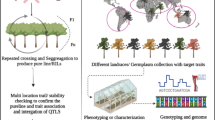
Abstract
The estimation of the population structure and genetic relatedness between individuals within a collection of accessions is important in the formation of core collections for the conservation of genetic resources, uncovering the demographic history of the population under study, as well as for association studies. With the recent development of high-throughput genotyping technologies, several algorithms and methods have been developed and implemented in software to estimate the extent of genetic diversity between individuals. In this chapter, our objective is to describe methods to capture population structure and relatedness in a step-by-step fashion. To exemplify the process, two pruned datasets (14K and 243K SNP markers) were used to investigate population structure and relatedness among a soybean GWAS panel using different approaches and methods.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jeong N, Kim K-S, Jeong S et al (2019) Korean soybean core collection: genotypic and phenotypic diversity population structure and genome-wide association study. PLoS One 14:e0224074. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0224074
Odong TL, van Heerwaarden J, Jansen J et al (2011) Determination of genetic structure of germplasm collections: are traditional hierarchical clustering methods appropriate for molecular marker data? Theor Appl Genet 123:195–205. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-011-1576-x
Patterson N, Price AL, Reich D (2006) Population structure and Eigenanalysis. PLoS Genet 2:e190. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.0020190
Kang HM, Zaitlen NA, Wade CM et al (2008) Efficient control of population structure in model organism association mapping. Genetics 178:1709–1723. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.107.080101
Stram DO (2014) Design, analysis, and interpretation of genome-wide association scans. Springer, New York, New York, NY
Yu J, Pressoir G, Briggs WH et al (2006) A unified mixed-model method for association mapping that accounts for multiple levels of relatedness. Nat Genet 38:203–208. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1702
Singh N, Choudhury DR, Singh AK et al (2013) Comparison of SSR and SNP markers in estimation of genetic diversity and population structure of Indian Rice varieties. PLoS One 8:e84136. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0084136
Dangl GS, Mendum ML, Prins BH et al (2001) Simple sequence repeat analysis of a clonally propagated species: a tool for managing a grape germplasm collection. Genome 44:432–438. https://doi.org/10.1139/g01-026
Flint-Garcia SA, Thuillet A-C, Yu J et al (2005) Maize association population: a high-resolution platform for quantitative trait locus dissection: high-resolution maize association population. Plant J 44:1054–1064. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2005.02591.x
Van Inghelandt D, Melchinger AE, Lebreton C, Stich B (2010) Population structure and genetic diversity in a commercial maize breeding program assessed with SSR and SNP markers. Theor Appl Genet 120:1289–1299. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-009-1256-2
Cho G T, Lee J, Moon JK, Yoon M S, Baek H J, Kang JH, Kim TS, Paek NC (2008) Genetic Diversity and Population Structure of Korean Soybean Landrace [Glycine max (L.) Merr.]. J. Crop Sci. Biotech. 2008 (June) 11(2):83–90
Jones ES, Sullivan H, Bhattramakki D, Smith JSC (2007) A comparison of simple sequence repeat and single nucleotide polymorphism marker technologies for the genotypic analysis of maize (Zea mays L.). Theor Appl Genet 115:361–371. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-007-0570-9
Semagn K, Magorokosho C, Vivek BS et al (2012) Molecular characterization of diverse CIMMYT maize inbred lines from eastern and southern Africa using single nucleotide polymorphic markers. BMC Genomics 13:113. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-13-113
Menozzi P, Piazza A, Cavalli-Sforza L (1978) Synthetic maps of human gene frequencies in Europeans. Science 201:786–792. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.356262
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P (2000) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetic 155:945–959
Ringnér M (2008) What is principal component analysis? Nat Biotechnol 26:303–304. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0308-303
Dutheil JY (2020) Statistical population genomics. Springer, US, New York, NY
Weir BS, Anderson AD, Hepler AB (2006) Genetic relatedness analysis: modern data and new challenges. Nat Rev Genet 7:771–780. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg1960
Wang B, Sverdlov S, Thompson E (2017) Efficient estimation of realized kinship from single nucleotide polymorphism genotypes. Genetics 205:1063–1078. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.116.197004
Raj A, Stephens M, Pritchard JK (2014) fastSTRUCTURE: Variational inference of population structure in large SNP data sets. Genetics 197:573–589. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.114.164350
Chaichoompu K, Abegaz F, Tongsima S et al (2019) IPCAPS: an R package for iterative pruning to capture population structure. Source Code Biol Med 14:2. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13029-019-0072-6
Lee C, Abdool A, Huang C-H (2009) PCA-based population structure inference with generic clustering algorithms. BMC Bioinformatics 10:S73. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-10-S1-S73
Alexander DH, Lange K (2011) Enhancements to the ADMIXTURE algorithm for individual ancestry estimation. BMC Bioinformatics 12:246. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-12-246
Alexander DH, Novembre J, Lange K (2009) Fast model-based estimation of ancestry in unrelated individuals. Genome Res 19:1655–1664. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.094052.109
Bradbury PJ, Zhang Z, Kroon DE et al (2007) TASSEL: software for association mapping of complex traits in diverse samples. Bioinformatics 23:2633–2635. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btm308
Loiselle BA, Sork VL, Nason J, Graham C (1995) Spatial genetic structure of a tropical understory shrub, Psychotria officinalis (Rubiaceae). Am J Bot 82:1420. https://doi.org/10.2307/2445869
VanRaden PM (2008) Efficient methods to compute genomic predictions. J Dairy Sci 91:4414–4423. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2007-0980
Sonah H, O’Donoughue L, Cober E et al (2014) Identification of loci governing eight agronomic traits using a GBS-GWAS approach and validation by QTL mapping in soya bean. Plant Biotechnol J 13:211–221. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12249
Torkamaneh D, Belzile F (2015) Scanning and filling: ultra-dense SNP genotyping combining genotyping-by-sequencing, SNP Array and whole-genome resequencing data. PLoS One 10:e0131533. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0131533
Malle S, Morrison M, Belzile F (2020) Identification of loci controlling mineral element concentration in soybean seeds. BMC Plant Biol 20:419. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-020-02631-w
Danecek P, Auton A, Abecasis G et al (2011) The variant call format and VCFtools. Bioinformatics 27:2156–2158. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btr330
Abraham G, Inouye M (2014) Fast principal component analysis of large-scale genome-wide data. PLoS One 9:e93766. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0093766
Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K et al (2007) PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet 81:559–575. https://doi.org/10.1086/519795
Earl DA, vonHoldt BM (2012) STRUCTURE HARVESTER: a website and program for visualizing STRUCTURE output and implementing the Evanno method. Conservation Genet Resour 4:359–361. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12686-011-9548-7
Francis RM (2017) pophelper: an R package and web app to analyse and visualize population structure. Mol Ecol Resour 17:27–32. https://doi.org/10.1111/1755-0998.12509
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Malle, S. (2022). Population Structure and Relatedness for Genome-Wide Association Studies. In: Torkamaneh, D., Belzile, F. (eds) Genome-Wide Association Studies. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2481. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-2237-7_12
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-2237-7_12
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-2236-0
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-2237-7
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols