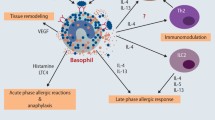
Abstract
The physiological role of the mast cell and basophil has for many years remained enigmatic. In this chapter we briefly summarize some of the more recent studies that shed new light on the role of mast cells and basophils in health and disease. What we gain from these studies is a new appreciation for mast cells and basophils as sentinels in host defense and a further understanding that dysregulation of mast cell and basophil function can be a component of various diseases other than allergies. Perhaps, the most important insight reaped from this work is the increasing awareness that mast cells and basophils can function as immunoregulatory cells that modulate the immune response in health and disease. Collectively, the recent knowledge provides new challenges and opportunities towards the development of novel therapeutic strategies to augment host protection and modify disease through manipulation of mast cell and basophil function.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ehrlich P (1877) Beitrage zur Kenntnis der Anilinfarbungen und ihrer Verwendung in der mikroskopischen Technik. Arch Mikrosk Anat 13:263–277
Ehrlich P (1878) Beitrage zur Theorie und Praxis der histologischen Farbung. 6-17-1878. Thesis, Leipzig University
Ehrlich P (1891) Farbenanalytische Untersuchungen zur Histologie und Klinik des Blutes. Hirschwald, Berlin
Ehrlich P, Lazarus A (1898) Die Anaemie, 1. Normale und pathologische Histologie des Blutes. Holder, Wien (revised and republished 1909)
Galli SJ (1993) New concepts about the mast cell. N Engl J Med 328:257–265
Metcalfe DD, Baram D, Mekori YA (1997) Mast cells. Physiol Rev 77:1033–1079
Karasuyama H, Mukai K, Obata K, Tsujimura Y, Wada T (2011) Nonredundant roles of basophils in immunity. Annu Rev Immunol 29:45–69
Dvorak AM, Nabel G, Pyne K, Cantor H, Dvorak HF, Galli SJ (1982) Ultrastructural identification of the mouse basophil. Blood 59:1279–1285
Galli SJ, Kalesnikoff J, Grimbaldeston MA, Piliponsky AM, Williams CM, Tsai M (2005) Mast cells as “tunable” effector and immunoregulatory cells: recent advances. Annu Rev Immunol 23:749–786
Kinet JP (1989) The high-affinity receptor for IgE. Curr Opin Immunol 2:499–505
Min B, Paul WE (2008) Basophils and type 2 immunity. Curr Opin Hematol 15:59–63
Falcone FH, Haas H, Gibbs BF (2000) The human basophil: a new appreciation of its role in immune responses. Blood 96:4028–4038
Galli SJ, Tsai M (2010) Mast cells in allergy and infection: versatile effector and regulatory cells in innate and adaptive immunity. Eur J Immunol 40:1843–1851
Tsai M, Grimbaldeston M, Galli SJ (2011) Mast cells and immunoregulation/immunomodulation. Adv Exp Med Biol 716:186–211
Reber LL, Marichal T, Galli SJ (2012) New models for analyzing mast cell functions in vivo. Trends Immunol 33:613–625
Rodewald HR, Feyerabend TB (2012) Widespread immunological functions of mast cells: fact or fiction? Immunity 37:13–24
Honda T, Egawa G, Grabbe S, Kabashima K (2013) Update of immune events in the murine contact hypersensitivity model: toward the understanding of allergic contact dermatitis. J Invest Dermatol 133:303–315
Matsumoto K, Mizukoshi K, Oyobikawa M, Ohshima H, Tagami H (2004) Establishment of an atopic dermatitis-like skin model in a hairless mouse by repeated elicitation of contact hypersensitivity that enables to conduct functional analyses of the stratum corneum with various non-invasive biophysical instruments. Skin Res Technol 10:122–129
Dudeck A, Dudeck J, Scholten J, Petzold A, Surianarayanan S, Köhler A, Peschke K, Vöhringer D, Waskow C, Krieg T, Müller W, Waisman A, Hartmann K, Gunzer M, Roers A (2011) Mast cells are key promoters of contact allergy that mediate the adjuvant effects of haptens. Immunity 34:973–984
Galli SJ, Nakae S, Tsai M (2005) Mast cells in the development of adaptive immune responses. Nat Immunol 6:135–142
Hershko AY, Suzuki R, Charles N, Alvarez-Errico D, Sargent JL, Laurence A, Rivera J (2011) Mast cell interleukin-2 production contributes to suppression of chronic allergic dermatitis. Immunity 35:562–571
Norman MU, Hwang J, Hulliger S, Bonder CS, Yamanouchi J, Santamaria P, Kubes P (2008) Mast cells regulate the magnitude and the cytokine microenvironment of the contact hypersensitivity response. Am J Pathol 172:1638–1649
Man MQ, Hatano Y, Lee SH, Man M, Chang S, Feingold KR, Leung DY, Holleran W, Uchida Y, Elias PM (2008) Characterization of a hapten-induced, murine model with multiple features of atopic dermatitis: structural, immunologic, and biochemical changes following single versus multiple oxazolone challenges. J Invest Dermatol 128:79–86
Hart PH, Grimbaldeston MA, Swift GJ, Jaksic A, Noonan FP, Finlay-Jones JJ (1998) Dermal mast cells determine susceptibility to ultraviolet B-induced systemic suppression of contact hypersensitivity responses in mice. J Exp Med 187:2045–2053
Depinay N, Hacini F, Beghdadi W, Peronet R, Mecheri S (2006) Mast cell-dependent down-regulation of antigen-specific immune responses by mosquito bites. J Immunol 176:4141–4146
Grimbaldeston MA, Nakae S, Kalesnikoff J, Tsai M, Galli SJ (2007) Mast cell-derived interleukin 10 limits skin pathology in contact dermatitis and chronic irradiation with ultraviolet B. Nat Immunol 8:1095–1104
Abraham SN, St John AL (2010) Mast cell-orchestrated immunity to pathogens. Nat Rev Immunol 10:440–452
Costa JJ, Weller PF, Galli SJ (1997) The cells of the allergic response: mast cells, basophils, and eosinophils. JAMA 278:1815–1822
Dvorak AM, Seder RA, Paul WE, Kissell-Rainville S, Plaut M, Galli SJ (1993) Ultrastructural characteristics of Fc epsilon R-positive basophils in the spleen and bone marrow of mice immunized with goat anti-mouse IgD antibody. Lab Invest 68:708–715
Seder RA, Paul WE, Dvorak AM, Sharkis SJ, Kagey-Sobotka A, Niv Y, Finkelman FD, Barbieri SA, Galli SJ, Plaut M (1991) Mouse splenic and bone marrow cell populations that express high-affinity Fc epsilon receptors and produce interleukin 4 are highly enriched in basophils. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 88:2835–2839
Seder RA, Plaut M, Barbieri S, Urban J Jr, Finkelman FD, Paul WE (1991) Purified Fc epsilon R+ bone marrow and splenic non-B, non-T cells are highly enriched in the capacity to produce IL-4 in response to immobilized IgE, IgG2a, or ionomycin. J Immunol 147:903–909
Ohnmacht C, Schwartz C, Panzer M, Schiedewitz I, Naumann R, Voehringer D (2010) Basophils orchestrate chronic allergic dermatitis and protective immunity against helminths. Immunity 33:364–374
Wada T, Ishiwata K, Koseki H, Ishikura T, Ugajin T, Ohnuma N, Obata K, Ishikawa R, Yoshikawa S, Mukai K, Kawano Y, Minegishi Y, Yokozeki H, Watanabe N, Karasuyama H (2010) Selective ablation of basophils in mice reveals their nonredundant role in acquired immunity against ticks. J Clin Invest 120:2867–2875
Min B, Prout M, Hu-Li J, Zhu J, Jankovic D, Morgan ES, Urban JF Jr, Dvorak AM, Finkelman FD, LeGros G, Paul WE (2004) Basophils produce IL-4 and accumulate in tissues after infection with a Th2-inducing parasite. J Exp Med 200:507–517
van Panhuys N, Prout M, Forbes E, Min B, Paul WE, Le Gros G (2011) Basophils are the major producers of IL-4 during primary helminth infection. J Immunol 186:2719–2728
Voehringer D, Shinkai K, Locksley RM (2004) Type 2 immunity reflects orchestrated recruitment of cells committed to IL-4 production. Immunity 20:267–277
Ohnmacht C, Voehringer D (2010) Basophils protect against reinfection with hookworms independently of mast cells and memory Th2 cells. J Immunol 184:344–350
Ohnmacht C, Voehringer D (2009) Basophil effector function and homeostasis during helminth infection. Blood 113:2816–2825
Voehringer D, Reese TA, Huang X, Shinkai K, Locksley RM (2006) Type 2 immunity is controlled by IL-4/IL-13 expression in hematopoietic non-eosinophil cells of the innate immune system. J Exp Med 203:1435–1446
Lantz CS, Min B, Tsai M, Chatterjea D, Dranoff G, Galli SJ (2008) IL-3 is required for increases in blood basophils in nematode infection in mice and can enhance IgE-dependent IL-4 production by basophils in vitro. Lab Invest 88:1134–1142
Perrigoue JG, Saenz SA, Siracusa MC, Allenspach EJ, Taylor BC, Giacomin PR, Nair MG, Du Y, Zaph C, van Rooijen N, Comeau MR, Pearce EJ, Laufer TM, Artis D (2009) MHC class II-dependent basophil-CD4+ T cell interactions promote T(H)2 cytokine-dependent immunity. Nat Immunol 10:697–705
Yoshimoto T, Yasuda K, Tanaka H, Nakahira M, Imai Y, Fujimori Y, Nakanishi K (2009) Basophils contribute to T(H)2-IgE responses in vivo via IL-4 production and presentation of peptide-MHC class II complexes to CD4+ T cells. Nat Immunol 10:706–712
Chen K, Xu W, Wilson M, He B, Miller NW, Bengtén E, Edholm ES, Santini PA, Rath P, Chiu A, Cattalini M, Litzman J, B Bussel J, Huang B, Meini A, Riesbeck K, Cunningham-Rundles C, Plebani A, Cerutti A (2009) Immunoglobulin D enhances immune surveillance by activating antimicrobial, proinflammatory and B cell-stimulating programs in basophils. Nat Immunol 10:889–898
Charles N, Hardwick D, Daugas E, Illei GG, Rivera J (2010) Basophils and the T helper 2 environment can promote the development of lupus nephritis. Nat Med 16:701–707
Charles N, Dema B, Rivera J (2012) Reply to: Basophils from humans with systemic lupus erythematosus do not express MHC-II. Nat Med 18:489–490
Charles N, Rivera J (2011) Basophils and autoreactive IgE in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep 11:378–387
Sokol CL, Chu NQ, Yu S, Nish SA, Laufer TM, Medzhitov R (2009) Basophils function as antigen-presenting cells for an allergen-induced T helper type 2 response. Nat Immunol 10:713–720
Caughey GH (2011) Mast cell proteases as protective and inflammatory mediators. Adv Exp Med Biol 716:212–234
Akahoshi M, Song CH, Piliponsky AM, Metz M, Guzzetta A, Abrink M, Schlenner SM, Feyerabend TB, Rodewald HR, Pejler G, Tsai M, Galli SJ (2011) Mast cell chymase reduces the toxicity of Gila monster venom, scorpion venom, and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in mice. J Clin Invest 121:4180–4191
Maurer M, Wedemeyer J, Metz M, Piliponsky AM, Weller K, Chatterjea D, Clouthier DE, Yanagisawa MM, Tsai M, Galli SJ (2004) Mast cells promote homeostasis by limiting endothelin-1-induced toxicity. Nature 432:512–516
Metz M, Piliponsky AM, Chen CC, Lammel V, Abrink M, Pejler G, Tsai M, Galli SJ (2006) Mast cells can enhance resistance to snake and honeybee venoms. Science 313:526–530
Malaviya R, Ikeda T, Ross E, Abraham SN (1996) Mast cell modulation of neutrophil influx and bacterial clearance at sites of infection through TNF-alpha. Nature 381:77–80
Piliponsky AM, Chen CC, Grimbaldeston MA, Burns-Guydish SM, Hardy J, Kalesnikoff J, Contag CH, Tsai M, Galli SJ (2010) Mast cell-derived TNF can exacerbate mortality during severe bacterial infections in C57BL/6-KitW-sh/W-sh mice. Am J Pathol 176:926–938
Piliponsky AM, Chen CC, Nishimura T, Metz M, Rios EJ, Dobner PR, Wada E, Wada K, Zacharias S, Mohanasundaram UM, Faix JD, Abrink M, Pejler G, Pearl RG, Tsai M, Galli SJ (2008) Neurotensin increases mortality and mast cells reduce neurotensin levels in a mouse model of sepsis. Nat Med 14:392–398
Cochrane DE, Carraway RE, Boucher W, Feldberg RS (1991) Rapid degradation of neurotensin by stimulated rat mast cells. Peptides 12:1187–1194
Piliponsky AM, Chen CC, Rios EJ, Treuting PM, Lahiri A, Abrink M, Pejler G, Tsai M, Galli SJ (2012) The chymase mouse mast cell protease 4 degrades TNF, limits inflammation, and promotes survival in a model of sepsis. Am J Pathol 181:875–886
Thakurdas SM, Melicoff E, Sansores-Garcia L, Moreira DC, Petrova Y, Stevens RL, Adachi R (2007) The mast cell-restricted tryptase mMCP-6 has a critical immunoprotective role in bacterial infections. J Biol Chem 282:20809–20815
Hendrix S, Kramer P, Pehl D, Warnke K, Boato F, Nelissen S, Lemmens E, Pejler G, Metz M, Siebenhaar F, Maurer M (2013) Mast cells protect from post-traumatic brain inflammation by the mast cell-specific chymase mouse mast cell protease-4. FASEB J 27:920–929
Waern I, Lundequist A, Pejler G, Wernersson S (2013) Mast cell chymase modulates IL-33 levels and controls allergic sensitization in dust-mite induced airway inflammation. Mucosal Immunol 6(5):911–920
Waern I, Karlsson I, Thorpe M, Schlenner SM, Feyerabend TB, Rodewald HR, Åbrink M, Hellman L, Pejler G, Wernersson S (2012) Mast cells limit extracellular levels of IL-13 via a serglycin proteoglycan-serine protease axis. Biol Chem 393:1555–1567
Hershko AY, Charles N, Olivera A, Alvarez-Errico D, Rivera J (2012) Cutting edge: persistence of increased mast cell numbers in tissues links dermatitis to enhanced airway disease in a mouse model of atopy. J Immunol 188:531–535
Hahn EL, Bacharier LB (2005) The atopic march: the pattern of allergic disease development in childhood. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am 25:231–246, v
McLachlan JB, Shelburne CP, Hart JP, Pizzo SV, Goyal R, Brooking-Dixon R, Staats HF, Abraham SN (2008) Mast cell activators: a new class of highly effective vaccine adjuvants. Nat Med 14:536–541
Paananen K, Kovanen PT (1994) Proteolysis and fusion of low density lipoprotein particles independently strengthen their binding to exocytosed mast cell granules. J Biol Chem 269:2023–2031
Pulendran B, Ono SJ (2008) A shot in the arm for mast cells. Nat Med 14:489–490
Galli SJ, Borregaard N, Wynn TA (2011) Phenotypic and functional plasticity of cells of innate immunity: macrophages, mast cells and neutrophils. Nat Immunol 12:1035–1044
Chmelar J, Chung KJ, Chavakis T (2013) The role of innate immune cells in obese adipose tissue inflammation and development of insulin resistance. Thromb Haemost 109:399–406
Xu JM, Shi GP (2012) Emerging role of mast cells and macrophages in cardiovascular and metabolic diseases. Endocr Rev 33:71–108
Anand P, Singh B, Jaggi AS, Singh N (2012) Mast cells: an expanding pathophysiological role from allergy to other disorders. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 385:657–670
Altintas MM, Nayer B, Walford EC, Johnson KB, Gaidosh G, Reiser J, De La Cruz-Munoz N, Ortega LM, Nayer A (2012) Leptin deficiency-induced obesity affects the density of mast cells in abdominal fat depots and lymph nodes in mice. Lipids Health Dis 11:21
Liu J, Divoux A, Sun J, Zhang J, Clement K, Glickman JN, Sukhova GK, Wolters PJ, Du J, Gorgun CZ, Doria A, Libby P, Blumberg RS, Kahn BB, Hotamisligil GS, Shi GP (2009) Genetic deficiency and pharmacological stabilization of mast cells reduce diet-induced obesity and diabetes in mice. Nat Med 15:940–945
Tanaka A, Nomura Y, Matsuda A, Ohmori K, Matsuda H (2011) Mast cells function as an alternative modulator of adipogenesis through 15-deoxy-delta-12, 14-prostaglandin J2. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 301:C1360–C1367
Divoux A, Moutel S, Poitou C, Lacasa D, Veyrie N, Aissat A, Arock M, Guerre-Millo M, Clément K (2012) Mast cells in human adipose tissue: link with morbid obesity, inflammatory status, and diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 97:E1677–E1685
Wang X, Chen H, Zhang M, Liu Z (2012) Roles of Mast Cells and Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 in the Renal Injury of Obesity-Related Glomerulopathy. Am J Med Sci 346(4):295–301
Fenger RV, Linneberg A, Vidal C, Vizcaino L, Husemoen LL, Aadahl M, Gonzalez-Quintela A (2012) Determinants of serum tryptase in a general population: the relationship of serum tryptase to obesity and asthma. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 157:151–158
Ward BR, Arslanian SA, Andreatta E, Schwartz LB (2012) Obesity is not linked to increased whole-body mast cell burden in children. J Allergy Clin Immunol 129:1164–1166
Poglio S, De Toni-Costes F, Arnaud E, Laharrague P, Espinosa E, Casteilla L, Cousin B (2010) Adipose tissue as a dedicated reservoir of functional mast cell progenitors. Stem Cells 28:2065–2072
Oka T, Kalesnikoff J, Starkl P, Tsai M, Galli SJ (2012) Evidence questioning cromolyn’s effectiveness and selectivity as a ‘mast cell stabilizer’ in mice. Lab Invest 92:1472–1482
Shi MA, Shi GP (2012) Different roles of mast cells in obesity and diabetes: lessons from experimental animals and humans. Front Immunol 3:7
Iyer A, Lim J, Poudyal H, Reid RC, Suen JY, Webster J, Prins JB, Whitehead JP, Fairlie DP, Brown L (2012) An inhibitor of phospholipase A2 group IIA modulates adipocyte signaling and protects against diet-induced metabolic syndrome in rats. Diabetes 61:2320–2329
Kim S, Moustaid-Moussa N (2000) Secretory, endocrine and autocrine/paracrine function of the adipocyte. J Nutr 130:3110S–3115S
Weber C, Zernecke A, Libby P (2008) The multifaceted contributions of leukocyte subsets to atherosclerosis: lessons from mouse models. Nat Rev Immunol 8:802–815
Jeziorska M, McCollum C, Woolley DE (1997) Mast cell distribution, activation, and phenotype in atherosclerotic lesions of human carotid arteries. J Pathol 182:115–122
Kaartinen M, Penttila A, Kovanen PT (1994) Mast cells of two types differing in neutral protease composition in the human aortic intima. Demonstration of tryptase- and tryptase/chymase-containing mast cells in normal intimas, fatty streaks, and the shoulder region of atheromas. Arterioscler Thromb 14:966–972
Kovanen PT, Kaartinen M, Paavonen T (1995) Infiltrates of activated mast cells at the site of coronary atheromatous erosion or rupture in myocardial infarction. Circulation 92:1084–1088
Ramalho LS, Oliveira LF, Cavellani CL, Ferraz ML, de Oliveira FA, Miranda Correa RR, de Paula Antunes Teixeira V, De Lima Pereira SA (2013) Role of mast cell chymase and tryptase in the progression of atherosclerosis: study in 44 autopsied cases. Ann Diagn Pathol 17:28–31
Bot I, Bot M, van Heiningen SH, van Santbrink PJ, Lankhuizen IM, Hartman P, Gruener S, Hilpert H, van Berkel TJ, Fingerle J, Biessen EA (2011) Mast cell chymase inhibition reduces atherosclerotic plaque progression and improves plaque stability in ApoE-/- mice. Cardiovasc Res 89:244–252
Heikkila HM, Trosien J, Metso J, Jauhiainen M, Pentikainen MO, Kovanen PT, Lindstedt KA (2010) Mast cells promote atherosclerosis by inducing both an atherogenic lipid profile and vascular inflammation. J Cell Biochem 109:615–623
Sun J, Sukhova GK, Wolters PJ, Yang M, Kitamoto S, Libby P, MacFarlane LA, Mallen-St Clair J, Shi GP (2007) Mast cells promote atherosclerosis by releasing proinflammatory cytokines. Nat Med 13:719–724
Smith DD, Tan X, Raveendran VV, Tawfik O, Stechschulte DJ, Dileepan KN (2012) Mast cell deficiency attenuates progression of atherosclerosis and hepatic steatosis in apolipoprotein E-null mice. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 302:H2612–H2621
Bot I, Biessen EA (2011) Mast cells in atherosclerosis. Thromb Haemost 106:820–826
Bot I, de Jager SC, Zernecke A, Lindstedt KA, van Berkel TJ, Weber C, Biessen EA (2007) Perivascular mast cells promote atherogenesis and induce plaque destabilization in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Circulation 115:2516–2525
Zhang J, Alcaide P, Liu L, Sun J, He A, Luscinskas FW, Shi GP (2011) Regulation of endothelial cell adhesion molecule expression by mast cells, macrophages, and neutrophils. PLoS One 6:e14525
Sun J, Sukhova GK, Yang M, Wolters PJ, MacFarlane LA, Libby P, Sun C, Zhang Y, Liu J, Ennis TL, Knispel R, Xiong W, Thompson RW, Baxter BT, Shi GP (2007) Mast cells modulate the pathogenesis of elastase-induced abdominal aortic aneurysms in mice. J Clin Invest 117:3359–3368
Lappalainen J, Lindstedt KA, Oksjoki R, Kovanen PT (2011) OxLDL-IgG immune complexes induce expression and secretion of proatherogenic cytokines by cultured human mast cells. Atherosclerosis 214:357–363
Wang J, Cheng X, Xiang MX, Alanne-Kinnunen M, Wang JA, Chen H, He A, Sun X, Lin Y, Tang TT, Tu X, Sjöberg S, Sukhova GK, Liao YH, Conrad DH, Yu L, Kawakami T, Kovanen PT, Libby P, Shi GP (2011) IgE stimulates human and mouse arterial cell apoptosis and cytokine expression and promotes atherogenesis in Apoe-/- mice. J Clin Invest 121:3564–3577
Coussens LM, Zitvogel L, Palucka AK (2013) Neutralizing tumor-promoting chronic inflammation: a magic bullet? Science 339:286–291
Oleinika K, Nibbs RJ, Graham GJ, Fraser AR (2013) Suppression, subversion and escape: the role of regulatory T cells in cancer progression. Clin Exp Immunol 171:36–45
Chang DZ (2012) Mast cells in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Oncoimmunology 1:754–755
Cheema VS, Ramesh V, Balamurali PD (2012) The relevance of mast cells in oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Clin Diagn Res 6:1803–1807
de Souza DA Jr, Toso VD, Campos MR, Lara VS, Oliver C, Jamur MC (2012) Expression of mast cell proteases correlates with mast cell maturation and angiogenesis during tumor progression. PLoS One 7:e40790
Gounaris E, Erdman SE, Restaino C, Gurish MF, Friend DS, Gounari F, Lee DM, Zhang G, Glickman JN, Shin K, Rao VP, Poutahidis T, Weissleder R, McNagny KM, Khazaie K (2007) Mast cells are an essential hematopoietic component for polyp development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:19977–19982
Maltby S, Khazaie K, McNagny KM (2009) Mast cells in tumor growth: angiogenesis, tissue remodelling and immune-modulation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1796:19–26
Mangia A, Malfettone A, Rossi R, Paradiso A, Ranieri G, Simone G, Resta L (2011) Tissue remodelling in breast cancer: human mast cell tryptase as an initiator of myofibroblast differentiation. Histopathology 58:1096–1106
Nelissen S, Lemmens E, Geurts N, Kramer P, Maurer M, Hendriks J, Hendrix S (2013) The role of mast cells in neuroinflammation. Acta Neuropathol 125:637–650
Pittoni P, Tripodo C, Piconese S, Mauri G, Parenza M, Rigoni A, Sangaletti S, Colombo MP (2011) Mast cell targeting hampers prostate adenocarcinoma development but promotes the occurrence of highly malignant neuroendocrine cancers. Cancer Res 71:5987–5997
Rabenhorst A, Schlaak M, Heukamp LC, Forster A, Theurich S, von Bergwelt-Baildon M, Büttner R, Kurschat P, Mauch C, Roers A, Hartmann K (2012) Mast cells play a protumorigenic role in primary cutaneous lymphoma. Blood 120:2042–2054
Ribatti D, Crivellato E (2011) Mast cells, angiogenesis and cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol 716:270–288
Souza LR, Fonseca-Silva T, Santos CC, Oliveira MV, Correa-Oliveira R, Guimaraes AL, De Paula AM (2010) Association of mast cell, eosinophil leucocyte and microvessel densities in actinic cheilitis and lip squamous cell carcinoma. Histopathology 57:796–805
Staser K, Yang FC, Clapp DW (2012) Pathogenesis of plexiform neurofibroma: tumor-stromal/hematopoietic interactions in tumor progression. Annu Rev Pathol 7:469–495
Cai SW, Yang SZ, Gao J, Pan K, Chen JY, Wang YL, Wei LX, Dong JH (2011) Prognostic significance of mast cell count following curative resection for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Surgery 149:576–584
Huang B, Lei Z, Zhang GM, Li D, Song C, Li B, Liu Y, Yuan Y, Unkeless J, Xiong H, Feng ZH (2008) SCF-mediated mast cell infiltration and activation exacerbate the inflammation and immunosuppression in tumor microenvironment. Blood 112:1269–1279
Soucek L, Lawlor ER, Soto D, Shchors K, Swigart LB, Evan GI (2007) Mast cells are required for angiogenesis and macroscopic expansion of Myc-induced pancreatic islet tumors. Nat Med 13:1211–1218
Xia Q, Wu XJ, Zhou Q, Jing Z, Hou JH, Pan ZZ, Zhang XS (2011) No relationship between the distribution of mast cells and the survival of stage IIIB colon cancer patients. J Transl Med 9:88
Starkey JR, Crowle PK, Taubenberger S (1988) Mast-cell-deficient W/Wv mice exhibit a decreased rate of tumor angiogenesis. Int J Cancer 42:48–52
Chang DZ, Ma Y, Ji B, Wang H, Deng D, Liu Y, Logsdon CD, Hwu P (2011) Mast cells in tumor microenvironment promotes the in vivo growth of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 17:7015–7023
Wasiuk A, Dalton DK, Schpero WL, Stan RV, Conejo-Garcia JR, Noelle RJ (2012) Mast cells impair the development of protective anti-tumor immunity. Cancer Immunol Immunother 61:2273–2282
Oldford SA, Haidl ID, Howatt MA, Leiva CA, Johnston B, Marshall JS (2010) A critical role for mast cells and mast cell-derived IL-6 in TLR2-mediated inhibition of tumor growth. J Immunol 185:7067–7076
Murata T, Aritake K, Matsumoto S, Kamauchi S, Nakagawa T, Hori M, Momotani E, Urade Y, Ozaki H (2011) Prostagladin D2 is a mast cell-derived antiangiogenic factor in lung carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:19802–19807
Sinnamon MJ, Carter KJ, Sims LP, Lafleur B, Fingleton B, Matrisian LM (2008) A protective role of mast cells in intestinal tumorigenesis. Carcinogenesis 29:880–886
Pittoni P, Piconese S, Tripodo C, Colombo MP (2011) Tumor-intrinsic and -extrinsic roles of c-Kit: mast cells as the primary off-target of tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Oncogene 30:757–769
Brown MA, Hatfield JK (2012) Mast Cells are Important Modifiers of Autoimmune Disease: With so Much Evidence, Why is There Still Controversy? Front Immunol 3:147
Costanza M, Colombo MP, Pedotti R (2012) Mast cells in the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Int J Mol Sci 13:15107–15125
Mican JM, Metcalfe DD (1990) Arthritis and mast cell activation. J Allergy Clin Immunol 86:677–683
Nakano S, Mishiro T, Takahara S, Yokoi H, Hamada D, Yukata K, Takata Y, Goto T, Egawa H, Yasuoka S, Furouchi H, Hirasaka K, Nikawa T, Yasui N (2007) Distinct expression of mast cell tryptase and protease activated receptor-2 in synovia of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Clin Rheumatol 26:1284–1292
Noordenbos T, Yeremenko N, Gofita I, van de Sande M, Tak PP, Caňete JD, Baeten D (2012) Interleukin-17-positive mast cells contribute to synovial inflammation in spondylarthritis. Arthritis Rheum 64:99–109
Tetlow LC, Woolley DE (1995) Distribution, activation and tryptase/chymase phenotype of mast cells in the rheumatoid lesion. Ann Rheum Dis 54:549–555
Pimentel TA, Sampaio AL, D’Acquisto F, Perretti M, Oliani SM (2011) An essential role for mast cells as modulators of neutrophils influx in collagen-induced arthritis in the mouse. Lab Invest 91:33–42
Shin K, Gurish MF, Friend DS, Pemberton AD, Thornton EM, Miller HR, Lee DM (2006) Lymphocyte-independent connective tissue mast cells populate murine synovium. Arthritis Rheum 54:2863–2871
Shiota N, Shimoura K, Okunishi H (2006) Pathophysiological role of mast cells in collagen-induced arthritis: study with a cysteinyl leukotriene receptor antagonist, montelukast. Eur J Pharmacol 548:158–166
Kneilling M, Hultner L, Pichler BJ, Mailhammer R, Morawietz L, Solomon S, Eichner M, Sabatino J, Biedermann T, Krenn V, Weber WA, Illges H, Haubner R, Röcken M (2007) Targeted mast cell silencing protects against joint destruction and angiogenesis in experimental arthritis in mice. Arthritis Rheum 56:1806–1816
Juurikivi A, Sandler C, Lindstedt KA, Kovanen PT, Juutilainen T, Leskinen MJ, Mäki T, Eklund KK (2005) Inhibition of c-kit tyrosine kinase by imatinib mesylate induces apoptosis in mast cells in rheumatoid synovia: a potential approach to the treatment of arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 64:1126–1131
Eklund KK, Joensuu H (2003) Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with imatinib mesylate: clinical improvement in three refractory cases. Ann Med 35:362–367
Mancardi DA, Jonsson F, Iannascoli B, Khun H, Van Rooijen N, Huerre M, Daëron M, Bruhns P (2011) Cutting Edge: The murine high-affinity IgG receptor FcgammaRIV is sufficient for autoantibody-induced arthritis. J Immunol 186:1899–1903
Nigrovic PA, Binstadt BA, Monach PA, Johnsen A, Gurish M, Iwakura Y, Benoist C, Mathis D, Lee DM (2007) Mast cells contribute to initiation of autoantibody-mediated arthritis via IL-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:2325–2330
Nigrovic PA, Malbec O, Lu B, Markiewski MM, Kepley C, Gerard N, Daëron M, Lee DM (2010) C5a receptor enables participation of mast cells in immune complex arthritis independently of Fcgamma receptor modulation. Arthritis Rheum 62:3322–3333
Tsuboi N, Ernandez T, Li X, Nishi H, Cullere X, Mekala D, Hazen M, Köhl J, Lee DM, Mayadas TN (2011) Regulation of human neutrophil Fcgamma receptor IIa by C5a receptor promotes inflammatory arthritis in mice. Arthritis Rheum 63:467–478
Zhou JS, Xing W, Friend DS, Austen KF, Katz HR (2007) Mast cell deficiency in Kit(W-sh) mice does not impair antibody-mediated arthritis. J Exp Med 204:2797–2802
Pitman N, Asquith DL, Murphy G, Liew FY, McInnes IB (2011) Collagen-induced arthritis is not impaired in mast cell-deficient mice. Ann Rheum Dis 70:1170–1171
Feyerabend TB, Weiser A, Tietz A, Stassen M, Harris N, Kopf M, Radermacher P, Möller P, Benoist C, Mathis D, Fehling HJ, Rodewald HR (2011) Cre-mediated cell ablation contests mast cell contribution in models of antibody- and T cell-mediated autoimmunity. Immunity 35:832–844
Rajasekaran N, Solomon S, Watanabe T, Ohtsu H, Gajda M, Bräuer R, Illges H (2009) Histidine decarboxylase but not histamine receptor 1 or 2 deficiency protects from K/BxN serum-induced arthritis. Int Immunol 21:1263–1268
McNeil HP, Shin K, Campbell IK, Wicks IP, Adachi R, Lee DM, Stevens RL (2008) The mouse mast cell-restricted tetramer-forming tryptases mouse mast cell protease 6 and mouse mast cell protease 7 are critical mediators in inflammatory arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 58:2338–2346
Shin K, Nigrovic PA, Crish J, Boilard E, McNeil HP, Larabee KS, Adachi R, Gurish MF, Gobezie R, Stevens RL, Lee DM (2009) Mast cells contribute to autoimmune inflammatory arthritis via their tryptase/heparin complexes. J Immunol 182:647–656
Magnusson SE, Pejler G, Kleinau S, Abrink M (2009) Mast cell chymase contributes to the antibody response and the severity of autoimmune arthritis. FASEB J 23:875–882
Ji H, Ohmura K, Mahmood U, Lee DM, Hofhuis FM, Boackle SA, Takahashi K, Holers VM, Walport M, Gerard C, Ezekowitz A, Carroll MC, Brenner M, Weissleder R, Verbeek JS, Duchatelle V, Degott C, Benoist C, Mathis D (2002) Arthritis critically dependent on innate immune system players. Immunity 16:157–168
Xu D, Jiang HR, Kewin P, Li Y, Mu R, Fraser AR, Pitman N, Kurowska-Stolarska M, McKenzie AN, McInnes IB, Liew FY (2008) IL-33 exacerbates antigen-induced arthritis by activating mast cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:10913–10918
Millauer N, Zuercher AW, Miescher SM, Gerber HA, Seitz M, Stadler BM (1999) High IgE in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients is complexed with anti-IgE autoantibodies. Clin Exp Immunol 115:183–188
Kikuchi Y, Kaplan AP (2001) Mechanisms of autoimmune activation of basophils in chronic urticaria. J Allergy Clin Immunol 107:1056–1062
Miller JF (1975) Cellular basis of the immune response. Acta Endocrinol Suppl (Copenh) 194:55–76
Nakae S, Suto H, Iikura M, Kakurai M, Sedgwick JD, Tsai M, Galli SJ (2006) Mast cells enhance T cell activation: importance of mast cell costimulatory molecules and secreted TNF. J Immunol 176:2238–2248
Mekori YA (2004) The mastocyte: the “other” inflammatory cell in immunopathogenesis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 114:52–57
Bachelet I, Levi-Schaffer F, Mekori YA (2006) Mast cells: not only in allergy. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am 26:407–425
Kalesnikoff J, Galli SJ (2008) New developments in mast cell biology. Nat Immunol 9:1215–1223
Inamura N, Mekori YA, Bhattacharyya SP, Bianchine PJ, Metcalfe DD (1998) Induction and enhancement of Fc(epsilon)RI-dependent mast cell degranulation following coculture with activated T cells: dependency on ICAM-1- and leukocyte function-associated antigen (LFA)-1-mediated heterotypic aggregation. J Immunol 160:4026–4033
Frandji P, Tkaczyk C, Oskeritzian C, David B, Desaymard C, Mecheri S (1996) Exogenous and endogenous antigens are differentially presented by mast cells to CD4+ T lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol 26:2517–2528
Kambayashi T, Allenspach EJ, Chang JT, Zou T, Shoag JE, Reiner SL, Caton AJ, Koretzky GA (2009) Inducible MHC class II expression by mast cells supports effector and regulatory T cell activation. J Immunol 182:4686–4695
Gaudenzio N, Espagnolle N, Mars LT, Liblau R, Valitutti S, Espinosa E (2009) Cell-cell cooperation at the T helper cell/mast cell immunological synapse. Blood 114:4979–4988
Stelekati E, Bahri R, D’Orlando O, Orinska Z, Mittrucker HW, Langenhaun R, Glatzel M, Bollinger A, Paus R, Bulfone-Paus S (2009) Mast cell-mediated antigen presentation regulates CD8+ T cell effector functions. Immunity 31:665–676
Frossi B, D’Inca F, Crivellato E, Sibilano R, Gri G, Mongillo M, Danelli L, Maggi L, Pucillo CE (2011) Single-cell dynamics of mast cell-CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T cell interactions. Eur J Immunol 41:1872–1882
Frossi B, Gri G, Tripodo C, Pucillo C (2010) Exploring a regulatory role for mast cells: ‘MCregs’? Trends Immunol 31:97–102
Gri G, Piconese S, Frossi B, Manfroi V, Merluzzi S, Tripodo C, Viola A, Odom S, Rivera J, Colombo MP, Pucillo CE (2008) CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells suppress mast cell degranulation and allergic responses through OX40-OX40L interaction. Immunity 29:771–781
Piconese S, Gri G, Tripodo C, Musio S, Gorzanelli A, Frossi B, Pedotti R, Pucillo CE, Colombo MP (2009) Mast cells counteract regulatory T-cell suppression through interleukin-6 and OX40/OX40L axis toward Th17-cell differentiation. Blood 114:2639–2648
Sibilano R, Frossi B, Suzuki R, D’Inca F, Gri G, Piconese S, Colombo MP, Rivera J, Pucillo CE (2012) Modulation of FcepsilonRI-dependent mast cell response by OX40L via Fyn, PI3K, and RhoA. J Allergy Clin Immunol 130(751–760):e752
Sibilano R, Gri G, Frossi B, Tripodo C, Suzuki R, Rivera J, MacDonald AS, Pucillo CE (2011) Technical advance: soluble OX40 molecule mimics regulatory T cell modulatory activity on FcepsilonRI-dependent mast cell degranulation. J Leukoc Biol 90:831–838
Tripodo C, Gri G, Piccaluga PP, Frossi B, Guarnotta C, Piconese S, Franco G, Vetri V, Pucillo CE, Florena AM, Colombo MP, Pileri SA (2010) Mast cells and Th17 cells contribute to the lymphoma-associated pro-inflammatory microenvironment of angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma. Am J Pathol 177:792–802
Merluzzi S, Frossi B, Gri G, Parusso S, Tripodo C, Pucillo C (2010) Mast cells enhance proliferation of B lymphocytes and drive their differentiation toward IgA-secreting plasma cells. Blood 115:2810–2817
Sokol CL, Barton GM, Farr AG, Medzhitov R (2008) A mechanism for the initiation of allergen-induced T helper type 2 responses. Nat Immunol 9:310–318
Tang H, Cao W, Kasturi SP, Ravindran R, Nakaya HI, Kundu K, Murthy N, Kepler TB, Malissen B, Pulendran B (2010) The T helper type 2 response to cysteine proteases requires dendritic cell-basophil cooperation via ROS-mediated signaling. Nat Immunol 11:608–617
Hammad H, Plantinga M, Deswarte K, Pouliot P, Willart MA, Kool M, Muskens F, Lambrecht BN (2010) Inflammatory dendritic cells–not basophils–are necessary and sufficient for induction of Th2 immunity to inhaled house dust mite allergen. J Exp Med 207:2097–2111
Rodriguez Gomez M, Talke Y, Goebel N, Hermann F, Reich B, Mack M (2010) Basophils support the survival of plasma cells in mice. J Immunol 185:7180–7185
Charles N, Watford WT, Ramos HL, Hellman L, Oettgen HC, Gomez G, Ryan JJ, O’Shea JJ, Rivera J (2009) Lyn kinase controls basophil GATA-3 transcription factor expression and induction of Th2 cell differentiation. Immunity 30:533–543
Denzel A, Maus UA, Rodriguez Gomez M, Moll C, Niedermeier M, Winter C, Maus R, Hollingshead S, Briles DE, Kunz-Schughart LA, Talke Y, Mack M (2008) Basophils enhance immunological memory responses. Nat Immunol 9:733–742
Wakahara K, Baba N, Van VQ, Begin P, Rubio M, Ferraro P, Panzini B, Wassef R, Lahaie R, Caussignac Y, Tamaz R, Richard C, Soucy G, Delespesse G, Sarfati M (2012) Human basophils interact with memory T cells to augment Th17 responses. Blood 120:4761–4771
Wakahara K, Van VQ, Baba N, Begin P, Rubio M, Delespesse G, Sarfati M (2013) Basophils are recruited to inflamed lungs and exacerbate memory Th2 responses in mice and humans. Allergy 68:180–189
Goldszmid RS, Trinchieri G (2012) The price of immunity. Nat Immunol 13:932–938
Rivera J, Tessarollo L (2008) Genetic background and the dilemma of translating mouse studies to humans. Immunity 28:1–4
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2014 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Olivera, A., Rivera, J. (2014). Paradigm Shifts in Mast Cell and Basophil Biology and Function: An Emerging View of Immune Regulation in Health and Disease. In: Gibbs, B., Falcone, F. (eds) Basophils and Mast Cells. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 1192. Humana Press, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-1173-8_1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-1173-8_1
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana Press, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4939-1172-1
Online ISBN: 978-1-4939-1173-8
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols