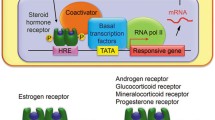
Abstract
MicroRNAs play critical roles through their impact on posttranscriptional gene regulation. In cancer, they can act as oncogenes or tumor suppressors and can also function as biomarkers. Here, we describe a method for robust characterization of estrogen-regulated microRNA profiles. The activity of estrogen is mediated by two nuclear receptors, estrogen receptor alpha and estrogen receptor beta, and a transmembrane G-protein coupled estrogen receptor 1. This chapter details how to prepare cells for optimal estrogen response, directions for estrogen treatment, RNA extraction, different microRNA profiling approaches, and subsequent confirmations.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116(2):281–297
Cui M, Wang H, Yao X, Zhang D, Xie Y, Cui R et al (2019) Circulating MicroRNAs in cancer: potential and challenge. Front Genet 10:626
Fromm B, Billipp T, Peck LE, Johansen M, Tarver JE, King BL et al (2015) A uniform system for the annotation of vertebrate microRNA genes and the evolution of the human microRNAome. Annu Rev Genet 49:213–242
McGeary SE, Lin KS, Shi CY, Pham TM, Bisaria N, Kelley GM et al (2019) The biochemical basis of microRNA targeting efficacy. Science 366(6472):eaav1741
Tao S, He H, Chen Q (2015) Estradiol induces HOTAIR levels via GPER-mediated miR-148a inhibition in breast cancer. J Transl Med 13:131
Tao S, He H, Chen Q, Yue W (2014) GPER mediated estradiol reduces miR-148a to promote HLA-G expression in breast cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 451(1):74–78
Vivacqua A, Sebastiani A, Miglietta AM, Rigiracciolo DC, Cirillo F, Galli GR et al (2018) miR-338-3p is regulated by estrogens through GPER in breast cancer cells and cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs). Cells 7(11):203
Andersson S, Sundberg M, Pristovsek N, Ibrahim A, Jonsson P, Katona B et al (2017) Insufficient antibody validation challenges oestrogen receptor beta research. Nat Commun 8:15840
The Human Protein Atlas. Available from: http://www.proteinatlas.org
Uhlen M, Fagerberg L, Hallstrom BM, Lindskog C, Oksvold P, Mardinoglu A et al (2015) Proteomics. Tissue-based map of the human proteome. Science 347(6220):1260419
Williams C, Lin CY (2013) Oestrogen receptors in breast cancer: basic mechanisms and clinical implications. Ecancermedicalscience 7:370
Pagano MT, Ortona E, Dupuis ML (2020) A role for estrogen receptor alpha36 in cancer progression. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 11:506
Sieh W, Kobel M, Longacre TA, Bowtell DD, deFazio A, Goodman MT et al (2013) Hormone-receptor expression and ovarian cancer survival: an ovarian tumor tissue analysis consortium study. Lancet Oncol 14(9):853–862
Li SF, Shiozawa T, Nakayama K, Nikaido T, Fujii S (1996) Stepwise abnormality of sex steroid hormone receptors, tumor suppressor gene products (p53 and Rb), and cyclin E in uterine endometrioid carcinoma. Cancer 77(2):321–329
Shih HC, Shiozawa T, Kato K, Imai T, Miyamoto T, Uchikawa J et al (2003) Immunohistochemical expression of cyclins, cyclin-dependent kinases, tumor-suppressor gene products, Ki-67, and sex steroid receptors in endometrial carcinoma: positive staining for cyclin A as a poor prognostic indicator. Hum Pathol 34(5):471–478
Langdon SP, Crew AJ, Ritchie AA, Muir M, Wakeling A, Smyth JF et al (1994) Growth inhibition of oestrogen receptor-positive human ovarian carcinoma by anti-oestrogens in vitro and in a xenograft model. Eur J Cancer 30A(5):682–686
Liao XH, Lu DL, Wang N, Liu LY, Wang Y, Li YQ et al (2014) Estrogen receptor alpha mediates proliferation of breast cancer MCF-7 cells via a p21/PCNA/E2F1-dependent pathway. FEBS J 281(3):927–942
Sanchez AM, Flamini MI, Baldacci C, Goglia L, Genazzani AR, Simoncini T (2010) Estrogen receptor-alpha promotes breast cancer cell motility and invasion via focal adhesion kinase and N-WASP. Mol Endocrinol 24(11):2114–2125
Smyth JF, Gourley C, Walker G, MacKean MJ, Stevenson A, Williams AR et al (2007) Antiestrogen therapy is active in selected ovarian cancer cases: the use of letrozole in estrogen receptor-positive patients. Clin Cancer Res 13(12):3617–3622
Stasenko M, Plegue M, Sciallis AP, McLean K (2015) Clinical response to antiestrogen therapy in platinum-resistant ovarian cancer patients and the role of tumor estrogen receptor expression status. Int J Gynecol Cancer 25(2):222–228
Chantalat E, Boudou F, Laurell H, Palierne G, Houtman R, Melchers D et al (2016) The AF-1-deficient estrogen receptor ERalpha46 isoform is frequently expressed in human breast tumors. Breast Cancer Res 18(1):123
Fanning SW, Mayne CG, Dharmarajan V, Carlson KE, Martin TA, Novick SJ et al (2016) Estrogen receptor alpha somatic mutations Y537S and D538G confer breast cancer endocrine resistance by stabilizing the activating function-2 binding conformation. Elife 5:e12792
Backes FJ, Walker CJ, Goodfellow PJ, Hade EM, Agarwal G, Mutch D et al (2016) Estrogen receptor-alpha as a predictive biomarker in endometrioid endometrial cancer. Gynecol Oncol 141(2):312–317
Langdon SP, Herrington CS, Hollis RL, Gourley C (2020) Estrogen signaling and its potential as a target for therapy in ovarian cancer. Cancers (Basel) 12(6):1647
Drummond AE, Fuller PJ (2012) Ovarian actions of estrogen receptor-beta: an update. Semin Reprod Med 30(1):32–38
Lurie G, Wilkens LR, Thompson PJ, Shvetsov YB, Matsuno RK, Carney ME et al (2011) Estrogen receptor beta rs1271572 polymorphism and invasive ovarian carcinoma risk: pooled analysis within the ovarian cancer association consortium. PLoS One 6(6):e20703
Chan KKL, Siu MKY, Jiang YX, Wang JJ, Wang Y, Leung THY et al (2017) Differential expression of estrogen receptor subtypes and variants in ovarian cancer: effects on cell invasion, proliferation and prognosis. BMC Cancer 17(1):606
Ciucci A, Zannoni GF, Travaglia D, Petrillo M, Scambia G, Gallo D (2014) Prognostic significance of the estrogen receptor beta (ERbeta) isoforms ERbeta1, ERbeta2, and ERbeta5 in advanced serous ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol 132(2):351–359
Bossard C, Busson M, Vindrieux D, Gaudin F, Machelon V, Brigitte M et al (2012) Potential role of estrogen receptor beta as a tumor suppressor of epithelial ovarian cancer. PLoS One 7(9):e44787
Hernandez-Silva CD, Villegas-Pineda JC, Pereira-Suarez AL (2020) Expression and role of the G protein-coupled estrogen receptor (GPR30/GPER) in the development and immune response in female reproductive cancers. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 11:544
Ignatov A, Ignatov T, Weissenborn C, Eggemann H, Bischoff J, Semczuk A et al (2011) G-protein-coupled estrogen receptor GPR30 and tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 128(2):457–466
Yu YT, Maroney PA, Darzynkiwicz E, Nilsen TW (1995) U6 snRNA function in nuclear pre-mRNA splicing: a phosphorothioate interference analysis of the U6 phosphate backbone. RNA 1(1):46–54
Krakstad C, Trovik J, Wik E, Engelsen IB, Werner HM, Birkeland E et al (2012) Loss of GPER identifies new targets for therapy among a subgroup of ERalpha-positive endometrial cancer patients with poor outcome. Br J Cancer 106(10):1682–1688
Smith HO, Arias-Pulido H, Kuo DY, Howard T, Qualls CR, Lee SJ et al (2009) GPR30 predicts poor survival for ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol 114(3):465–471
Skrzypczak M, Schuler S, Lattrich C, Ignatov A, Ortmann O, Treeck O (2013) G protein-coupled estrogen receptor (GPER) expression in endometrial adenocarcinoma and effect of agonist G-1 on growth of endometrial adenocarcinoma cell lines. Steroids 78(11):1087–1091
Bhat-Nakshatri P, Wang G, Collins NR, Thomson MJ, Geistlinger TR, Carroll JS et al (2009) Estradiol-regulated microRNAs control estradiol response in breast cancer cells. Nucleic Acids Res 37(14):4850–4861
Klinge CM (2012) miRNAs and estrogen action. Trends Endocrinol Metab 23(5):223–233
An JH, Ohn JH, Song JA, Yang JY, Park H, Choi HJ et al (2014) Changes of microRNA profile and microRNA-mRNA regulatory network in bones of ovariectomized mice. J Bone Miner Res 29(3):644–656
Kangas R, Pollanen E, Rippo MR, Lanzarini C, Prattichizzo F, Niskala P et al (2014) Circulating miR-21, miR-146a and Fas ligand respond to postmenopausal estrogen-based hormone replacement therapy--a study with monozygotic twin pairs. Mech Ageing Dev 143-144:1–8
Kangas R, Tormakangas T, Fey V, Pursiheimo J, Miinalainen I, Alen M et al (2017) Aging and serum exomiR content in women-effects of estrogenic hormone replacement therapy. Sci Rep 7:42702
Abe S, Iwasaki M, Habata S, Mariya T, Tamate M, Matsuura M et al (2021) ERalpha increases endometrial cancer cell resistance to cisplatin via upregulation of BAG3. Oncol Lett 21(1):20
Kong X, Xu X, Yan Y, Guo F, Li J, Hu Y et al (2014) Estrogen regulates the tumour suppressor MiRNA-30c and its target gene, MTA-1, in endometrial cancer. PLoS One 9(3):e90810
Li S, Li Y, Wen Z, Kong F, Guan X, Liu W (2014) microRNA-206 overexpression inhibits cellular proliferation and invasion of estrogen receptor alpha-positive ovarian cancer cells. Mol Med Rep 9(5):1703–1708
Ma H, Tian T, Liang S, Liu X, Shen H, Xia M et al (2016) Estrogen receptor-mediated miR-486-5p regulation of OLFM4 expression in ovarian cancer. Oncotarget 7(9):10594–10605
Bailey ST, Westerling T, Brown M (2015) Loss of estrogen-regulated microRNA expression increases HER2 signaling and is prognostic of poor outcome in luminal breast cancer. Cancer Res 75(2):436–445
Gupta A, Caffrey E, Callagy G, Gupta S (2012) Oestrogen-dependent regulation of miRNA biogenesis: many ways to skin the cat. Biochem Soc Trans 40(4):752–758
Wickramasinghe NS, Manavalan TT, Dougherty SM, Riggs KA, Li Y, Klinge CM (2009) Estradiol downregulates miR-21 expression and increases miR-21 target gene expression in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Nucleic Acids Res 37(8):2584–2595
Katchy A, Edvardsson K, Aydogdu E, Williams C (2012) Estradiol-activated estrogen receptor alpha does not regulate mature microRNAs in T47D breast cancer cells. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 128(3–5):145–153
Milevskiy MJG, Gujral U, Del Lama MC, Stone A, Northwood K, Burke LJ et al (2019) MicroRNA-196a is regulated by ER and is a prognostic biomarker in ER+ breast cancer. Br J Cancer 120(6):621–632
Katchy A, Williams C (2014) Profiling of estrogen-regulated microRNAs in breast cancer cells. J Vis Exp 84:e51285
Edvardsson K, Nguyen-Vu T, Kalasekar SM, Ponten F, Gustafsson JA, Williams C (2013) Estrogen receptor beta expression induces changes in the microRNA pool in human colon cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 34(7):1431–1441
Katchy A, Williams C (2016) Expression profiles of estrogen-regulated MicroRNAs in breast cancer cells. Methods Mol Biol 1366:373–393
Williams C, Edvardsson K, Lewandowski SA, Strom A, Gustafsson JA (2008) A genome-wide study of the repressive effects of estrogen receptor beta on estrogen receptor alpha signaling in breast cancer cells. Oncogene 27(7):1019–1032
Tsouko E, Wang J, Frigo DE, Aydogdu E, Williams C (2015) miR-200a inhibits migration of triple-negative breast cancer cells through direct repression of the EPHA2 oncogene. Carcinogenesis 36(9):1051–1060
Zhou X, Zhu Q, Eicken C, Sheng N, Zhang X, Yang L et al (2012) MicroRNA profiling using microParaflo microfluidic array technology. Methods Mol Biol 822:153–182
Kugelberg U, Natt D, Skog S, Kutter C, Ost A (2020) 5 XP sRNA-seq: efficient identification of transcripts with and without 5 phosphorylation reveals evolutionary conserved small RNA. RNA Biol 31:1–12
Griffiths-Jones S, Grocock RJ, van Dongen S, Bateman A, Enright AJ (2006) miRBase: microRNA sequences, targets and gene nomenclature. Nucleic Acids Res 34(Database issue):D140–D144
Chen C, Ridzon DA, Broomer AJ, Zhou Z, Lee DH, Nguyen JT et al (2005) Real-time quantification of microRNAs by stem-loop RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 33(20):e179
Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia—CCLE. Available from: https://portals.broadinstitute.org/ccle
Kao J, Salari K, Bocanegra M, Choi YL, Girard L, Gandhi J et al (2009) Molecular profiling of breast cancer cell lines defines relevant tumor models and provides a resource for cancer gene discovery. PLoS One 4(7):e6146
Lacroix M, Leclercq G (2004) Relevance of breast cancer cell lines as models for breast tumours: an update. Breast Cancer Res Treat 83(3):249–289
Neve RM, Chin K, Fridlyand J, Yeh J, Baehner FL, Fevr T et al (2006) A collection of breast cancer cell lines for the study of functionally distinct cancer subtypes. Cancer Cell 10(6):515–527
Ross DT, Perou CM (2001) A comparison of gene expression signatures from breast tumors and breast tissue derived cell lines. Dis Markers 17(2):99–109
Frasor J, Danes JM, Komm B, Chang KC, Lyttle CR, Katzenellenbogen BS (2003) Profiling of estrogen up- and down-regulated gene expression in human breast cancer cells: insights into gene networks and pathways underlying estrogenic control of proliferation and cell phenotype. Endocrinology 144(10):4562–4574
Benes V, Castoldi M (2010) Expression profiling of microRNA using real-time quantitative PCR, how to use it and what is available. Methods 50(4):244–249
Schmittgen TD, Jiang J, Liu Q, Yang L (2004) A high-throughput method to monitor the expression of microRNA precursors. Nucleic Acids Res 32(4):e43
Welshons WV, Wolf MF, Murphy CS, Jordan VC (1988) Estrogenic activity of phenol red. Mol Cell Endocrinol 57(3):169–178
Wesierska-Gadek J, Schreiner T, Maurer M, Waringer A, Ranftler C (2007) Phenol red in the culture medium strongly affects the susceptibility of human MCF-7 cells to roscovitine. Cell Mol Biol Lett 12(2):280–293
Katchy A, Pinto C, Jonsson J, Nguyen-Vu T, Pandelova M, Riu A et al (2014) Co-exposure to phytoestrogens and bisphenol A mimics estrogenic effects in an additive manner. Toxicol Sci 138(1):21–35
Kim YK, Yeo J, Kim B, Ha M, Kim VN (2012) Short structured RNAs with low GC content are selectively lost during extraction from a small number of cells. Mol Cell 46(6):893–895
Setiawan AN, Lokman PM (2010) The use of reference gene selection programs to study the silvering transformation in a freshwater eel Anguilla australis: a cautionary tale. BMC Mol Biol 11:75
Yuan JS, Reed A, Chen F, Stewart CN Jr (2006) Statistical analysis of real-time PCR data. BMC Bioinformatics 7:85
Baker M (2010) MicroRNA profiling: separating signal from noise. Nat Methods 7(9):687–692
Kang W, Eldfjell Y, Fromm B, Estivill X, Biryukova I, Friedlander MR (2018) miRTrace reveals the organismal origins of microRNA sequencing data. Genome Biol 19(1):213
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Swedish Cancer Society (Cancerfonden CAN 2018/596 to C.W.), the Stockholm County Council (Region Stockholm, HMT 2020-0346 to C.W.), the Swedish Research Council (2017-01658 to C.W.; 2019–05165 to C.K.), Knut & Alice Wallenberg foundation (KAW 2016.0174 to C.K.), Ruth & Richard Julin foundation (2020-00294 to C.K.), and Lillian Sagen & Curt Ericsson research foundation (2021-00427, C.K.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Archer, A., Kutter, C., Williams, C. (2022). Expression Profiles of Estrogen-Regulated MicroRNAs in Cancer Cells. In: Eyster, K.M. (eds) Estrogen Receptors. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2418. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1920-9_18
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1920-9_18
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-1919-3
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-1920-9
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols