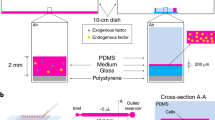
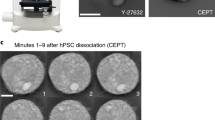
Abstract
Human induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) are generated from somatic cells by the expression of a cocktail of transcription factors, and iPSCs have the capacity to generate in vitro all cell types of the human body. In addition to primed (conventional) iPSCs, several groups recently reported the generation of human naïve iPSCs, which are in a more primitive developmental state and have a broader developmental potential, as shown by their ability to form cells of the placenta. Human iPSCs have broad medical potential but their generation is often time-consuming, not scalable and requires viral vectors or stable genetic manipulations. To overcome such limitations, we developed protocols for high-efficiency generation of either conventional or naïve iPSCs by delivery of messenger RNAs (mRNAs) using a microfluidic system. In this protocol we describe how to produce microfluidic devices, and how to reprogram human somatic cells into naïve and primed iPSCs using these devices. We also describe how to transfer the iPSC colonies from the microfluidic devices over to standard multiwell plates for subsequent expansion of the cultures. Our approach does not require stable genetic modifications, is reproducible and cost-effective, allowing to produce patient-specific iPSCs for cell therapy, disease modeling, and in vitro developmental studies.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thomson JA, Itskovitz-Eldor J, Shapiro SS et al (1998) Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts. Science 282:1145–1147
Takahashi K, Tanabe K, Ohnuki M et al (2007) Induction of pluripotent stem cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell 131:861–872
Yu J, Vodyanik MA, Smuga-Otto K et al (2007) Induced pluripotent stem cell lines derived from human somatic cells. Science 318:1917–1920
Osafune K, Caron L, Borowiak M et al (2008) Marked differences in differentiation propensity among human embryonic stem cell lines. Nat Biotechnol 26:313–315
Tchieu J, Kuoy E, Chin MH et al (2010) Female human iPSCs retain an inactive X chromosome. Cell Stem Cell 7:329–342
Lister R, Pelizzola M, Kida YS et al (2011) Hotspots of aberrant epigenomic reprogramming in human induced pluripotent stem cells. Nature 471:68–73
Perrera V, Martello G (2019) How does reprogramming to pluripotency affect genomic imprinting? Front Cell Dev Biol 7:76
Takashima Y, Guo G, Loos R et al (2014) Resetting transcription factor control circuitry toward ground-state pluripotency in human. Cell 158:1254–1269
Theunissen TW, Friedli M, He Y et al (2016) Molecular criteria for defining the naïve human pluripotent state. Cell Stem Cell 19:502–515
Guo G, von Meyenn F, Santos F et al (2016) naive pluripotent stem cells derived directly from isolated cells of the human inner cell mass. Stem Cell Reports 6:437–446
Giulitti S, Pellegrini M, Zorzan I et al (2019) Direct generation of human naive induced pluripotent stem cells from somatic cells in microfluidics. Nat Cell Biol 21:275–286
Liu X, Nefzger CM, Rossello FJ et al (2017) Comprehensive characterization of distinct states of human naive pluripotency generated by reprogramming. Nat Methods 14:1055–1062
Wang Y, Zhao C, Hou Z et al (2018) Unique molecular events during reprogramming of human somatic cells to induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) at naïve state. elife 7:1–21
Kilens S, Meistermann D, Moreno D et al (2018) Parallel derivation of isogenic human primed and naive induced pluripotent stem cells. Nat Commun 9:360
Dong C, Beltcheva M, Gontarz P et al (2020) Derivation of trophoblast stem cells from naïve human pluripotent stem cells. elife 9:e52504
Cinkornpumin JK, Kwon SY, Guo Y et al (2020) naive human embryonic stem cells can give rise to cells with a trophoblast-like transcriptome and Methylome. Stem Cell Reports 15:198–213
Guo G, Stirparo GG, Strawride S et al (2021) Human naïve epiblast cells possess unrestricted lineage potential. Cell Stem Cell 28:1040–1056
Linneberg-Agerholm M, Wong YF, Herrera JAR et al (2019) Naïve human pluripotent stem cells respond to Wnt, nodal and LIF signalling to produce expandable naïve extra-embryonic endoderm. Development 146:dev180620
Sahakyan A, Kim R, Chronis C et al (2017) Human naive pluripotent stem cells model X chromosome dampening and X inactivation. Cell Stem Cell 20:87–101
Luni C, Giulitti S, Serena E et al (2016) High-efficiency cellular reprogramming with microfluidics. Nat Methods 13:446–452
Gagliano O, Luni C, Qin W et al (2019) Microfluidic reprogramming to pluripotency of human somatic cells. Nat Protoc 14:722–737
Warren L, Manos PD, Ahfeldt T et al (2010) Highly efficient reprogramming to pluripotency and directed differentiation of human cells with synthetic modified mRNA. Cell Stem Cell 7:618–630
Chen G, Gulbranson DR, Hou Z et al (2011) Chemically defined conditions for human iPSC derivation and culture. Nat Methods 8:424–429
Acknowledgments
We thank the Martello and Elvassore laboratories for comments and suggestions. GM is supported by the Giovanni Armenise-Harvard Foundation, the Telethon Foundation (TCP13013) and The ERC Starting Grant (MetEpiStem). OG is supported by 2019 STARS Starting Grant of University of Padova. NE is supported by 2017 STARS-WiC Grant of University of Padova and Progetti di Eccellenza Cariparo.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Zorzan, I., Gagliano, O., Elvassore, N., Martello, G. (2022). Using Microfluidics to Generate Human Naïve and Primed Pluripotent Stem Cells. In: Rugg-Gunn, P. (eds) Human Naïve Pluripotent Stem Cells. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2416. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1908-7_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1908-7_5
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-1907-0
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-1908-7
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols