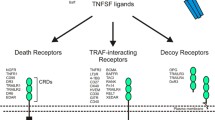
Abstract
In vivo research of the last decade revealed that the anchoring of antitumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor superfamily (TNFRSF) receptor antibodies to cell-expressed Fcγ receptors (FcγR) can be of decisive relevance for their receptor-stimulatory activity. Indeed, FcγR anchoring may even result in the conversion of antagonistic to agonistic anti-TNFR antibody activity. The knowledge on this issue is obviously not only relevant to understand the in vivo effects of anti-TNFR antibodies but also of overwhelming importance for the rational clinical development of antibodies and antibody derivatives. Based on the fact that with exception of the decoy TNFRSF receptors (TNFRs) all TNFRs are able to trigger proinflammatory NFκB signaling, resulting in the production of chemokines and cytokines, we established an easy and broadly applicable coculture assay for the evaluation of the FcγR-dependency of the agonism of anti-TNFR antibodies. In this assay, TNFR responder cells, which produce high amounts of IL8 in response to TNFR stimulation, were pairwise incubated with empty vector- and FcγR-transfected HEK293 cells, which produce only very low amounts of IL8. This cocultures were then comparatively analyzed with respect to anti-TNFR antibody-induced IL8 production as a readout for TNFR activation to uncover proagonistic effects of FcγR binding.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggarwal BB, Gupta SC, Kim JH (2012) Historical perspectives on tumor necrosis factor and its superfamily: 25 years later, a golden journey. Blood 119:651–665
Wajant H (2015) Principles of antibody-mediated TNF receptor activation. Cell Death Differ 22:1727–1741
Dahan R, Barnhart BC, Li F et al (2016) Therapeutic activity of agonistic, human anti-CD40 monoclonal antibodies requires selective FcgammaR engagement. Cancer Cell 29:820–831
Jodo S, Kung JT, Xiao S et al (2003) Anti-CD95-induced lethality requires radioresistant Fcgamma RII+ cells. A novel mechanism for fulminant hepatic failure. J Biol Chem 278:7553–7557
Li F, Ravetch JV (2011) Inhibitory Fcgamma receptor engagement drives adjuvant and anti-tumor activities of agonistic CD40 antibodies. Science 333:1030–1034
Li F, Ravetch JV (2012) Apoptotic and antitumor activity of death receptor antibodies require inhibitory Fcgamma receptor engagement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:10966–10971
Li F, Ravetch JV (2013) Antitumor activities of agonistic anti-TNFR antibodies require differential FcgammaRIIB coengagement in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:19501–19506
Medler J, Nelke J, Weisenberger D et al (2019) TNFRSF receptor-specific antibody fusion proteins with targeting controlled FcgammaR-independent agonistic activity. Cell Death Dis 10:224
Salzmann S, Seher A, Trebing J et al (2013) Fibroblast growth factor inducible (Fn14)-specific antibodies concomitantly display signaling pathway-specific agonistic and antagonistic activity. J Biol Chem 288:13455–13466
Trebing J, Lang I, Chopra M et al (2014) A novel llama antibody targeting Fn14 exhibits anti-metastatic activity in vivo. MAbs 6:297–308
White AL, Chan HT, Roghanian A et al (2011) Interaction with FcgammaRIIB is critical for the agonistic activity of anti-CD40 monoclonal antibody. J Immunol 187(4):1754–1763. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1101135
White AL, Dou L, Chan HT et al (2014) Fcgamma receptor dependency of agonistic CD40 antibody in lymphoma therapy can be overcome through antibody multimerization. J Immunol 193:1828–1835
Wilson NS, Yang B, Yang A et al (2011) An Fcgamma receptor-dependent mechanism drives antibody-mediated target-receptor signaling in cancer cells. Cancer Cell 19:101–113
Xu Y, Szalai AJ, Zhou T et al (2003) Fc gamma Rs modulate cytotoxicity of anti-Fas antibodies: implications for agonistic antibody-based therapeutics. J Immunol 171:562–568
Zhang P, Tu GH, Wei J et al (2019) Ligand-blocking and membrane-proximal domain targeting anti-OX40 antibodies mediate potent T cell-stimulatory and anti-tumor activity. Cell Rep 27:3117–3123
Lang I, Kums J, Wajant H (2017) Generation and application of bioluminescent CD95 ligand fusion proteins. Methods Mol Biol 1557:63–77
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG, German Research Foundation)—Projektnummer 324392634—TRR 221 and WA 1025/31-1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Medler, J., Wajant, H. (2021). Analysis of FcγR-Dependent Agonism of Antibodies Specific for Receptors of the Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) Receptor Superfamily (TNFRSF). In: Bayry, J. (eds) The TNF Superfamily. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2248. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1130-2_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1130-2_6
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-1129-6
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-1130-2
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols