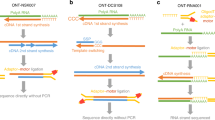
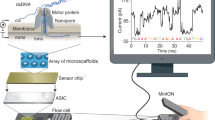
Abstract
Whole genome and transcriptome analyses represent powerful tools. Despite improvements in sequencing methodology, whole transcriptome analyses are still tedious, especially for methodologies producing long reads. Here, we compare the sequence data analysis software MinKNOW and our tool Alignator. Furthermore, we provide a walk-through from RNA isolation and preparation for MinION sequencing as well as insides in the processing of sequencing data using both tools.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Han SS, Kim WJ, Hong Y et al (2014) RNA sequencing identifies novel markers of non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 84(3):229–235
Horvath A, Pakala SB, Mudvari P et al (2013) Novel insights into breast cancer genetic variance through RNA sequencing. Sci Rep 3:2256
Nikas JB, Mitanis NT, Nikas EG (2020) Whole Exome and Transcriptome RNA-Sequencing Model for the Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer. ACS Omega 5(1):481–486
Sanger F, Nicklen S, Coulson AR (1977) DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 74(12):5463–5467
Maxam AM, Gilbert W (1977) A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 74(2):560–564
Saccone C, Pesole G (2005) Handbook of comparative genomics: principles and methodology. Wiley
Lu H, Giordano F, Ning Z (2016) Oxford Nanopore MinION Sequencing and Genome Assembly. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics 14(5):265–279
Jain M, Olsen HE, Paten B et al (2016) The Oxford Nanopore MinION: delivery of nanopore sequencing to the genomics community. Genome Biol 17(1):239
Ip CLC, Loose M, Tyson JR et al (2015) MinION Analysis and Reference Consortium: Phase 1 data release and analysis. F1000Res 4:1075
Wick RR, Judd LM, Holt KE (2019) Performance of neural network basecalling tools for Oxford Nanopore sequencing. Genome Biol 20(1):129
Liao Y, Smyth GK, Shi W (2013) The Subread aligner: fast, accurate and scalable read mapping by seed-and-vote. Nucleic Acids Res 41(10):e108
Oeck S, Tuns AI, Hurst S et al (2020) Streamlining Quantitative Analysis of Long RNA Sequencing Reads. Int J Mol Sci 21(19)
Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK et al (2005) Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102(43):15545–15550
Liberzon A, Subramanian A, Pinchback R et al (2011) Molecular signatures database (MSigDB) 3.0. Bioinformatics 27(12):1739–1740
Liberzon A, Birger C, Thorvaldsdottir H et al (2015) The Molecular Signatures Database (MSigDB) hallmark gene set collection. Cell Syst 1(6):417–425
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Oeck, S., Tüns, A.I., Schramm, A. (2023). Nanopore Sequencing Techniques: A Comparison of the MinKNOW and the Alignator Sequencers. In: Mitra, S. (eds) Metagenomic Data Analysis. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2649. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-3072-3_10
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-3072-3_10
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-3071-6
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-3072-3
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols