Abstract
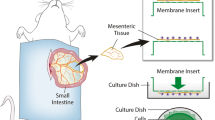
Stromal vascular fraction (SVF), isolated from adipose tissue, identifies as a rich cell source comprised of endothelial cells, endothelial progenitor cells, pericytes, smooth muscle cells, fibroblasts, and immune cells. SVF represents a promising therapeutic heterogonous cell source for growing new blood microvessels due to its rich niche of cells. However, the spatiotemporal dynamics of SVF within living tissues remain largely unknown. The objective of this chapter is to describe a protocol for culturing SVF on mouse mesentery tissues in order to aid in the discovery of SVF dynamics and associated vessel growth over time. SVF was isolated from the inguinal adipose from adult mice and seeded onto mesentery tissues. Tissues were then cultured for up to 5 days and labeled with endothelial cell and pericyte markers. Representative results demonstrate the observation of SVF-derived vasculogenesis characterized by de novo vessel formation and subsequent vessel connection.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
31 January 2022
A correction has been published.
References
Jones VM, Suarez-Martinez AD, Hodges NA, Murfee WL, Llull R, Katz AJ (2021) A clinical perspective on adipose-derived cell therapy for enhancing microvascular health and function: implications and applications for reconstructive surgery. Microcirculation 28(3):e12672. https://doi.org/10.1111/micc.12672
Brown JC, Shang H, Li Y, Yang N, Patel N, Katz AJ (2017) Isolation of adipose-derived stromal vascular fraction cells using a novel point-of-care device: cell characterization and review of the literature. Tissue Eng Part C Methods 23(3):125–135. https://doi.org/10.1089/ten.TEC.2016.0377
Leblanc AJ, Nguyen QT, Touroo JS, Aird AL, Chang RC, Ng CK et al (2013) Adipose-derived cell construct stabilizes heart function and increases microvascular perfusion in an established infarct. Stem Cells Transl Med 2(11):896–905. https://doi.org/10.5966/sctm.2013-0046
Nunes SS, Maijub JG, Krishnan L, Ramakrishnan VM, Clayton LR, Williams SK et al (2013) Generation of a functional liver tissue mimic using adipose stromal vascular fraction cell-derived vasculatures. Sci Rep 3:2141. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep02141
Maijub JG, Boyd NL, Dale JR, Hoying JB, Morris ME, Williams SK (2015) Concentration-dependent vascularization of adipose stromal vascular fraction cells. Cell Transplant 24(10):2029–2039. https://doi.org/10.3727/096368914X685401
Muller S, Ader I, Creff J, Lemenager H, Achard P, Casteilla L et al (2019) Human adipose stromal-vascular fraction self-organizes to form vascularized adipose tissue in 3D cultures. Sci Rep 9(1):7250. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-43624-6
Madri JA, Williams SK (1983) Capillary endothelial cell cultures: phenotypic modulation by matrix components. J Cell Biol 97(1):153–165. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.97.1.153
Koh YJ, Koh BI, Kim H, Joo HJ, Jin HK, Jeon J et al (2011) Stromal vascular fraction from adipose tissue forms profound vascular network through the dynamic reassembly of blood endothelial cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 31(5):1141–1150. https://doi.org/10.1161/ATVBAHA.110.218206
Strassburg S, Nienhueser H, Bjorn Stark G, Finkenzeller G, Torio-Padron N (2016) Co-culture of adipose-derived stem cells and endothelial cells in fibrin induces angiogenesis and vasculogenesis in a chorioallantoic membrane model. J Tissue Eng Regen Med 10(6):496–506. https://doi.org/10.1002/term.1769
Karagergou E, Dionyssopoulos A, Karayannopoulou M, Psalla D, Theodoridis A, Demiri E et al (2018) Adipose-derived stromal vascular fraction aids epithelialisation and angiogenesis in an animal model. J Wound Care 27(10):637–644. https://doi.org/10.12968/jowc.2018.27.10.637
Leblanc AJ, Touroo JS, Hoying JB, Williams SK (2012) Adipose stromal vascular fraction cell construct sustains coronary microvascular function after acute myocardial infarction. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 302(4):H973–H982. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00735.2011
Zakhari JS, Zabonick J, Gettler B, Williams SK (2018) Vasculogenic and angiogenic potential of adipose stromal vascular fraction cell populations in vitro. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 54(1):32–40. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-017-0213-7
Norrby K (2006) In vivo models of angiogenesis. J Cell Mol Med 10(3):588–612. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1582-4934.2006.tb00423.x
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by NIH grant R01AG049821 and funding from the University of Florida’s Division of Research Program Development.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Majbour, D. et al. (2022). An Ex Vivo Tissue Culture Method for Discovering Cell Dynamics Involved in Stromal Vascular Fraction Vasculogenesis Using the Mouse Mesentery . In: Benest, A.V. (eds) Angiogenesis. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2441. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-2059-5_12
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-2059-5_12
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-2058-8
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-2059-5
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols