Abstract
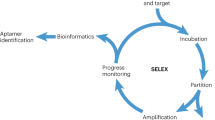
Systematic Evolution of Ligands by Exponential Enrichment (SELEX) is an in vitro process enabling selection of nucleic acid molecules binding to target ligands with high binding affinity and specificity. The selection process involves several rounds of two successive steps: (1) binding of the oligonucleotides to the target under stringent conditions and (2) amplification of the target-bound nucleic acids by polymerase chain reaction. Using this strategy, RNA or DNA aptamers are selected upon recognition and binding to specific surface structures of the target. Aptamers generated during the final rounds of selection can be notably used in applications dedicated to diagnosis of diseases or therapeutic approaches.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tuerk C, Gold L (1990) Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment: RNA ligands to bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase. Science 249:505–510
Ellington AD, Szostak JW (1990) In vitro selection of RNA molecules that bind specific ligands. Nature 346:818–822
Patel DJ (1997) Structural analysis of nucleic acid aptamers. Curr Opin Chem Biol 1:32–46
Hermann T, Patel DJ (2000) Adaptive recognition by nucleic acid aptamers. Science 287:820–825
Patel DJ, Suri AK (2000) Structure, recognition and discrimination in RNA aptamer complexes with cofactors, amino acids, drugs and aminoglycoside antibiotics. J Biotechnol 74:39–60
Schneider DJ, Feigon J, Hostomsky Z et al (1995) High-affinity ssDNA inhibitors of the reverse transcriptase of type 1 human immunodeficiency virus. Biochemistry 34:9599–9610
Mosing RK, Mendonsa SD, Bowser MT (2005) Capillary electrophoresis-SELEX selection of aptamers with affinity for HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Anal Chem 77:6107–6112
Chen F, Hu Y, Li D et al (2009) CS-SELEX generates high-affinity ssDNA aptamers as molecular probes for hepatitis C virus envelope glycoprotein E2. PLoS One 4:e8142
Kawakami J, Imanaka H, Yokota Y et al (2000) In vitro selection of aptamers that act with Zn2+. J Inorg Biochem 82:197–206
Mann D, Reinemann C, Stoltenburg R et al (2005) In vitro selection of DNA aptamers binding ethanolamine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 338:1928–1934
Lauhon CT, Szostak JW (1995) RNA aptamers that bind flavin and nicotinamide redox cofactors. J Am Chem Soc 117:1246–1257
Holland CA, Henry AT, Whinna HC et al (2000) Effect of oligodeoxynucleotide thrombin aptamer on thrombin inhibition by heparin cofactor II and antithrombin. FEBS Lett 484:87–91
Bruno JG, Carrillo MP, Phillips T et al (2008) Competitive FRET-aptamer-based detection of methylphosphonic acid, a common nerve agent metabolite. J Fluoresc 18:867–876
Ruckman J, Green LS, Beeson J et al (1998) 2′-Fluoropyrimidine RNA-based aptamers to the 165-amino acid form of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF165). Inhibition of receptor binding and VEGF-induced vascular permeability through interactions requiring the exon 7-encoded domain. J Biol Chem 273:20556–20567
White R, Rusconi C, Scardino E et al (2001) Generation of species cross-reactive aptamers using “toggle” SELEX. Mol Ther 4:567–573
Savla R, Taratula O, Garbuzenko O et al (2011) Tumor targeted quantum dot-mucin 1 aptamer-doxorubicin conjugate for imaging and treatment of cancer. J Control Release 153:16–22
Tang Z, Parekh P, Turner P et al (2009) Generating aptamers for recognition of virus-infected cells. Clin Chem 55:813–822
Hamula CL, Le XC, Li XF (2011) DNA aptamers binding to multiple prevalent M-types of Streptococcus pyogenes. Anal Chem 83:3640–3647
Kolesnikova O, Kazakova H, Comte C et al (2010) Selection of RNA aptamers imported into yeast and human mitochondria. RNA 16:926–941
Stoltenburg R, Reinemann C, Strehlitz B (2005) FluMag-SELEX as an advantageous method for DNA aptamer selection. Anal Bioanal Chem 383:83–91
Bianchini M, Radrizzani M, Brocardo MG et al (2001) Specific oligobodies against ERK-2 that recognize both the native and the denatured state of the protein. J Immunol Methods 252:191–197
Fitzwater T, Polisky B (1996) A SELEX primer. Methods Enzymol 267:275–301
Schutze T, Wilhelm B, Greiner N et al (2011) Probing the SELEX process with next-generation sequencing. PLoS One 6:e29604
Zuker M (2003) Mfold web server for nucleic acid folding and hybridization prediction. Nucleic Acids Res 31:3406–3415
Famulok M, Hartig JS, Mayer G (2007) Functional aptamers and aptazymes in biotechnology, diagnostics, and therapy. Chem Rev 107:3715–3743
Tucker CE, Chen LS, Judkins MB et al (1999) Detection and plasma pharmacokinetics of an anti-vascular endothelial growth factor oligonucleotide-aptamer (NX1838) in rhesus monkeys. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl 732:203–212
Ng EW, Shima DT, Calias P et al (2006) Pegaptanib, a targeted anti-VEGF aptamer for ocular vascular disease. Nat Rev Drug Discov 5:123–132
Higgins DG, Thompson JD, Gibson TJ (1996) Using CLUSTAL for multiple sequence alignments. Methods Enzymol 266:383–402
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP et al (2007) Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 23:2947–2948
Schneider TD, Stephens RM (1990) Sequence logos: a new way to display consensus sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 18:6097–6100
Crooks GE, Hon G, Chandonia JM et al (2004) WebLogo: a sequence logo generator. Genome Res 14:1188–1190
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Dickinson, H., Lukasser, M., Mayer, G., Hüttenhofer, A. (2015). Cell-SELEX: In Vitro Selection of Synthetic Small Specific Ligands. In: Rederstorff, M. (eds) Small Non-Coding RNAs. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 1296. Humana Press, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-2547-6_20
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-2547-6_20
Publisher Name: Humana Press, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4939-2546-9
Online ISBN: 978-1-4939-2547-6
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols