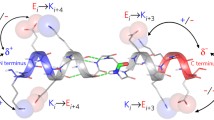
Abstract
Stable, single α-helical (SAH) domains exist in a number of unconventional myosin isoforms, as well as other proteins. These domains are formed from sequences rich in charged residues (Arg, Lys, and Glu), they can be hundreds of residues long, and in isolation they can tolerate significant changes in pH and salt concentration without loss in helicity. Here we describe methods for the preparation and purification of SAH domains and SAH domain-containing constructs, using the myosin 10 SAH domain as an example. We go on to describe the use of circular dichroism spectroscopy and force spectroscopy with the atomic force microscope for the elucidation of structural and mechanical properties of these unusual helical species.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Knight PJ, Thirumurugan K, Xu Y, Wang F, Kalverda AP, Stafford WF III, Sellers JR, Peckham M, (2005) The Predicted Coiled-coil Domain of Myosin 10 Forms a Novel Elongated Domain That Lengthens the Head. J Biol Chem 280:34702–34708
Spink BJ, Sivaramakrishnan S, Lipfert J, Doniach S, Spudich JA (2008) Long single alpha-helical tail domains bridge the gap between structure and function of myosin VI. Nat Struct Mol Biol 15:591–597
Baboolal TG, Sakamoto T, Forgacs E, White HD, Jackson SM, Takagi Y, Farrow RE, Molloy JE, Knight PJ, Sellers JR, Peckham M (2009) The SAH domain extends the functional length of the myosin lever. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:22193–22198
Li J, Chen Y, Deng Y, Unarta IC, Lu Q, Huang X, Zhang M (2017) Ca2+-induced rigidity change of the myosin VIIa IQ motif-single α helix lever arm extension. Structure 25:579–591
Yang Y, Baboolal TG, Siththanandan V, Chen M, Walker ML, Knight PJ, Peckham M, Sellers JR (2009) A FERM domain autoregulates Drosophila myosin 7a activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:4189–4194
Peckham M, Knight PJ (2009) When a predicted coiled coil is really a single α-helix, in myosins and other proteins. Soft Matter 5:2493–2503
Wolny M, Batchelor M, Knight PJ, Paci E, Dougan L, Peckham M (2014) Stable single α-helices are constant force springs in proteins. J Biol Chem 289:27825–27835
Wang CL, Chalovich JM, Graceffa P, Lu RC, Mabuchi K, Stafford W (1991) A long helix from the central region of smooth muscle caldesmon. J Biol Chem 266:13958–13963
Sivaramakrishnan S, Sung J, Ali M, Doniach S, Flyvbjerg H, Spudich JA (2009) Combining single-molecule optical trapping and small-angle X-ray scattering measurements to compute the persistence length of a protein ER/K α-helix. Biophys J 97:2993–2999
Samejima K, Platani M, Wolny M, Ogawa H, Vargiu G, Knight PJ, Peckham M, Earnshaw WC (2015) The inner centromere protein (INCENP) coil is a single α-helix (SAH) domain that binds directly to microtubules and is important for chromosome passenger complex (CPC) localization and function in mitosis. J Biol Chem 290:21460–21472
Wolny M, Batchelor M, Bartlett GJ, Baker EG, Kurzawa M, Knight PJ, Dougan L, Woolfson DN, Paci E, Peckham M (2017) Characterization of long and stable de novo single alpha-helix domains provides novel insight into their stability. Sci Rep 7:44341
Greenfield NJ (2006) Using circular dichroism spectra to estimate protein secondary structure. Nat Protoc 1:2876–2890
Greenfield NJ (2006) Using circular dichroism collected as a function of temperature to determine the thermodynamics of protein unfolding and binding interactions. Nat Protoc 1:2527–2535
Wolny M, Colegrave M, Colman L, White E, Knight PJ, Peckham M (2013) Cardiomyopathy mutations in the tail of β-cardiac myosin modify the coiled-coil structure and affect integration into thick filaments in muscle sarcomeres in adult cardiomyocytes. J Biol Chem 288:31952–31962
Mitsui K, Hara M, Ikai A (1996) Mechanical unfolding of α2-macroglobulin molecules with atomic force microscope. FEBS Lett 385:29–33
Rief M, Gautel M, Oesterhelt F, Fernandez JM, Gaub HE (1997) Reversible unfolding of individual titin immunoglobulin domains by AFM. Science 276:1109–1112
Hoffmann T, Dougan L (2012) Single molecule force spectroscopy using polyproteins. Chem Soc Rev 41:4781–4796
Best RB, Li B, Steward A, Daggett V, Clarke J (2001) Can non-mechanical proteins withstand force? Stretching barnase by atomic force microscopy and molecular dynamics simulation. Biophys J 81:2344–2356
Li H, Oberhauser AF, Redick SD, Carrion-Vazquez M, Erickson HP, Fernandez JM (2001) Multiple conformations of PEVK proteins detected by single-molecule techniques. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:10682–10686
Oroz J, Hervas R, Valbuena A, Carrion-Vazquez M (2012) Unequivocal single-molecule force spectroscopy of intrinsically disordered proteins. Methods Mol Biol 896:71–87
Tskhovrebova L, Trinick J, Sleep JA, Simmons RM (1997) Elasticity and unfolding of single molecules of the giant muscle protein titin. Nature 387:308–312
Carrion-Vazquez M, Oberhauser AF, Fowler SB, Marszalek PE, Broedel SE, Clarke J, Fernandez JM (1999) Mechanical and chemical unfolding of a single protein: a comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:3694–3699
Improta S, Politou AS, Pastore A (1996) Immunoglobulin-like modules from titin I-band: extensible components of muscle elasticity. Structure 4:323–337
Brockwell DJ, Beddard GS, Clarkson J, Zinober RC, Blake AW, Trinick J, Olmsted PD, Smith DA, Radford SE (2002) The effect of core destabilization on the mechanical resistance of I27. Biophys J 83:458–472
Muller S, Hoege C, Pyrowolakis G, Jentsch S (2001) SUMO, ubiquitin’s mysterious cousin. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2:202–210
Zinober RC, Brockwell DJ, Beddard GS, Blake AW, Olmsted PD, Radford SE, Smith DA (2002) Mechanically unfolding proteins: the effect of unfolding history and the supramolecular scaffold. Protein Sci 11:2759–2765
Lobley A, Whitmore L, Wallace BA (2002) DICHROWEB: an interactive website for the analysis of protein secondary structure from circular dichroism spectra. Bioinformatics 18:211–212
Whitmore L, Wallace BA (2004) DICHROWEB, an online server for protein secondary structure analyses from circular dichroism spectroscopic data. Nucleic Acids Res 32:W668–W673
Kelly SM, Jess TJ, Price NC (2005) How to study proteins by circular dichroism. Biochim Biophys Acta 1751:119–139
Greenfield N, Fasman GD (1969) Computed circular dichroism spectra for the evaluation of protein conformation. Biochemistry 8:4108–4116
Chen YH, Yang JT, Chau KH (1974) Determination of the helix and β form of proteins in aqueous solution by circular dichroism. Biochemistry 13:3350–3359
Woody RW (1995) Circular dichroism. Methods Enzymol 246:34–71
Law R, Carl P, Harper S, Dalhaimer P, Speicher DW, Discher DE (2003) Cooperativity in forced unfolding of tandem spectrin repeats. Biophys J 84:533–544
Hutter J, Bechhoefer J (1993) Calibration of atomic-force microscope tips. Rev Sci Instrum 64:1868–1873
Cappella B, Dietler G (1999) Force-distance curves by atomic force microscopy. Surf Sci Rep 34:1–104
Rounsevell R, Forman JR, Clarke J (2004) Atomic force microscopy: mechanical unfolding of proteins. Methods 34:100–111
Zocher M, Zhang C, Rasmussen SG, Kobilka BK, Muller DJ (2012) Cholesterol increases kinetic, energetic, and mechanical stability of the human β2-adrenergic receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:E3463–E3472
Leitner M, Fantner GE, Fantner EJ, Ivanova K, Ivanov T, Rangelow I, Ebner A, Rangl M, Tang J, Hinterdorfer P (2012) Increased imaging speed and force sensitivity for bio-applications with small cantilevers using a conventional AFM setup. Micron 43:1399–1407
Berkemeier F, Bertz M, Xiao S, Pinotsis N, Wilmanns M, Grater F, Rief M (2011) Fast-folding α-helices as reversible strain absorbers in the muscle protein myomesin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:14139–14144
Smith PK, Krohn RI, Hermanson GT, Mallia AK, Gartner FH, Provenzano MD, Fujimoto EK, Goeke NM, Olson BJ, Klenk DC (1985) Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem 150:76–85
Edelhoch H (1967) Spectroscopic determination of tryptophan and tyrosine in proteins. Biochemistry 6:1948–1954
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council grants BB/I007423/1 and BB/M009114/1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Batchelor, M., Wolny, M., Kurzawa, M., Dougan, L., Knight, P.J., Peckham, M. (2018). Determining Stable Single Alpha Helical (SAH) Domain Properties by Circular Dichroism and Atomic Force Microscopy. In: Lavelle, C. (eds) Molecular Motors. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 1805. Humana Press, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-8556-2_10
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-8556-2_10
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana Press, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4939-8554-8
Online ISBN: 978-1-4939-8556-2
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols