Abstract
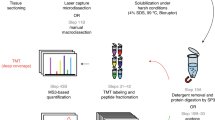
Laser microdissection-based proteomics on formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded tissues is usually performed from relatively large tissue areas or pools of multiple tissue pieces. However, several molecular pathology studies require working on very limited amounts of tissue. This is for example the case when very early cancer lesions have to be handled. Hereby, we present a method for the processing of very small pieces of formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded tissues for proteomic purposes. This approach is designed in order to avoid sample loss during technical processing and to optimize the digestion of tissue areas containing as little as 2700 cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Emmert-Buck MR, Bonner RF, Smith PD et al (1996) Laser capture microdissection. Science 274:998–1001
Wisniewski JR, Ostasiewicz P, Mann M (2011) High recovery FASP applied to the proteomic analysis of microdissected formalin fixed paraffin embedded cancer tissues retrieves known colon cancer markers. J Proteome Res 10:3040–3049
De Marchi T, Braakman RB, Stingl C et al (2016) The advantage of laser-capture microdissection over whole tissue analysis in proteomic profiling studies. Proteomics 16:1474–1485
Delahunty C, Yates JR III (2005) Protein identification using 2D-LC-MS/MS. Methods 35:248–255
Wisniewski JR (2013) Proteomic sample preparation from formalin fixed and paraffin embedded tissue. J Vis Exp (79)
Michalski A, Damoc E, Hauschild JP et al (2011) Mass spectrometry-based proteomics using Q Exactive, a high-performance benchtop quadrupole Orbitrap mass spectrometer. Mol Cell Proteomics 10:M111.011015
Beck S, Michalski A, Raether O et al (2015) The impact II, a very high-resolution quadrupole time-of-flight instrument (QTOF) for deep shotgun proteomics. Mol Cell Proteomics 14:2014–2029
Longuespée R, Fléron M, Pottier C et al (2014) Tissue proteomics for the next decade? Towards a molecular dimension in histology. OMICS 18:539–552
Longuespée R, Alberts D, Pottier C et al (2016) A laser microdissection-based workflow for FFPE tissue microproteomics: important considerations for small sample processing. Methods 104:154–162
Herfs M, Longuespée R, Quick CM et al (2016) Proteomic signatures reveal a dualistic and clinically relevant classification of anal canal carcinoma. J Pathol 241:522–533
Longuespée R, Casadonte R, Kriegsmann M et al (2016) Proteomic investigation of human cystic echinococcosis in the liver. Mol Biochem Parasitol 211:9–14
Fox CH, Johnson FB, Whiting J, Roller PP (1985) Formaldehyde fixation. J Histochem Cytochem 33:845–853
Marée R, Rollus L, Stevens B et al (2016) Collaborative analysis of multi-gigapixel imaging data using Cytomine. Bioinformatics 32:1395–1401
Tyanova S, Temu T, Cox J (2016) The MaxQuant computational platform for mass spectrometry-based shotgun proteomics. Nat Protoc 11:2301–2319
Tyanova S, Temu T, Sinitcyn P et al (2016) The Perseus computational platform for comprehensive analysis of (prote)omics data. Nat Methods 13:731–740
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge Lisette Trzpiot and Nancy Rosiere for their efficient technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Longuespée, R., Baiwir, D., Mazzucchelli, G., Smargiasso, N., De Pauw, E. (2018). Laser Microdissection-Based Microproteomics of Formalin-Fixed and Paraffin-Embedded (FFPE) Tissues. In: Murray, G. (eds) Laser Capture Microdissection. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 1723. Humana Press, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-7558-7_2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-7558-7_2
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana Press, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4939-7557-0
Online ISBN: 978-1-4939-7558-7
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols