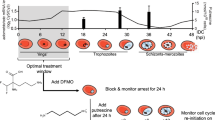
Abstract
Synchronisation of Plasmodium cultures is essential to investigate the complexities of time-dependent events associated with the asexual blood stage of the malaria parasite life cycle. Here we describe a procedure using ML10, a highly specific inhibitor of the parasite cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase (PKG), to attain high synchronicity of Plasmodium falciparum and P. knowlesi asexual blood-stage cultures and to obtain high levels of arrested mature schizonts as well as viable released merozoites. Additionally, we describe how to use ML10 to improve the transfection efficiency of P. falciparum parasites and also how to derive the half maximal effective concentration (EC50) of ML10 in other P. falciparum laboratory lines and clinical isolates.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bozdech Z, Llinas M, Pulliam BL, Wong ED, Zhu J, DeRisi JL (2003) The transcriptome of the intraerythrocytic developmental cycle of Plasmodium falciparum. PLoS Biol 1:e5
Grüring C, Heiber A, Kruse F, Ungefehr J, Gilberger TW, Spielmann T (2011) Development and host cell modifications of Plasmodium falciparum blood stages in four dimensions. Nat Commun 2:1–11
Sakaguchi M, Miyazaki N, Fujioka H, Kaneko O, Murata K (2016) Three-dimensional analysis of morphological changes in the malaria parasite infected red blood cell by serial block-face scanning electron microscopy. J Struct Biol 193:162–117
de Koning-Ward TF, Dixon MW, Tilley L, Gilson PR (2016) Plasmodium species: master renovators of their host cells. Nat Rev Microbiol 14:494–507
Ressurreição M, Thomas JA, Nofal SD, Flueck C, Moon RW, Baker DA, van Ooij C (2020) Use of a highly specific kinase inhibitor for rapid, simple and precise synchronization of Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium knowlesi asexual blood-stage parasites. PLoS One 15:e0235798
Burns AL, Dans MG, Balbin JM, de Koning-Ward TF, Gilson PR, Beeson JG, Boyle MJ, Wilson DW (2019) Targeting malaria parasite invasion of red blood cells as an antimalarial strategy. FEMS Microbiol Rev 43:223–238
Miller LH, Ackerman HC, Su XZ, Wellems TE (2013) Malaria biology and disease pathogenesis: insights for new treatments. Nat Med 19:156–167
Tanner M, Greenwood B, Whitty CJ, Ansah EK, Price RN, Dondorp AM, Von Seidlein L, Baird JK, Beeson JG, Fowkes FJ, Hemingway J (2015) Malaria eradication and elimination: views on how to translate a vision into reality. BMC Med 13:167–188
Trager W, Jensen JB (1976) Human malaria parasites in continuous culture. Science 193:673–675
Kocken CH, Ozwara H, van der Wel A, Beetsma AL, Mwenda JM, Thomas AW (2002) Plasmodium knowlesi provides a rapid in vitro and in vivo transfection system that enables double-crossover gene knockout studies. Infect Immun 70:655–660
Moon RW, Hall J, Rangkuti F, Ho YS, Almond N, Mitchell GH, Pain A, Holder AA, Blackman MJ (2013) Adaptation of the genetically tractable malaria pathogen Plasmodium knowlesi to continuous culture in human erythrocytes. PNAS 110:531–536
Lim C, Hansen E, DeSimone TM, Moreno Y, Junker K, Bei A, Brugnara C, Buckee CO, Duraisingh MT (2013) Expansion of host cellular niche can drive adaptation of a zoonotic malaria parasite to humans. Nat Commun 4:1–9
Chua AC, Ong JJY, Malleret B, Suwanarusk R, Kosaisavee V, Zeeman AM, Cooper CA, Tan KS, Zhang R, Tan BH, Abas SN (2019) Robust continuous in vitro culture of the Plasmodium cynomolgi erythrocytic stages. Nat Commun 10:1–13
Baker DA, Stewart LB, Large JM, Bowyer PW, Ansell KH, Jiménez-Díaz MB, El Bakkouri M, Birchall K, Dechering KJ, Bouloc NS, Coombs PJ (2017) A potent series targeting the malarial cGMP-dependent protein kinase clears infection and blocks transmission. Nat Commun 8:1–9
Taylor HM, McRobert L, Grainger M, Sicard A, Dluzewski AR, Hopp CS, Holder AA, Baker DA (2010) The malaria parasite cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase plays a central role in blood-stage schizogony. Eukaryot Cell 9:37–34
Collins CR, Hackett F, Strath M, Penzo M, Withers-Martinez C, Baker DA, Blackman MJ (2013) Malaria parasite cGMP-dependent protein kinase regulates blood stage merozoite secretory organelle discharge and egress. PLoS Pathog 9:e1003344
Alam MM, Solyakov L, Bottrill AR, Flueck C, Siddiqui FA, Singh S, Mistry S, Viskaduraki M, Lee K, Hopp CS, Chitnis CE (2015) Phosphoproteomics reveals malaria parasite Protein Kinase G as a signalling hub regulating egress and invasion. Nat Commun 6:1–15
Thomas JA, Tan MS, Bisson C, Borg A, Umrekar TR, Hackett F, Hale VL, Vizcay-Barrena G, Fleck RA, Snijders AP, Saibil HR (2018) A protease cascade regulates release of the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum from host red blood cells. Nat Microbiol 3:447–455
Penzo M, de Las Heras-Dueña L, Mata-Cantero L, Diaz-Hernandez B, Vazquez-Muñiz MJ, Ghidelli-Disse S, Drewes G, Fernandez-Alvaro E, Baker DA (2019) High-throughput screening of the Plasmodium falciparum cGMP-dependent protein kinase identified a thiazole scaffold which kills erythrocytic and sexual stage parasites. Sci Rep 9:1–13
Koussis K, Withers-Martinez C, Baker DA, Blackman MJ (2020) Simultaneous multiple allelic replacement in the malaria parasite enables dissection of PKG function. Life Sci Alliance 3:e21900626
Fierro MA, Asady B, Brooks CF, Cobb DW, Villegas A, Moreno SN, Muralidharan V (2020) An endoplasmic reticulum CREC family protein regulates the egress proteolytic cascade in malaria parasites. MBio 11:e03078–e03019
van Schalkwyk DA, Moon RW, Blasco B, Sutherland CJ (2017) Comparison of the susceptibility of Plasmodium knowlesi and Plasmodium falciparum to antimalarial agents. J Antimicrob Chemother 72:3051–3058
Janse CJ, Waters AP (1995) Plasmodium berghei: the application of cultivation and purification techniques to molecular studies of malaria parasites. Parasitol Today 11:138–143
Ngernna S, Chim-Ong A, Roobsoong W, Sattabongkot J, Cui L, Nguitragool W (2019) Efficient synchronization of Plasmodium knowlesi in vitro cultures using guanidine hydrochloride. Malar J 18:1–7
Mohring F, Hart MN, Rawlinson TA, Henrici R, Charleston JA, Benavente ED, Patel A, Hall J, Almond N, Campino S, Clark TG, Colin SJ, Baker DA, Draper SJ, Moon RW (2019) Rapid and iterative genome editing in the malaria parasite Plasmodium knowlesi provides new tools for P. vivax research. elife 8:e45829
Collins CR, Das S, Wong EH, Andenmatten N, Stallmach R, Hackett F, Herman JP, Müller S, Meissner M, Blackman MJ (2013) Robust inducible Cre recombinase activity in the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum enables efficient gene deletion within a single asexual erythrocytic growth cycle. Mol Microbiol 88:687–701
Ghorbal M, Gorman M, Macpherson CR, Martins RM, Scherf A, Lopez-Rubio JJ (2014) Genome editing in the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum using the CRISPR-Cas9 system. Nat Biotechnol 32:819–821
de Koning-Ward TF, Gilson PR, Crabb BS (2015) Advances in molecular genetic systems in malaria. Nat Rev Microbiol 13:373–387
Kudyba HM, Cobb DW, Florentin A, Krakowiak M, Muralidharan V (2018) CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing to make conditional mutants of human malaria parasite P. falciparum. J Vis Exp 139:e57747
Skinner-Adams TS, Lawrie PM, Hawthorne PL, Gardiner DL, Trenholme KR (2003) Comparison of Plasmodium falciparum transfection methods. Malar J 2:19–23
Hasenkamp S, Russell KT, Horrocks P (2012) Comparison of the absolute and relative efficiencies of electroporation-based transfection protocols for Plasmodium falciparum. Malar J 11:210–214
Mohring F, Hart MN, Patel A, Baker DA, Moon RW (2020) CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing of Plasmodium knowlesi. Bio-protocol 10(4):e3522–e3522
Smilkstein M, Sriwilaijaroen N, Kelly JX, Wilairat P, Riscoe M (2004) Simple and inexpensive fluorescence-based technique for high-throughput antimalarial drug screening. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 48:1803–1809
Mohring F, Rawlinson TA, Draper SJ, Moon RW (2020) Multiplication and growth inhibition activity assays for the zoonotic malaria parasite, Plasmodium knowlesi. Bio-protocol 10:e3743–e3743
Gadagkar SR, Call GB (2015) Computational tools for fitting the Hill equation to dose–response curves. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods 71:68–76
Acknowledgments
We thank Gisela Henriques, Franziska Mohring, Christian Flueck, Stefanie Nofal, and Avnish Patel for their expert advice, Melissa Hart for supplying Plasmodium knowlesi parasites and James Thomas for contributing toward the original published research. Finally, we thank Simon Osborne at LifeArc for supplying ML10.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Ressurreição, M., Moon, R.W., Baker, D.A., van Ooij, C. (2022). Synchronisation of Plasmodium falciparum and P. knowlesi In Vitro Cultures Using a Highly Specific Protein Kinase Inhibitor. In: Jensen, A.T.R., Hviid, L. (eds) Malaria Immunology. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2470. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-2189-9_10
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-2189-9_10
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-2188-2
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-2189-9
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols