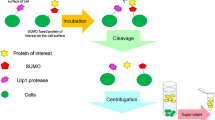
Abstract
Maltose-Binding Protein (MBP) is one of the most popular fusion partners being used for producing recombinant proteins in bacterial cells. MBP allows the use of a simple capture affinity step on Amylose-Agarose or Dextrin-Sepharose columns, resulting in a protein that is often 70–90 % pure in a single step. In addition to protein isolation applications, MBP provides a high degree of translation, and facilitates the proper folding and solubility of the target protein. This paper describes efficient procedures for isolating highly purified MBP target proteins. Special attention is given to considerations for downstream applications such as structural determination studies, protein activity assays, and assessing the chemical characteristics of the target protein.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nikaido H (1994) Maltose transport system of Escherichia coli: an ABC-type transporter. FEBS Lett 346:55–58
Baneyx F, Mujacic M (2004) Recombinant protein folding and misfolding in Escherichia coli. Nat Biotechnol 22:1399–1408
Randall LL, Topping TB, Smith VF, Diamond DL, Hardy SJ (1998) SecB: a chaperone from Escherichia coli. Methods Enzymol 290:444–459
Nomine Y, Ristriani T, Laurent C, Lefevre JF, Weiss E, Trave G (2001) A strategy for optimizing the monodispersity of fusion proteins: application to purification of recombinant HPV E6 oncoprotein. Protein Eng 14:297–305
Sachdev D, Chirgwin JM (1998) Order of fusions between bacterial and mammalian proteins can determine solubility in Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 244:933–937
Nallamsetty S, Waugh DS (2006) Solubility-enhancing proteins MBP and NusA play a passive role in the folding of their fusion partners. Protein Expr Purif 45:175–182
Raran-Kurussi S, Waugh DS (2012) The ability to enhance the solubility of its fusion partners is an intrinsic property of maltose-binding protein but their folding is either spontaneous or chaperone-mediated. PLoS One 7(11):e49589
Lebendiker M, Danieli T (2014) Production of prone to aggregate proteins. FEBS Lett 588:236–246. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2013.10.044
Clifton M et al (2015) A maltose-binding protein fusion construct yields a robust crystallography platform for MCL1. PLoS One 10(4):e0125010
Moon A et al (2010) A synergistic approach to protein crystallization: combination of a fixed-arm carrier with surface entropy reduction. Protein Sci 19(5):901–913
Sheffield P, Garrard S, Derewenda Z (1999) Overcoming expression and purification problems of RhoGDI using a family of “parallel” expression vectors. Protein Expr Purif 15(1):34–39
Lebendiker M, Maes M, Friedler A (2015) A screening methodology for purifying proteins with aggregation problems. Methods Mol Biol 1258:261–281
Kapust RB, Waugh DS (2000) Controlled intracellular processing of fusion proteins by TEV protease. Protein Expr Purif 19:312–318
Nallamsetty S, Waugh DS (2007) A generic protocol for the expression and purification of recombinant proteins in Escherichia coli using a combinatorial His6-maltose binding protein fusion tag. Nat Protoc 2:383–391
Mohanty A, Simmons CR, Wiener MC (2003) Inhibition of tobacco etch virus protease activity by detergents. Protein Expr Purif 27:109–114
Kapust RB, Tözsér J, Fox JD, Anderson DE, Cherry S, Copeland TD, Waugh DS (2001) Tobacco etch virus protease: mechanism of autolysis and rational design of stable mutants with wild-type catalytic efficiency. Protein Eng 14:993–1000
Nallamsetty S, Austin BP, Penrose KJ, Waugh DS (2005) Gateway vectors for the production of combinatorially-tagged His6-MBP fusion proteins in the cytoplasm and periplasm of Escherichia coli. Protein Sci 14:2964–2971
Kobe B, Ve T, Williams S (2015) Fusion-protein-assisted protein crystallization. Acta Crystallogr F71:861–869
Smith D (2003) Crystal structures of fusion proteins with large-affinity tags. Protein Sci 12:1313–1322
Golovanov AP, Hautbergue GM, Wilson SA, Lian LY (2004) A simple method for improving protein solubility and long-term stability. J Am Chem Soc 126:8933–8939
Riggs P (2000) Expression and purification of recombinant proteins by fusion to maltose-binding protein. Mol Biotechnol 15:51–63
Tropea JE, Cherry S, Nallamsetty S, Bignon C, Waugh DS (2007) A generic method for the production of recombinant proteins in Escherichia coli using a dual His6-MBP affinity tag. Methods Mol Biol 363:1–19
Austin BP, Nallamsetty S, Waugh DS (2009) Hexahistidine-tagged maltose-binding protein as a fusion partner for the production of soluble recombinant proteins in Escherichia coli. Methods Mol Biol 498:157–172
Pattenden LK, Thomas WG (2008) Amylose affinity chromatography of maltose-binding protein: purification by both native and novel matrix-assisted dialysis refolding methods. Methods Mol Biol 421:169–189
Nettleship JE, Brown J, Groves MR et al (2008) Methods for protein characterization by mass spectrometry, thermal shift (thermofluor) assay, and multiangle or static light scattering. Methods Mol Biol 426:299–318
Raynal B, Lenormand P, Baron B, Hoos S, England P (2014) Quality assessment and optimization of purified protein samples: why and how? Microb Cell Fact 13:180
Lebendiker M, Danieli T, de Marco A (2014) The Trip Adviser guide to the protein science world: a proposal to improve the awareness concerning the quality of recombinant proteins. BMC Res Notes 7:585
Sahin E, Roberts C (2012) Size-exclusion chromatography with multi-angle light scattering for elucidating protein aggregation mechanisms. In: Voynov V, Caravella JA (eds) Therapeutic proteins: methods and protocols, vol 899, Methods in molecular biology. Humana, Totowa, NJ, pp 403–423
Ye H (2006) Simultaneous determination of protein aggregation, degradation, and absolute molecular weight by size exclusion chromatography multiangle laser light scattering. Anal Biochem 356:76–85
Acknowledgments
We thank Nina Vinograd from the Biological Chemistry Department of The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, for cloning, and expressing the fusion protein, and Hadar Amarteli from the Institute of Chemistry, Hebrew University of Jerusalem, for performing the analysis of the SEC-MALS results.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Lebendiker, M., Danieli, T. (2017). Purification of Proteins Fused to Maltose-Binding Protein. In: Walls, D., Loughran, S. (eds) Protein Chromatography. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 1485. Humana Press, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-6412-3_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-6412-3_13
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana Press, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4939-6410-9
Online ISBN: 978-1-4939-6412-3
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols