26:993–1000
Moors M, Rockel TD, Abel J, Cline JE, Gassmann K, Schreiber T, Schuwald J, Weinmann N, Fritsche E (2009) Human neurospheres as three-dimensional cellular systems for developmental neurotoxicity testing. Environ Health Perspect 117:1131–1138
Schreiber T, Gassmann K, Götz C et al (2010) Polybrominated diphenyl ethers induce developmental neurotoxicity in a human in vitro model: evidence for endocrine disruption. Environ Health Perspect 118:572–578
Tofighi R, Wan Ibrahim WN, Rebellato P et al (2011) Non-dioxin-like polychlorinated biphenyls interfere with neuronal differentiation of embryonic neural stem cells. Toxicol Sci 124:192–201
Choi BH (1989) The effects of methylmercury on the developing brain. Prog Neurobiol 32:447–470
Moors M, Cline JE, Abel J, Fritsche E (2007) ERK-dependent and -independent pathways trigger human neural progenitor cell migration. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 221:57–67
Edoff K, Raciti M, Moors M et al (2017) Gestational age and sex influence the susceptibility of human neural progenitor cells to low levels of MeHg. Neurotox Res 32:683–693
Fritsche E, Barenys M, Klose J, Masjosthusmann S, Nimtz L, Schmuck M, Wuttke S, Tigges J (2018) Current availability of stem cell-based in vitro methods for developmental neurotoxicity (DNT) testing. Toxicol Sci 165:21–30
Barenys M, Gassmann K, Baksmeier C, Heinz S, Reverte I, Schmuck M, Temme T, Bendt F, Zschauer TC, Rockel TD (2017) Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) inhibits adhesion and migration of neural progenitor cells in vitro. Arch Toxicol 91:827–837
Schmuck MR, Temme T, Dach K et al (2017) Omnisphero: a high-content image analysis (HCA) approach for phenotypic developmental neurotoxicity (DNT) screenings of organoid neurosphere cultures in vitro. Arch Toxicol 91:2017–2028
Bal-Price A, Lein PJ, Keil KP, Sethi S, Shafer T, Barenys M, Fritsche E, Sachana M, Meek MEB (2017) Developing and applying the adverse outcome pathway concept for understanding and predicting neurotoxicity. Neurotoxicology 59:240–255
Moors M, Bose R, Johansson-Hague K et al (2012) Dickkopf 1 mediates glucocorticoid-induced changes in human neural progenitor cell proliferation and differentiation. Toxicol Sci 125:488–495
TECHNICAL BULLETIN, CellTiter-Blue® cell viability assay, revised 3/16, TB317, Promega, USA
TECHNICAL BULLETIN, CytoTox-ONE™ homogeneous membrane integrity assay, revised 5/09, TB306, Promega, USA
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Nimtz, L., Klose, J., Masjosthusmann, S., Barenys, M., Fritsche, E. (2019). The Neurosphere Assay as an In Vitro Method for Developmental Neurotoxicity (DNT) Evaluation. In: Aschner, M., Costa, L. (eds) Cell Culture Techniques. Neuromethods, vol 145. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-9228-7_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-9228-7_8
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4939-9227-0
Online ISBN: 978-1-4939-9228-7
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols