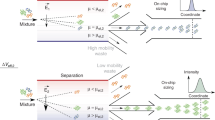
Abstract
The separation of complex mixtures is ubiquitous throughout molecular biology, and techniques such as gel-based electrophoresis are common laboratory practice. Such methods are not without their drawbacks, however, which include non-specific interactions between analyte and the separation matrix, poor yields in purification and non-continuous analyte throughput. Microfluidic techniques, which exploit physical phenomena unique to the microscale, promise to improve many aspects of traditional laboratory procedures. These methods offer a quantitative, solution-based alternative to traditional gel electrophoresis, with rapid measurement times enabling the analysis of transient or weak biomolecular interactions that would be challenging to observe with traditional methods. Here, we present a protocol for the lithographic fabrication and operation of microfluidic chips capable of free-flow electrophoretic (FFE) fractionation and analysis of biological analytes. We demonstrate the efficacy of our approach through a protein-sensing methodology based on FFE fractionation of DNA–protein mixtures. In addition, the FFE technique described here can be readily adapted to suit a variety of preparative and analytical applications, providing information on the charge, zeta-potential, and interactions of analytes.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fonslow BR, Bowser MT (2006) Optimizing band width and resolution in micro-free flow electrophoresis. Anal Chem 78:8236–8244
Kohlheyer D, Eijkel JCT, van den Berg A, Schasfoort RBM (2008) Miniaturizing free-flow electrophoresis—a critical review. Electrophoresis 29:977–993
Turgeon RT, Bowser MT (2009) Micro free-flow electrophoresis: theory and applications. Anal Bioanal Chem 394:187–198
Beebe DJ, Mensing GA, Walker GM (2002) Physics and applications of microfluidics in biology. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 4:261–286
Saar KL, Zhang Y, Muller T, Challa PK, Devenish S, Andrew L, Knowles TPJ (2018) On chip label free protein analysis with downstream electrodes for direct removal of electrolysis products. Lab Chip 18:162–170
Herling TW, Arosio P, Müller T, Linse S, Knowles TPJ (2015) A microfluidic platform for quantitative measurements of effective protein charges and single ion binding in solution. Phys Chem Chem Phys 17:12161–12167
Arter WE, Charmet J, Kong J, Saar KL, Herling TW, Müller T, Keyser UF, Knowles TPJ (2018) Combining affinity selection and specific ion mobility for microchip protein sensing. Anal Chem 90:10302–10310
Karger BL, Guttman A (2009) DNA sequencing by CE. Electrophoresis 30:196–202
Harstad RK, Johnson AC, Weisenberger MM, Bowser MT (2015) Capillary electrophoresis. Anal Chem 88:299–399
Saar KL, Peter Q, Müller T, Challa PK, Herling TW, Knowles TPJ (2019) Rapid two-dimensional characterisation of proteins in solution. Microsyst Nanoeng 5:33
Herling TW, O'Connell DJ, Bauer MC, Persson J, Weininger U, Knowles TPJ, Linse S (2016) A microfluidic platform for real-time detection and quantification of protein-ligand interactions. Biophys J 110:1957–1966
Łapińska U, Saar KL, Yates EV, Herling TW, Müller T, Challa PK, Dobson CM, Knowles TPJ (2017) Gradient-free determination of isoelectric points of proteins on chip. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics 19:23060–23067
Challa PK, Kartanas T, Charmet J, Knowles TPJ (2017) Microfluidic devices fabricated using fast wafer-scale LED-lithography patterning. Biomicrofluidics 11:014113. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4976690
Howarth M, Ting A (2008) Imaging proteins in live mammalian cells with biotin ligase and monovalent streptavidin. Nat Protoc 3:534–545. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2008.20
Song YAK, Chan M, Cello C, Tannenbaum SR, Wishnok JS, Han J (2010) Free-flow zone electrophoresis of peptides and proteins in PDMS microchip for narrow pi range sample prefractionation coupled with mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 82:2317–2325
Li B, Ellington AD, Chen X (2011) Rational, modular adaptation of enzyme-free dna circuits to multiple detection methods. Nucleic Acids Res 39:e110
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Arter, W.E., Saar, K.L., Herling, T.W., Knowles, T.P.J. (2022). Microchip Free-Flow Electrophoresis for Bioanalysis, Sensing, and Purification. In: Rasooly, A., Baker, H., Ossandon, M.R. (eds) Biomedical Engineering Technologies. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2394. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1811-0_16
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1811-0_16
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-1810-3
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-1811-0
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols