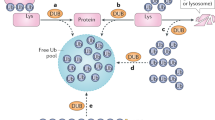
Abstract
A key regulatory node in NF-κB signaling is the removal of the IκBα inhibitor, whose levels are tightly controlled by the ubiquitin–proteasome system. In response to signal activation and transmission, ubiquitin E1, E2, and E3 enzymes are employed to generate a lysine 48-linked ubiquitin chain that triggers degradation of IκBα by the proteasome. In this chapter we describe an in vitro biochemical approach to reconstitute the ubiquitination system. To do so, we detail methods for the preparation of the relevant enzymes and substrate, as well as for the execution of the reaction with high efficiency. This sensitive and highly reproducible readout can be applied to the study of proteins, small molecules, and other factors that modulate IκBα ubiquitination, thereby producing outcomes that impact NF-κB signaling to advance the course of improving human health.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Skaug B, Jiang X, Chen ZJ (2009) The role of ubiquitin in NF-kappaB regulatory pathways. Annu Rev Biochem 78:769–796
Chen ZJ, Parent L, Maniatis T (1996) Site-specific phosphorylation of IkappaBalpha by a novel ubiquitination-dependent protein kinase activity. Cell 84:853–862
Scherer DC, Brockman JA, Chen Z et al (1995) Signal-induced degradation of I kappa B alpha requires site-specific ubiquitination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92:11259–11263
Chen Z, Hagler J, Palombella VJ et al (1995) Signal-induced site-specific phosphorylation targets I kappa B alpha to the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Genes Dev 9:1586–1597
Tan P, Fuchs SY, Chen A et al (1999) Recruitment of a ROC1-CUL1 ubiquitin ligase by Skp1 and HOS to catalyze the ubiquitination of I kappa B alpha. Mol Cell 3:527–533
Yamoah K, Oashi T, Sarikas A et al (2008) Autoinhibitory regulation of SCF-mediated ubiquitination by human cullin 1’s C-terminal tail. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:12230–12235
Duda DM, Borg LA, Scott DC et al (2008) Structural insights into NEDD8 activation of cullin-RING ligases: conformational control of conjugation. Cell 134:995–1006
Wu K, Kovacev J, Pan Z-Q (2010) Priming and extending: a UbcH5/Cdc34 E2 handoff mechanism for polyubiquitination on a SCF substrate. Mol Cell 37:784–796
Iwai K (2012) Diverse ubiquitin signaling in NF-κB activation. Trends Cell Biol 22:355–364
Xu S, Patel P, Abbasian M et al (2005) In vitro SCFβ-Trcp1-mediated IκBα ubiquitination assay for high-throughput screen. Methods Enzymol 399:729–740
Soucy TA, Smith PG, Milhollen MA et al (2009) An inhibitor of NEDD8-activating enzyme as a new approach to treat cancer. Nature 458:732–736
Ceccarelli DF, Tang X, Pelletier B et al (2011) An allosteric inhibitor of the human Cdc34 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme. Cell 145:1075–1087
Shen M, Schmitt S, Buac D et al (2013) Targeting the ubiquitin-proteasome system for cancer therapy. Expert Opin Ther Targets 17(9):1091–1108
Gazdoiu S, Yamoah K, Wu K et al (2007) Human Cdc34 employs distinct sites to coordinate attachment of ubiquitin to a substrate and assembly of polyubiquitin chains. Mol Cell Biol 27:7041–7052
Ohta T, Michel JJ, Schottelius AJ et al (1999) ROC1, a homolog of APC11, represents a family of cullin partners with an associated ubiquitin ligase activity. Mol Cell 3:535–541
Zheng N, Schulman B, Song L et al (2002) Structure of the Cul 1–Rbx 1–Skp 1–F boxSkp 2 SCF ubiquitin ligase complex. Nature 416:703–709
Li T, Pavletich NP, Schulman BA et al (2005) High-level expression and purification of recombinant SCF ubiquitin ligases. Methods Enzymol 398:125–142
Mercurio F (1997) IKK-1 and IKK-2: cytokine-activated IB kinases essential for NF-B activation. Science (New York, NY) 278:860–866
Delhase M, Hayakawa M, Chen Y et al (1999) Positive and negative regulation of IkappaB kinase activity through IKKbeta subunit phosphorylation. Science (New York, NY) 284:309–313
Kovacev J, Wu K, Spratt DE et al (2014) A snapshot at ubiquitin chain elongation: lysine 48-tetra-ubiquitin slows down ubiquitination. J Biol Chem 289(10):7068–7081
Acknowledgements
We thank J. Nayak and other members of the Pan lab for their assistance with protocols and careful reading of the method. We are grateful to J. Hurwitz and I. Tappin for assistance with baculovirus preparation. R.A.C. was supported by NIH fellowship 1F30DK095572-01. Z.-Q.P. is the receipt of the 2013 Jiangsu special medical expert award. This work was supported by Public Health Service grants GM61051 and CA095634 to Z.-Q. P.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Chong, R.A., Wu, K., Kovacev, J., Pan, ZQ. (2015). Generation of a Proteolytic Signal: E3/E2-Mediated Polyubiquitination of IκBα. In: May, M. (eds) NF-kappa B. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 1280. Humana Press, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-2422-6_20
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-2422-6_20
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana Press, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4939-2421-9
Online ISBN: 978-1-4939-2422-6
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols