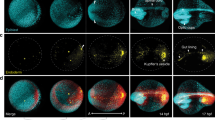
Abstract
During vertebrate development, Erk is activated and regulates multiple cellular processes such as cell growth, differentiation, migration, and adhesion in a spatiotemporal manner. Whole-mount immunohistochemistry using antibodies against diphosphorylated Erk (p-Erk; active form of Erk) is a very useful method for understanding the spatial and temporal patterns of Erk activity during embryonic development. However, the fixation step of this method stops embryo development at a certain time point, making it very difficult to observe and interpret Erk activity dynamics. In this chapter, we describe a strategy that combines immunohistochemistry and quantitative analyses of multiple fixed embryos to reconstruct Erk activity dynamics during zebrafish somitogenesis.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pourquie O (2001) Vertebrate somitogenesis. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 17:311–350
Bessho Y, Kageyama R (2003) Oscillations, clocks and segmentation. Curr Opin Genet Dev 13:379–384
Hubaud A, Pourquie O (2014) Signalling dynamics in vertebrate segmentation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 15:709–721
Holley S, Takeda H (2002) Catching a wave: the oscillator and wavefront that create the zebrafish somite. Semin Cell Dev Biol 13: 481–488
Dubrulle J, McGrew MJ, Pourquie O (2001) FGF signaling controls somite boundary position and regulates segmentation clock control of spatiotemporal hox gene activation. Cell 106:219–232
Sawada A, Shinya M, Jiang YJ et al (2001) Fgf/MAPK signalling is a crucial positional cue in somite boundary formation. Development 128:4873–4880
Akiyama R, Masuda M, Tsuge S et al (2014) An anterior limit of FGF/Erk signal activity marks the earliest future somite boundary in zebrafish. Development 141:1104–1109
Niwa Y, Masamizu Y, Liu T et al (2007) The initiation and propagation of Hes7 oscillation are cooperatively regulated by Fgf and notch signaling in the somite segmentation clock. Dev Cell 13:298–304
Dorey K, Amaya E (2010) FGF signalling: diverse roles during early vertebrate embryogenesis. Development 137:3731–3742
Tsang M, Dawid IB (2004) Promotion and attenuation of FGF signaling through the ras-MAPK pathway. Sci STKE 228:ep17
Matsui T, Thitamadee S, Murata T et al (2011) Canopy1, a positive feedback regulator of FGF signaling, controls progenitor cell clustering during Kupffer’s vesicle organogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:9881–9886
Henry CA, Urban MK, Dill KK et al (2002) Two linked hairy/enhancer of split-related zebrafish genes, her1 and her7, function together to refine alternating somite boundaries. Development 129:3693–3704
Acknowledgement
We thank Fiqri Dizar Khaidizar and Ryutaro Akiyama for critical reading of the manuscript. We are grateful to the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT), the Uehara Memorial Foundation, the Nakajima Foundation and the Mochida Memorial Foundation for past and current support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Matsui, T., Bessho, Y. (2017). Analyzing ERK Signal Dynamics During Zebrafish Somitogenesis. In: Jimenez, G. (eds) ERK Signaling. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 1487. Humana Press, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-6424-6_27
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-6424-6_27
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana Press, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4939-6422-2
Online ISBN: 978-1-4939-6424-6
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols